
Dichorisandra thyrsiflora or blue ginger is a species of tropical flowering plant which resembles ginger in growth and habit, but is actually related to the spiderworts. The plant is native to the tropical woodlands of North, Central and South America, especially in Atlantic Forest vegetation in Brazil. Of the family Commelinaceae, it is cultivated for its handsome spotted stems and large shiny foliage which is held horizontally, surmounted by striking blue flowers.

Banksia nobilis, commonly known as the golden dryandra, great dryandra or kerosene bush, is a shrub of the family Proteaceae which is endemic to Western Australia. It occurs on lateritic rises from Eneabba to Katanning in the state's Southwest Botanic Province. With large pinnatifid leaves with triangular lobes, and a golden or reddish pink inflorescence, it is a popular garden plant. It was known as Dryandra nobilis until 2007, when all Dryandra species were transferred to Banksia by Austin Mast and Kevin Thiele. There are two subspecies, B. nobilis subsp. nobilis and B. nobilis subsp. fragrans.

Banksia proteoides, commonly known as king dryandra, is a shrub endemic to Western Australia. It was known as Dryandra proteoides until 2007, when all Dryandra species were transferred to Banksia by Austin Mast and Kevin Thiele.

Parsonsia is a genus of woody vines in the family Apocynaceae. Species occur throughout Indomalaya, Australasia and Melanesia.

Melilotus indicus, sometimes incorrectly written Melilotus indica, is a yellow-flowered herb native to northern Africa, Europe and Asia, but naturalized throughout the rest of the world.

Parsonsia straminea, commonly known as common silkpod or monkey rope, is a woody vine of the dogbane family, Apocynaceae. It occurs in the states of New South Wales and Queensland in Australia.

Parsonsia brownii, commonly known as twining silkpod or mountain silkpod, is a woody vine of the dogbane family, Apocynaceae. It occurs in rainforest in the states of New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania in Australia.

Parsonsia capsularis is a climbing plant endemic to New Zealand belonging to the dogbane family Apocynaceae.

Periploca is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described for modern science by Linnaeus in 1753. It is native to Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- Periploca aphyllaDecne. - Middle East from Sinai to Pakistan
- Periploca calophylla(Wight) Falc. - S China, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam, E Himalayas, Vietnam
- Periploca chevalieriBrowicz - Cape Verde Islands
- Periploca chrysanthaD.S. Yao, X.D. Chen & J.W. Ren - Gansu Province in China
- Periploca floribundaTsiang - Yunnan, Vietnam
- Periploca forrestiiSchltr. - Guangxi, Guizhou, Qinghai, Sichuan, Tibet, Yunnan, India, Kashmir, Myanmar, Nepal
- Periploca graecaL. - Mediterranean
- Periploca hydaspidisFalc. - Kashmir
- Periploca laevigataAiton - Canary Islands, Savage Islands
- Periploca linearifoliaQuart.-Dill. & A. Rich - Ethiopia
- Periploca nigrescensAfzel. - W Africa
- Periploca refractifoliaGilli - Tanzania
- Periploca sepiumBunge - widespread across much of China
- Periploca tsiangiiD. Fang & H.Z. Ling - Guangxi Province in China
- Periploca visciformis(Vatke) K. Schum. - Somalia

Thomasia purpurea is a small, flowering shrub in the family Malvaceae that is endemic to the southwest of Western Australia. It has green oblong-shaped leaves and pinkish purple flowers.

Bossiaea prostrata, commonly known as creeping bossiaea, is a prostrate understory shrub in the pea family, Fabaceae. It is a widespread species with orange-yellow flowers, purple-brown keels and trailing branches.
Melodinus acutiflorus is a species of vine, commonly named white-flowered melodinus, byamurra, or merangarra and constituting part of the plant family Apocynaceae. They grow naturally in Papua New Guinea, Queensland and New South Wales in Australia.

Tabernaemontana pandacaqui, known as windmill bush and banana bush, is a species of plant in the dogbane family Apocynaceae.

Dysoxylum parasiticum, known as yellow mahogany, is a species of rainforest trees in the family Meliaceae. The specific epithet parasiticum is from the Latin meaning "parasitic", referring to the idea that the flowers are parasitic on another tree species.

Lysiphyllum cunninghamii is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is native to northern Australia where it occurs from Western Australia through the Northern Territory to Queensland.

Ceropegia candelabrum is the type species in its genus of plants, belonging the subfamily Asclepiadoideae. The Latin specific epithet candelabrum is derived from the candelabra-like appearance of the inflorescences.

Parsonsia diaphanophleba is a woody vine of the family Apocynaceae. It is found in Western Australia and is listed as a priority 4 species.

Parsonsia eucalyptophylla, whose common names are gargaloo and monkey vine, is a woody vine in the family Apocynaceae. It is native to the east coast states of Australia.
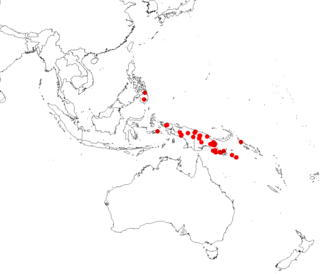
Parsonsia curvisepala is a woody vine of the family Apocynaceae, found in Malaysia, New Guinea, the Philippines, the Solomon Islands, and Sulawesi. This species is second only to Parsonsia alboflavescens in its variability and wide geographic distribution.

Decaisnina brittenii is a species of flowering plant, an epiphytic hemiparasitic plant of the family Loranthaceae native to the Northern Territory, Queensland and northern Western Australia.
























