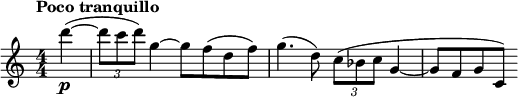Structure
A typical performance of the symphony lasts about 35 minutes. The symphony is in four movements:
- Molto moderato

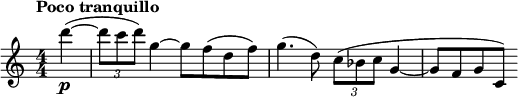
- Lento moderato – Moderato maestoso – the slow movement opens with an F major natural-horn solo above an F minor chord, a theme that is developed by a solo cello.[ citation needed ]

Just as in the first movement, the ideas flow gently from one to the next, ultimately leading to the trumpet cadenza. Here, the instrument is in effect a natural trumpet (a trumpet without valves) in E♭, since the player is instructed not to use the valves. As a result, the seventh harmonic is played instead of the ordinary minor seventh, and so it sounds slightly out-of-tune with its nearest equivalent in 12-tone equal temperament.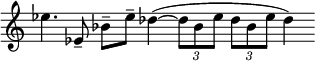
The entire cadenza is played over a pedal note in the strings.[ original research? ] The cadenza material later reappears on the natural horn in F, gently accompanied by a returning theme now played on the cor anglais. [7] The movement ends with a quiet chord in the violins' high register. - Moderato pesante – Vaughan Williams described this movement, the symphony's scherzo function, as a "slow dance".[ This quote needs a citation ]

The trio, introduced by the brass section, has a quicker, brighter quality but retains some of the heaviness of the earlier music.[ original research? ]
After the shortened return of the main material there is a coda with some fugal writing. This is the only time truly fast music appears in the symphony. A theme from the main section of the movement creeps into this fugue. The movement ends in a major chord. - Lento – the final movement returns to the contemplative manner of the first two movements, and functions as a summing-up and coda to the rest of the symphony. [8] It begins with a pentatonic passage for a wordless soprano voice (silent until this point), sung over a soft drumroll.[ original research? ]

The orchestra then begins an elegiac rhapsody. The high point of the symphony comes when the violins all state the opening soprano melody appassionato.[ citation needed ] At the very end of the symphony, the soprano returns to sing the music into silence.