
Mevastatin is a hypolipidemic agent that belongs to the statins class.

Rhizoxin is an antimitotic agent with anti-tumor activity. It is isolated from a pathogenic plant fungus which causes rice seedling blight.

Kynapcin is a general name for a number of dibenzofuranyl derivatives of the molecule polyozellin, present in the fungus Polyozellus multiplex. Like polyozellin, some kynapcins inhibit prolyl endopeptidase, an enzyme that has a role in processing proteins including amyloid precursor protein. Chemicals that inhibit prolyl endopeptidase have attracted research interest due to their potential therapeutic effects. Several kynapcins have been found in P. multiplex, each with different chemical properties, including kynapcin-12, kynapcin-13 and -28, and -24. A total synthesis of kynapcin-24 was achieved in 2009.

Cerevisterol (5α-ergosta-7,22-diene-3β,5,6β-triol) is a sterol. Originally described in the 1930s from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, it has since been found in several other fungi and, recently, in deep water coral. Cerevisterol has some in vitro bioactive properties, including cytotoxicity to some mammalian cell lines.
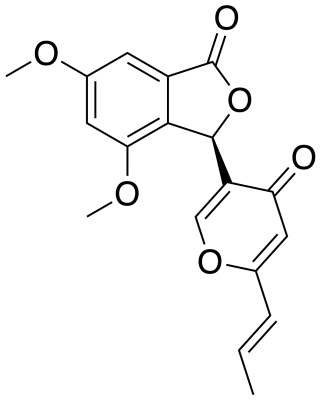
Vermistatin is an organic compound and a metabolite of mine-dwelling Penicillium vermiculatum found in Berkeley Pit Lake, Butte, Montana. Penisimplicissin is a vermistatin analog with anticancer activity.
Fungal isolates have been researched for decades. Because fungi often exist in thin mycelial monolayers, with no protective shell, immune system, and limited mobility, they have developed the ability to synthesize a variety of unusual compounds for survival. Researchers have discovered fungal isolates with anticancer, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, and other bio-active properties. The first statins, β-Lactam antibiotics, as well as a few important antifungals, were discovered in fungi.
Penicillium brocae is a fungal species of the genus Penicillium, which was isolated in Chiapas in Mexico. It is a symbiont of the mangrove tree Avicennia marina.
Penicillium citrinum is an anamorph, mesophilic fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces tanzawaic acid A-D, ACC, Mevastatin, Quinocitrinine A, Quinocitrinine B, and nephrotoxic citrinin. Penicillium citrinum is often found on moldy citrus fruits and occasionally it occurs in tropical spices and cereals. This Penicillium species also causes mortality for the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus. Because of its mesophilic character, Penicillium citrinum occurs worldwide. The first statin (Mevastatin) was 1970 isolated from this species.
Penicillium cluniae is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces the antinematodal and antiparasitic agents paraherquamide B, paraherquamide C, paraherquamide D, paraherquamide E, paraherquamide F, paraherquamide G, paraherquamide H
Penicillium decaturense is a species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from a fungus in North America. Penicillium decaturense produces citrinin, 15-Deoxyoxalicine B, decaturins A and decaturins A
Penicillium dipodomyicola is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces peniphenone A, peniphenone B, peniphenone C, peniphenone D, cyclopiazonic acid and patulin.
Penicillium herquei is an anamorph, filamentous species of the genus of Penicillium which produces citreorosein, emodin, hualyzin, herquline B, janthinone, citrinin and duclauxin,.
Penicillium janczewskii is an anamorph and filamentous species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from the rhizosphere of Vernonia herbacea. Penicillium janczewskii produces griseofulvin
Penicillium paneum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which can spoil cereal grains. Penicillium paneum produces 1-Octen-3-ol and penipanoid A, penipanoid B, penipanoid C, patulin and roquefortine C
Penicillium restrictum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from the stems of the plant Silybum marianum. Penicillium restrictum produces calbistrin A
Penicillium sumatrense is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from the rhizosphere of the plant Lumnitzera racemosa. Penicillium sumatrense produces sumalarin A, sumalarin B, sumalarin C
Penicillium turbatum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from Taxus baccata. Penicillium turbatum produces pipolythiopiperazinedione-antibiotics, hyalodendrin A and hadacitin.

Anicequol is a naturally occurring ergostane steroid produced by Acremonium sp. TF-0356 which has nerve growth factor-like neurotrophic activity. It was under investigation by Taisho Pharmaceutical in Japan for the treatment of cognitive disorders in the 1990s, but development was discontinued and the drug was never marketed.

The phomoxanthones are a loosely defined class of natural products. The two founding members of this class are phomoxanthone A and phomoxanthone B. Other compounds were later also classified as phomoxanthones, although a unifying nomenclature has not yet been established. The structure of all phomoxanthones is derived from a dimer of two covalently linked tetrahydroxanthones, and they differ mainly in the position of this link as well as in the acetylation status of their hydroxy groups. The phomoxanthones are structurally closely related to other tetrahydroxanthone dimers such as the secalonic acids and the eumitrins. While most phomoxanthones were discovered in fungi of the genus Phomopsis, most notably in the species Phomopsis longicolla, some have also been found in Penicillium sp.
Tautomycetin is a natural product first isolated from Streptomyces griseochromogenes, a bacterium found in the soil of the Zhejiang Province, China. It was also later found in Penicillium urticae. It is a linear polyketide very similar in structure to tautomycin, both of which contain a unique dialkylmaleic anhydride moiety, which is essential for their pharmacological activity. Tautomycetin is a selective inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1.






