
Mindat.org is a non-commercial interactive online database covering minerals across the world. Originally created by Jolyon Ralph as a private project in 1993, it was launched as a community-editable website in October 2000. As of 2023 it is operated by the Hudson Institute of Mineralogy.

Zapodidae, the jumping mice, is a family of mouse-like rodents in North America and China.

Anomaluromorpha is a clade that unites the anomalures, springhares, and zenkerella. It has alternately been designated as either a suborder or infraorder. Most recently, Carleton & Musser 2005 recognized it as one of five suborders of rodents.

Latimeriidae is the only extant family of coelacanths, an ancient lineage of lobe-finned fish. It contains two extant species in the genus Latimeria, found in deep waters off the coasts of southern Africa and east-central Indonesia. In addition, several fossil genera are known from the Mesozoic of Europe, the Middle East, and the southeastern United States, dating back to the Triassic.

Epihippus is an extinct genus of the modern horse family Equidae that lived in the Eocene, from 46 to 38 million years ago.
Ganorhynchus is an extinct genus of prehistoric lungfish from the Devonian period. It is only found in Mansfield, Pennsylvania.
The Belden Shale is a geologic formation in Colorado near the town of McCoy. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carboniferous period.

The Kupferschiefer or Kupfermergel, is an extensive and remarkable sedimentary unit in Central Europe. The relatively monotonous succession is typically 30 to 60 centimetres and maximum 2 metres (6.6 ft) thick, but extends over an area of 600,000 square kilometres (230,000 sq mi) across the Southern Permian Basin. The Kupferschiefer can be found in outcrop or in the subsurface straddling six countries, including parts of the southern North Sea. The lateral equivalent outcropping in England is called Marl Slate.

Serratolamna is an extinct genus of mackerel sharks that is placed in the monotypic family Serratolamnidae.
Frogmore is a village in the Southern Tablelands of New South Wales, Australia. It was previously a mining town.
Kiamba is a small Queensland, rural locality within Australia. Region of Kiamba is sunshine coast, state of Queensland, Australia. Koppen climate type is Cfa : Humid subtropical climate. It is located approximately 100 km from the capital Brisbane covering an area of 16.481 square kilometres. Kiamba has a recorded population of 191 residents. There is Australian Eastern Standard Time zone Australia/Brisbane.
The fluoride phosphates or phosphate fluorides are inorganic double salts that contain both fluoride and phosphate anions. In mineralogy, Hey's Chemical Index of Minerals groups these as 22.1. The Nickel-Strunz grouping is 8.BN.
The sulfate chlorides are double salts containing both sulfate (SO42–) and chloride (Cl–) anions. They are distinct from the chlorosulfates, which have a chlorine atom attached to the sulfur as the ClSO3− anion.

The sulfate carbonates are a compound carbonates, or mixed anion compounds that contain sulfate and carbonate ions. Sulfate carbonate minerals are in the 7.DG and 5.BF Nickel-Strunz groupings.
The sulfate fluorides are double salts that contain both sulfate and fluoride anions. They are in the class of mixed anion compounds. Some of these minerals are deposited in fumaroles.
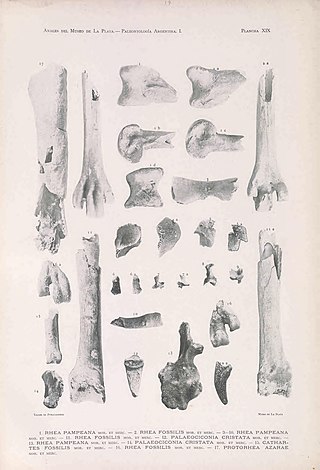
Rhea fossilis is an extinct species of bird in the genus Rhea that inhabited the Southern Cone of South America during the Neogene period. Its closest living relatives are the greater rhea and the lesser rhea.

Thanatosdrakon is a genus of quetzalcoatline azhdarchid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous Plottier Formation of the Neuquén Basin in western Argentina. The genus name is derived from the Greek words thanatos (=death) and drakon (=dragon), while the specific name is a Quechuan word meaning "flying serpent" and refers to the Incan deity Amaru. The type and only species is Thanatosdrakon amaru, known from two specimens consisting of several well-preserved axial and appendicular bones including material previously undescribed in giant azhdarchids. Thanatosdrakon is one of the oldest known members of the Quetzalcoatlinae. T. amaru lived from about 90 to 86 million years ago.

Paratropes is a genus of cockroaches within the family Ectobiidae. There are currently 14 species assigned to the genus. Members of this genus are distributed across North and South America in countries such as Mexico, Colombia, Panama and Peru.
Paratropes bilunata is a species of cockroach within the family Ectobiidae, that can be found in Costa Rica and Panama.

Fistuliporidae is an extinct family of bryozoans within the order Cystoporida. Members of this family have lived from the early Ordovician to the late Triassic period.











