Related Research Articles

Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels.

Echo sounding or depth sounding is the use of sonar for ranging, normally to determine the depth of water (bathymetry). It involves transmitting acoustic waves into water and recording the time interval between emission and return of a pulse; the resulting time of flight, along with knowledge of the speed of sound in water, allows determining the distance between sonar and target. This information is then typically used for navigation purposes or in order to obtain depths for charting purposes.

Acoustical engineering is the branch of engineering dealing with sound and vibration. It includes the application of acoustics, the science of sound and vibration, in technology. Acoustical engineers are typically concerned with the design, analysis and control of sound.
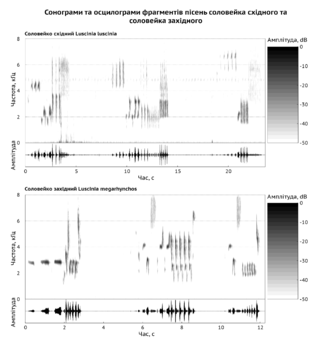
Bioacoustics is a cross-disciplinary science that combines biology and acoustics. Usually it refers to the investigation of sound production, dispersion and reception in animals. This involves neurophysiological and anatomical basis of sound production and detection, and relation of acoustic signals to the medium they disperse through. The findings provide clues about the evolution of acoustic mechanisms, and from that, the evolution of animals that employ them.
(Acoustic homing) is the process in which a system uses the sound or acoustic signals of a target or destination to guide a moving object. There are two types of acoustic homing: passive acoustic homing and active acoustic homing. Objects using passive acoustic homing rely on detecting acoustic emissions produced by the target. Conversely, objects using active acoustic homing make use of sonar to emit a signal and detect its reflection off the target. The signal detected is then processed by the system to determine the proper response for the object. Acoustic homing is useful for applications where other forms of navigation and tracking can be ineffective. It is commonly used in environments where radio or GPS signals can not be detected, such as underwater.

A sonobuoy is a small expendable sonar buoy dropped from aircraft or ships for anti-submarine warfare or underwater acoustic research. Sonobuoys are typically around 13 cm (5 in) in diameter and 91 cm (3 ft) long. When floating on the water, sonobuoys have both a radio transmitter above the surface and hydrophone sensors underwater.
Acoustic ecology, sometimes called ecoacoustics or soundscape studies, is a discipline studying the relationship, mediated through sound, between human beings and their environment. Acoustic ecology studies started in the late 1960s with R. Murray Schafer a musician, composer and former professor of communication studies at Simon Fraser University with the help of his team there as part of the World Soundscape Project. The original WSP team included Barry Truax and Hildegard Westerkamp, Bruce Davies and Peter Huse, among others. The first study produced by the WSP was titled The Vancouver Soundscape. This innovative study raised the interest of researchers and artists worldwide, creating enormous growth in the field of acoustic ecology. In 1993, the members of the by now large and active international acoustic ecology community formed the World Forum for Acoustic Ecology.
A scientific echosounder is a device which uses sonar technology for the calibrated backscatter measurement of underwater physical and biological components—this device is also known as scientific sonar. Applications include bathymetry, substrate classification, studies of aquatic vegetation, fish, and plankton, and differentation of water masses.
Acoustic tags are small sound-emitting devices that allow the detection and/or remote tracking of organisms in aquatic ecosystems. Acoustic tags are commonly used to monitor the behavior of fish. Studies can be conducted in lakes, rivers, tributaries, estuaries or at sea. Acoustic tag technology allows researchers to obtain locational data of tagged fish: depending on tag and receiver array configurations, researchers can receive simple presence/absence data, 2D positional data, or even 3D fish tracks in real-time with sub-meter resolutions.
Sensory ecology is a relatively new field focusing on the information organisms obtain about their environment. It includes questions of what information is obtained, how it is obtained, and why the information is useful to the organism.

Underwater acoustics is the study of the propagation of sound in water and the interaction of the mechanical waves that constitute sound with the water, its contents and its boundaries. The water may be in the ocean, a lake, a river or a tank. Typical frequencies associated with underwater acoustics are between 10 Hz and 1 MHz. The propagation of sound in the ocean at frequencies lower than 10 Hz is usually not possible without penetrating deep into the seabed, whereas frequencies above 1 MHz are rarely used because they are absorbed very quickly.

Fisheries acoustics includes a range of research and practical application topics using acoustical devices as sensors in aquatic environments. Acoustical techniques can be applied to sensing aquatic animals, zooplankton, and physical and biological habitat characteristics.

Geographic Information Systems (GIS) has become an integral part of aquatic science and limnology. Water by its very nature is dynamic. Features associated with water are thus ever-changing. To be able to keep up with these changes, technological advancements have given scientists methods to enhance all aspects of scientific investigation, from satellite tracking of wildlife to computer mapping of habitats. Agencies like the US Geological Survey, US Fish and Wildlife Service as well as other federal and state agencies are utilizing GIS to aid in their conservation efforts.
An autonomous recording unit (ARU) is a self-contained audio recording device that is deployed in marine or terrestrial environments for bioacoustical monitoring. The unit is used in both marine and terrestrial environments to track the behavior of animals and monitor their ecosystems. On a terrestrial level, the ARU can detect noises coming from bird habitats and determine relative emotions that each bird conveys along with the population of the birds and the relative vulnerability of the ecosystem. The ARU can also be used to understand noises made by marine life to see how the animals' communication affects the operation of their ecosystem. When underwater, the ARU can track the sound that human made machines make and see the effect those sounds have on marine life ecosystems. Up to 44 work days can be saved through the utilization of ARU's, along with their ability to discover more species.
Ecomusicology is an area of study that explores the relationships between music or sound, and the natural environment. It is a study which encompasses a variety of academic disciplines including musicology, biology, ecology and anthropology. Ecomusicology combines these disciplines to explore how sound is produced by natural environments and, more broadly how cultural values and concerns about nature are expressed through sonic mediums. Ecomusicology explores the ways that music is composed to replicate natural imagery, as well as how sounds produced within the natural environment are used within musical composition. Ecological studies of sounds produced by animals within their habitat are also considered to be part of the field of ecomusicology. In the 21st century, studies within the field the ecomusicology have also become increasingly interested in the sustainability of music production and performance.

Conservation behavior is the interdisciplinary field about how animal behavior can assist in the conservation of biodiversity. It encompasses proximate and ultimate causes of behavior and incorporates disciplines including genetics, physiology, behavioral ecology, and evolution.

JASCO Applied Sciences provides scientific consulting services and equipment related to underwater acoustics. JASCO operates from 7 international locations and provides services to the oil and gas, marine construction, energy, renewable energy, fisheries, maritime transport and defence sectors. The head office is located in Halifax, NS Canada. JASCO employs acousticians, bioacousticians, physicists, marine mammal scientists, engineers, technologists, and project managers.

Communication occurs when an animal produces a signal and uses it to influences the behaviour of another animal. A signal can be any behavioural, structural or physiological trait that has evolved specifically to carry information about the sender and/or the external environment and to stimulate the sensory system of the receiver to change their behaviour. A signal is different from a cue in that cues are informational traits that have not been selected for communication purposes. For example, if an alerted bird gives a warning call to a predator and causes the predator to give up the hunt, the bird is using the sound as a signal to communicate its awareness to the predator. On the other hand, if a rat forages in the leaves and makes a sound that attracts a predator, the sound itself is a cue and the interaction is not considered a communication attempt.
An underwater survey is a survey performed in an underwater environment or conducted remotely on an underwater object or region. Survey can have several meanings. The word originates in Medieval Latin with meanings of looking over and detailed study of a subject. One meaning is the accurate measurement of a geographical region, usually with the intention of plotting the positions of features as a scale map of the region. This meaning is often used in scientific contexts, and also in civil engineering and mineral extraction. Another meaning, often used in a civil, structural, or marine engineering context, is the inspection of a structure or vessel to compare actual condition with the specified nominal condition, usually with the purpose of reporting on the actual condition and compliance with, or deviations from, the nominal condition, for quality control, damage assessment, valuation, insurance, maintenance, and similar purposes. In other contexts it can mean inspection of a region to establish presence and distribution of specified content, such as living organisms, either to establish a baseline, or to compare with a baseline.
Haikubox is an artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled device which automatically and continuously identifies backyard birds using their vocalizations. Haikubox was developed by Loggerhead Instruments which also develops and manufactures bioacoustics equipment for oceanographic research.
References
- 1 2 3 Ross, Samuel R. P.‐J.; O'Connell, Darren P.; Deichmann, Jessica L.; Desjonquères, Camille; Gasc, Amandine; Phillips, Jennifer N.; Sethi, Sarab S.; Wood, Connor M.; Burivalova, Zuzana (April 2023). "Passive acoustic monitoring provides a fresh perspective on fundamental ecological questions" (PDF). Functional Ecology. 37 (4): 959–975. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.14275 . ISSN 0269-8463.
- David A. Mann, Anthony D. Hawkins, and J. Michael Jech, Active and Passive Acoustics to Locate and Study Fish, from book Fish Bioacoustics: With 81 Illustrations (pp.279-309), April 2008
- Marco Brunoldi, Giorgio Bozzini, et al., A Permanent Automated Real-Time Passive Acoustic Monitoring System for Bottlenose Dolphin Conservation in the Mediterranean Sea, 2016
