
Ophichthidae is a family of fish in the order Anguilliformes, commonly known as the snake eels. The term "Ophichthidae" comes from Greek ophis ("serpent") and ichthys ("fish"). Snake eels are also burrowing eels. They are named for their physical appearance, as they have long, cylindrical, snake-like bodies. This family is found worldwide in tropical to warm temperate waters. They inhabit a wide range of habitats, from coastal shallows and even rivers, to depths below 800 m (2,600 ft). Most species are bottom dwellers, hiding in mud or sand to capture their prey of crustaceans and small fish, but some are pelagic.

The cusk-eel family, Ophidiidae, is a group of marine bony fishes in the Ophidiiformes order. The scientific name is from the Greek ophis meaning "snake", and refers to their eel-like appearance. True eels diverged from other ray-finned fish during the Jurassic, while cusk-eels are part of the Percomorpha clade, along with tuna, perch, seahorses and others.

Uropterygius is a genus of moray eels in the family Muraenidae.

Myrichthys is a genus of snake eels currently containing 11 recognized species found in tropical and warm temperate oceans worldwide.

Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes, which consists of eight suborders, 20 families, 164 genera, and about 1000 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage and are usually predators.

Callechelys is a genus of eels in the snake eel family Ophichthidae. It currently contains the following fifteen species:
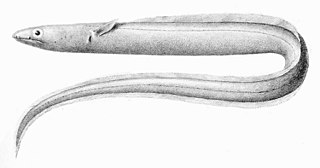
Echelus is a genus of eels in the snake-eel family Ophichthidae.
Ichthyapus is a genus of eels in the snake eel family Ophichthidae.

Ophichthus is a genus of eels in the snake eel family Ophichthidae.

Pisodonophis is a genus of eels in the snake eel family Ophichthidae. It currently contains the following species:
Yirrkala is a genus of eels in the snake eel family Ophichthidae. It is named after Yirrkala, an indigenous community in Arnhem Land, in the Northern Territory of Australia.

The saddled snake-eel, also known commonly as the halfbanded snake-eel, the banded snake eel, or the culverin, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by George Tradescant Lay and Edward Turner Bennett in 1839, originally under the genus Ophisurus. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and southeastern Atlantic Ocean, including East and South Africa, the Hawaiian Islands, the Marquesan Islands, the Mangaréva islands, Japan, and Australia. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 70 metres, most often around 0 to 10 metres, and inhabits lagoons and reefs, in which it forms burrows in beds of seagrass and sandy areas. Males can reach a maximum total length of 66 centimetres (2.17 ft).
The Sailfin eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Raymond Carroll Osburn and John Treadwell Nichols in 1916, originally under the genus Letharchus. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Costa Rica, Mexico, and Panama. It is known to dwell at a depth of 35 metres (115 ft), and inhabits rock and sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 81 centimetres (32 in).

The goldspotted eel, also known as the goldspotted snake eel or the dark-spotted snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Alexandre Lesueur in 1825, originally under the genus Muraenophis. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Bermuda, southern Florida, USA; the Bahamas, Santa Catarina, and Brazil. It dwells at a maximum depth of 15 metres (49 ft), and inhabits rocky and coral reefs. Males can reach a maximum total length of 110 centimetres (3.6 ft).

The highfin snake eel (Ophichthus altipennis, also known as the blackfin snake eel or the black-finned snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Johann Jakob Kaup in 1856, originally under the genus Microdonophis. It is a marine, tropical eel known from the eastern Indian Ocean and northwestern and western central Pacific Ocean, including Australia, French Polynesia, Indonesia, Japan, the Marshall Islands, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Papua New Guinea. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 40 m, and forms burrows in soft inshore sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 103 cm.
The faintsaddled snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John E. McCosker and Eugenia Brandt Böhlke in 1984. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 108 meters.
The longarmed snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John E. McCosker and Richard Heinrich Rosenblatt in 1998. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Mexico, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Nicaragua, and Panama. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 24 to 79 metres, and inhabits soft substrates. Males can reach a maximum total length of 27.4 centimetres (10.8 in).
The dottedline snake eel is a species of eels in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John E. McCosker and Eugenia Brandt Böhlke in 1984. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 183 meters.
The Pouch snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by George S. Myers and Charles Barkley Wade in 1941, originally under the genus Letharchus. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including the Galapagos Islands, the Revillagigedo Islands, and the Cocos Islands. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 10 metres (33 ft), and inhabits sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 64.3 centimetres (25.3 in).

The rice-paddy eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Francis Buchanan-Hamilton in 1822, originally in the genus Ophisurus. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-West Pacific, including Somalia, Tanzania, South Africa, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Polynesia, Australia, Bangladesh, Cambodia, Kenya, Madagascar, the Philippines, Malaysia, Mozambique, Seychelles, Saudi Arabia, Taiwan, China, Thailand, Vietnam, and southern Yemen. It is an anadromous species and spawns in freshwater, often in rice paddies during the rainy season, earning it its common name. It also spends time in lagoons, estuaries and coastal rivers, in which it lives in burrows in the river bottom and bank. Males can reach a maximum total length (TL) of 100 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 70 cm.











