
A brass instrument is a musical instrument that produces sound by sympathetic vibration of air in a tubular resonator in sympathy with the vibration of the player's lips. The term labrosone, from Latin elements meaning "lip" and "sound", is also used for the group, since instruments employing this "lip reed" method of sound production can be made from other materials like wood or animal horn, particularly early or traditional instruments such as the cornett, alphorn or shofar.

The cornet is a brass instrument similar to the trumpet but distinguished from it by its conical bore, more compact shape, and mellower tone quality. The most common cornet is a transposing instrument in B♭. There is also a soprano cornet in E♭ and cornets in A and C. All are unrelated to the Renaissance and early Baroque cornett.

The French horn is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell. The double horn in F/B♭ is the horn most often used by players in professional orchestras and bands, although the descant and triple horn have become increasingly popular. A musician who plays a horn is known as a horn player or hornist.

The pitch of a brass instrument corresponds to the lowest playable resonance frequency of the open instrument. The combined resonances resemble a harmonic series. The fundamental frequency of the harmonic series can be varied by adjusting the length of the tubing using the instrument's valve, slide, key or crook system, while the player's embouchure, lip tension and air flow serve to select a specific harmonic from the available series for playing. The fundamental is essentially missing from the resonances and is impractical to play on most brass instruments, but the overtones account for most pitches.

The trombone is a musical instrument in the brass family. As with all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player's vibrating lips cause the air column inside the instrument to vibrate. Nearly all trombones use a telescoping slide mechanism to alter the pitch instead of the valves used by other brass instruments. The valve trombone is an exception, using three valves similar to those on a trumpet, and the superbone has valves and a slide.

The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard B♭ or C trumpet.

The tuba is the largest and lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibration – a buzz – into a mouthpiece. It first appeared in the mid-19th century, making it one of the newer instruments in the modern orchestra and concert band, and largely replaced the ophicleide. Tuba is Latin for "trumpet".

A quarter tone is a pitch halfway between the usual notes of a chromatic scale or an interval about half as wide as a semitone, which itself is half a whole tone. Quarter tones divide the octave by 50 cents each, and have 24 different pitches.

The keyed trumpet is a cylindrical-bore brass instrument in the trumpet family that makes use of tone holes operated by keys to alter pitch and provide a full chromatic scale, rather than extending the length of tubing with a slide or valves. It was developed from the natural trumpet in the 18th century and reached its high-point in popularity c. 1800 when two important trumpet concertos were written for it by Austrian composers Joseph Haydn and Johann Nepomuk Hummel, but waned with the invention of valves in the 1820s and the subsequent emergence of the modern valved trumpet. It is rarely seen in modern performances.

A natural trumpet is a valveless brass instrument that is able to play the notes of the harmonic series.

The alto trombone is the alto member of the trombone family of brass instruments, smaller than the tenor trombone. It is almost always pitched in E♭ a fourth higher than the tenor, although examples pitched in F are occasionally found. The alto trombone was commonly used from the 16th to the 18th centuries in church music to strengthen the alto voice, particularly in the Mass. Alto trombone parts are usually notated in alto clef.

A crook, also sometimes called a shank, is an exchangeable segment of tubing in a natural horn which is used to change the length of the pipe, altering the fundamental pitch and harmonic series which the instrument can sound, and thus the key in which it plays.
Heinrich David Stölzel was a German horn player who developed some of the first valves for brass instruments. He developed the first valve for a brass musical instrument, the Stölzel valve, in 1818, and went on to develop various other designs, some jointly with other inventor musicians.
Hand-stopping is a technique by which a natural horn or a natural trumpet can be made to produce notes outside of its normal harmonic series. By inserting the hand, cupped, into the bell, the player can reduce the pitch of a note by a semitone or more. This, combined with the use of crooks changing the key of the instrument, allowed composers to write fully chromatic music for the horn and almost fully chromatic music for the trumpet before the invention of piston and valve horns and trumpets in the early 19th Century. A stopped note is called gestopft in German and bouché in French.
Anton Joseph Hampel was a horn player who is generally credited with having developed, somewhere between 1750 and 1760, the technique of hand-stopping which allows natural horns to play fully chromatically. This was one of the most important innovations in the history of the horn, comparable with Heinrich Stölzel's development of the first valve horn in 1817.
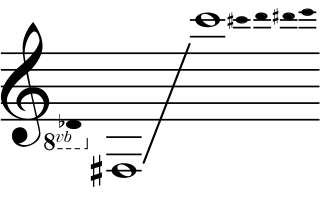
The saxotromba is a valved brass instrument invented by the Belgian instrument-maker Adolphe Sax around 1844. It was designed for the mounted bands of the French military, probably as a substitute for the French horn. The saxotrombas comprised a family of half-tube instruments of different pitches. By about 1867 the saxotromba was no longer being used by the French military, but specimens of various sizes continued to be manufactured until the early decades of the twentieth century, during which time the instrument made sporadic appearances in the opera house, both in the pit and on stage. The instrument is often confused with the closely related saxhorn.

The saxtuba is an obsolete valved brass wind instrument conceived by the Belgian instrument-maker Adolphe Sax around 1845. The design of the instrument was inspired by the ancient Roman cornu and tuba. The saxtubas, which comprised a family of half-tube and whole-tube instruments of varying pitches, were first employed in Fromental Halévy's opera Le Juif errant in 1852. Their only other public appearance of note was at a military ceremony on the Champ de Mars in Paris in the same year. The term "saxtuba" may also refer to the bass saxhorn.

A horn is any of a family of musical instruments made of a tube, usually made of metal and often curved in various ways, with one narrow end into which the musician blows, and a wide end from which sound emerges. In horns, unlike some other brass instruments such as the trumpet, the bore gradually increases in width through most of its length—that is to say, it is conical rather than cylindrical. In jazz and popular-music contexts, the word may be used loosely to refer to any wind instrument, and a section of brass or woodwind instruments, or a mixture of the two, is called a horn section in these contexts.

The German horn is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell, and in bands and orchestras is the most widely used of three types of horn, the other two being the French horn and the Vienna horn. Its use among professional players has become so universal that it is only in France and Vienna that any other kind of horn is used today. A musician who plays the German horn is called a horn player. The word "German" is used only to distinguish this instrument from the now-rare French and Viennese instruments. Although the expression "French horn" is still used colloquially in English for any orchestral horn, since the 1930s professional musicians and scholars have generally avoided this term in favour of just "horn". Vienna horns today are played only in Vienna, and are made only by Austrian firms. German horns, by contrast, are not all made by German manufacturers, nor are all French-style instruments made in France.

















