
In botany, a bulb is a short underground stem with fleshy leaves or leaf bases that function as food storage organs during dormancy. In gardening, plants with other kinds of storage organ are also called ornamental bulbous plants or just bulbs.

Narcissus is a genus of predominantly spring flowering perennial plants of the amaryllis family, Amaryllidaceae. Various common names including daffodil, narcissus, and jonquil, are used to describe all or some members of the genus. Narcissus has conspicuous flowers with six petal-like tepals surmounted by a cup- or trumpet-shaped corona. The flowers are generally white and yellow, with either uniform or contrasting coloured tepals and corona.

Hippeastrum is a genus of about 90 species, and over 600 hybrids and cultivars, of perennial, herbaceous and bulbous plants, native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas, from Mexico south to Argentina and on some islands in the Caribbean. The majority have large, fleshy bulbs—usually about the size of a softball—and tall, broad, strap-like leaves that are (generally) evergreen, and large red or purple flowers. Numerous colors and cultivars have been created over the past hundred years.

Leucojum is a small genus of bulbous plants native to Eurasia belonging to the amaryllis family, subfamily Amaryllidoideae. As currently circumscribed, the genus includes only two known species, most former species having been moved into the genus Acis. Both genera are known as snowflakes.

American sweetgum, also known as American storax, hazel pine, bilsted, redgum, satin-walnut, star-leaved gum, alligatorwood, gumball tree, or simply sweetgum, is a deciduous tree in the genus Liquidambar native to warm temperate areas of eastern North America and tropical montane regions of Mexico and Central America. Sweetgum is one of the main valuable forest trees in the southeastern United States, and is a popular ornamental tree in temperate climates. It is recognizable by the combination of its five-pointed star-shaped leaves and its hard, spiked fruits. It is currently classified in the plant family Altingiaceae, but was formerly considered a member of the Hamamelidaceae.

Commonly known as hellebores, the Eurasian genus Helleborus consists of approximately 20 species of herbaceous or evergreen perennial flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae, within which it gave its name to the tribe of Helleboreae. Many hellebore species are poisonous.

Berberis, commonly known as barberry, is a large genus of deciduous and evergreen shrubs from 1–5 m (3.3–16.4 ft) tall, found throughout temperate and subtropical regions of the world. Species diversity is greatest in South America and Asia; Europe, Africa and North America have native species as well. The best-known Berberis species is the European barberry, Berberis vulgaris, which is common in Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, and central Asia, and has been widely introduced in North America. Many of the species have spines on the shoots and all along the margins of the leaves.

Camellia japonica, known as common camellia, or Japanese camellia, is a species of Camellia, a flowering plant genus in the family Theaceae. There are thousands of cultivars of C. japonica in cultivation, with many colors and forms of flowers. Despite its common name, it is native to China, not Japan. The cultivation of Camellia japonica also started in China. Its widespread cultivation can be traced back to the Song Dynasty, when 15 varieties of Camellia japonica were recorded in literature. It was later introduced to Japan. It grows in forests, at altitudes of around 300–1,100 metres (980–3,600 ft).

Corynespora cassiicola is a species of fungus well known as a plant pathogen. It is a sac fungus in the family Corynesporascaceae. It is the type species of the genus Corynespora.

Diplocarpon earlianum is a species of fungus that causes disease in strawberry plants called strawberry leaf scorch. The disease overwinters in plant debris and infects strawberry plants during the spring season when it is wet. The five main methods to reduce strawberry leaf scorch include: irrigation techniques, crop rotation, planting resistant and disease-free seeds, fungicide use, and sanitation measures. Control of strawberry leaf scorch is important because it is responsible for the majority of disease in strawberries. Diplocarpon earliana affects the fruit quality and yield of the strawberry crop. Losses range from negligible to severe depending on numerous epidemiological factors including cultivar susceptibility, type of cropping system, and weather conditions

Stagonospora is a genus of fungi clustering in the Phaeosphaeriaceae (Quaedvlieg). Several of the species in this genus are plant pathogens.
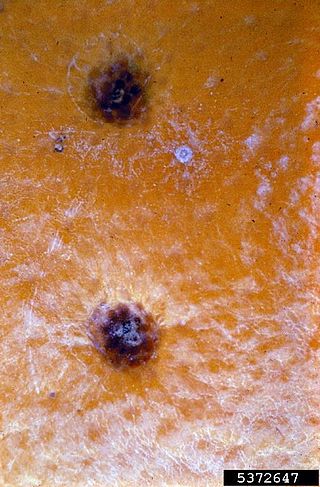
Citrus black spot is a fungal disease caused by Phyllosticta citricarpa(previously known as Guignardia citricarpa). This Ascomycete fungus affects citrus plants throughout subtropical climates, causing a reduction in both fruit quantity and quality.

Cherry leaf spot is a fungal disease which infects cherries and plums. Sweet, sour, and ornamental cherries are susceptible to the disease, being most prevalent in sour cherries. The variety of sour cherries that is the most susceptible are the English morello cherries. This is considered a serious disease in the Midwest, New England states, and Canada. It has also been estimated to infect 80 percent of orchards in the Eastern states. It must be controlled yearly to avoid a significant loss of the crop. If not controlled properly, the disease can dramatically reduce yields by nearly 100 percent. The disease is also known as yellow leaf or shothole disease to cherry growers due to the characteristic yellowing leaves and shot holes present in the leaves upon severe infection.

Hippeastrinae is a subtribe of plants classified under the tribe Hippeastreae. It belongs to the subfamily Amaryllidoideae of the Amaryllis family (Amaryllidaceae).

Hippeastrum calyptratum is a flowering perennial herbaceous bulbous plant, in the family Amaryllidaceae, native to Brazil.

The taxonomy of Narcissus is complex, and still not fully resolved. Known to the ancients, the genus name appears in Graeco-Roman literature, although their interest was as much medicinal as botanical. It is unclear which species the ancients were familiar with. Although frequently mentioned in Mediaeval and Renaissance texts it was not formally described till the work of Linnaeus in 1753. By 1789 it had been grouped into a family (Narcissi) but shortly thereafter this was renamed Amaryllideae, from which comes the modern placement within Amaryllidaceae, although for a while it was considered part of Liliaceae.
Botryotinia polyblastis is a fungal plant pathogen that causes Narcissus Fire of daffodils, genus Narcissus.
Phoma narcissi is a fungal plant pathogen of Narcissus, Hippeastrum and other Amaryllidaceae, where it causes a leaf scorch, neck rot and red leaf spot disease
Blumeriella kerriae is a species of fungus in the family Drepanopezizaceae.














