
Hallucigenia is a genus of lobopodian known from Cambrian aged fossils in Burgess Shale-type deposits in Canada and China, and from isolated spines around the world. The generic name reflects the type species' unusual appearance and eccentric history of study; when it was erected as a genus, H. sparsa was reconstructed as an enigmatic animal upside down and back to front. Lobopodians are a grade of Paleozoic panarthropods from which the velvet worms, water bears, and arthropods arose.

Sidneyia is an extinct arthropod known from fossils found from the Early to the Mid Cambrian of China and the Mid Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada.

Fuxianhuia is a genus of Lower Cambrian fossil arthropod known from the Chengjiang fauna in China. Its purportedly primitive features have led to its playing a pivotal role in discussions about the euarthropod stem group. Nevertheless, despite being known from many specimens, disputes about its morphology, in particular its head appendages, have made it one of the most controversial of the Chengjiang taxa, and it has been discussed extensively in the context of the arthropod head problem.
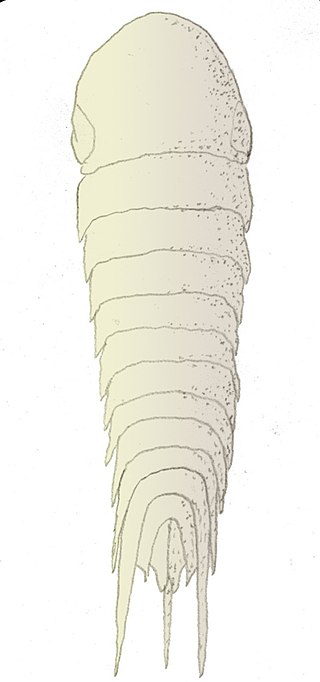
Acanthomeridion is an extinct arthropod found in the Chengjiang fauna deposits of China. In 1997, it was placed in its own, monotypic family, Acanthomeridiidae. It is known from eight specimens, all found in China.

Plenocaris plena is a genus of extinct bivalved hymenocarine arthropod that lived in the Cambrian aged Burgess Shale and Chengjiang. Originally described as a species of Yohoia by Walcott in 1912, it was placed into its own genus in 1974.
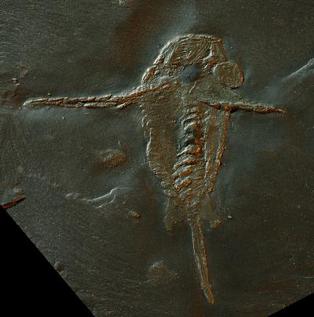
Schinderhannes bartelsi is a species of hurdiid radiodont (anomalocaridid), known from one specimen from the Lower Devonian Hunsrück Slates. Its discovery was astonishing because the latest definitive radiodonts were known only from the Early Ordovician, at least 66 million years earlier than this taxon.

Chuandianella ovata is an extinct bivalved arthropod that lived during Cambrian Stage 3 of the Early Cambrian. It is the only species classified under the genus Chuandianella. Its fossils were recovered from the Chengjiang Biota in Yunnan, China.

Haikoucaris is a genus of megacheiran arthropod that contains the single species Haikoucaris ercaiensis. It was discovered in the Cambrian Chengjiang biota of China.
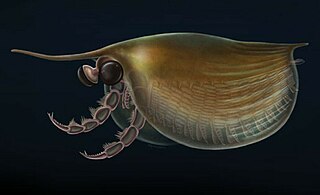
Isoxys is a genus of extinct bivalved Cambrian arthropod; the various species of which are thought to have been freely swimming predators. It had a pair of large spherical eyes, and two large frontal appendages used to grasp prey.

Occacaris oviformis is an extinct nektonic predatory arthropod from the Lower Cambrian Maotianshan shale Lagerstätte. It bears a superficial resemblance to the Cambrian arthropod, Canadaspis, though, was much smaller, and had a pair of "great appendages", with which it may have grasped prey. It was originally considered to belong to Megacheira, however it is questioned in later study.

The palaeoscolecids are a group of extinct ecdysozoan worms resembling armoured priapulids. They are known from the Lower Cambrian to the lower Ludfordian ; they are mainly found as disarticulated sclerites, but are also preserved in many of the Cambrian lagerstätten. They take their name from the typifying genus Palaeoscolex. Other genera include Cricocosmia from the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang biota. Their taxonomic affinities within Ecdysozoa have been the subject of debate.

Cucumericrus ("cucumber-leg") is an extinct genus of stem-arthropod. The type and only species is Cucumericrus decoratus, with fossils discovered from the Maotianshan Shales of Yunnan, China.

Strabops is a genus of strabopid, an extinct group of arthropods. Strabops is known from a single specimen from the Late Cambrian of the Potosi Dolomite, Missouri, collected by a former professor, Arthur Thacher. It is classified in the family Strabopidae of the monotypic order Strabopida, a group closely related to the aglaspidids with uncertain affinities. The generic name is composed by the Ancient Greek words στραβός, meaning "squinting", and ὄψῐς, meaning "face".

Paleomerus is a genus of strabopid, a group of extinct arthropods. It has been found in deposits from the Cambrian period. It is classified in the family Strabopidae of the monotypic order Strabopida. It contains two species, P. hamiltoni from Sweden and P. makowskii from Poland. The generic name is composed by the Ancient Greek words παλαιός (palaiós), meaning "ancient", and μέρος (méros), meaning "part".

Luohuilinella is an extinct genus of xandarellid artiopodan arthropod known from the Chengjiang biota of China. The type species Luohuilinella rarus was described in 2012. A second species Luohuilinella deletres was described in 2018. Both taxa are rare components of the assemblage. Like other Xandarellids and most artiopodans, it possessed an unmineralised exoskeleton. The type and currently only known specimen of L. rarus is known from a dorsal exoskeleton, around 17 mm long and 9 mm wide which consists of 27 tergites with pronounced pleural spines. L. deletres is much larger, with specimens being over 10 cm long, L. deletres possessed at least 11 pairs of biramous appendages. Both taxa are dorsoventrally flattened, making a benthic or nektobenthic lifestyle probable. Both taxa have pronounced notches in the cephalon to accommodate the stalked eyes.

Kylinxia is a genus of extinct arthropod described in 2020. It was described from six specimens discovered in Yu'anshan Formation in southern China. The specimens are assigned to one species Kylinxia zhangi. Dated to 518 million years, the fossils falls under the Cambrian period. Announcing the discovery on 4 November 2020 at a press conference, Zeng Han of the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Paleontology, said that the animal "bridges the evolutionary gap from Anomalocaris to true arthropods and forms a key ‘missing link’ in the origin of arthropods," which was "predicted by Darwin’s evolutionary theory." The same day the formal description was published in Nature.
Luolishania is an extinct genus of lobopodian panarthropod and known from the Lower Cambrian Chiungchussu Formation of the Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China. A monotypic genus, it contains one species Luolishania longicruris. It was discovered and described by Hou Xian-Guang and Chen Jun-Yuan in 1989. It is one of the superarmoured Cambrian lobopodians suspected to be either an intermediate form in the origin of velvet worms (Onychophora) or basal to at least Tardigrada and Arthropoda. It is the basis of the family name Luolishaniidae, which also include other related lobopods such as Acinocricus, Collinsium, Facivermis, and Ovatiovermis. Along with Microdictyon, it is the first lobopodian fossil discovered from China.

Hallucigeniidae is a family of extinct worms belonging to the group Lobopodia that originated during the Cambrian explosion. It is based on the species Hallucigenia sparsa, the fossil of which was discovered by Charles Doolittle Walcott in 1911 from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia. The name Hallucigenia was created by Simon Conway Morris in 1977, from which the family was erected after discoveries of other hallucigeniid worms from other parts of the world. Classification of these lobopods and their relatives are still controversial, and the family consists of at least four genera.

Lenisambulatrix is a genus of extinct worm belonging to the group Lobopodia and known from the Lower Cambrian Maotianshan shale of China. It is represented by a single species L. humboldti. The incomplete fossil was discovered and described by Qiang Ou and Georg Mayer in 2018. Due to its missing parts, its relationship with other lobopodians is not clear. It shares many structural features with another Cambrian lobopodian Diania cactiformis, a fossil of which was found alongside it.

Kwanyinaspis is a genus of arthropod from the Cambrian aged Chengjiang biota of Yunnan, China. It was described in 2005 based on a single specimen, ELI-2004001. Around 6 cm long, It has twelve trunk tergites with well developed posterior facing pleural spines, along with a tail spine and ventral eyes. In the original description, it was tenatively considered a member of Aglaspidida. However, later studies have considered it a trilobitomorph, and possibly the closest known relative of trilobites.


















