
Hepatica is a genus of herbaceous perennials in the buttercup family, native to central and northern Europe, Asia and eastern North America. Some botanists include Hepatica within a wider interpretation of Anemone.
Sage or SAGE may refer to:

Phlomis is a genus of over 100 species of herbaceous plants, subshrubs and shrubs in the family Lamiaceae, native from the Mediterranean region east across central Asia to China.

Grevillea longifolia, the fern-leaf spider flower, is a plant of the family Proteaceae, formerly known as Grevillea aspleniifolia. Commonly growing in the Sydney basin of central New South Wales, Australia Grevillea longifolia is recognizable by its deep red "toothbrush" flowers which appear in spring, and narrow, sawtoothed leaves. It is fairly readily grown in gardens.

Euphorbia milii, the crown of thorns, Christ plant, or Christ thorn, is a species of flowering plant in the spurge family Euphorbiaciae, native to Madagascar. The species name commemorates Baron Milius, once Governor of Réunion, who introduced the species to France in 1821. It is imagined that the species was introduced to the Middle East in ancient times, and legend associates it with the crown of thorns worn by Christ.< It is commonly used as an ornamental houseplant that can be grown in warmer climates. The common name is due to the thorns and deep red bracts referring to the crown thorn Jesus had to wear during his crucification and his blood.

Dianella is a genus of about forty species of flowering plants in the monocot family Asphodelaceae and are commonly known as flax lilies. Plants in this genus are tufted herbs with more or less linear leaves and bisexual flowers with three sepals more or less similar to three petals and a superior ovary, the fruit a berry. They occur in Africa, South-east Asia, the Pacific Islands, New Zealand and Australia.

Yucca gloriosa is a species of flowering plant in the family Asparagaceae, native to the southeastern United States. Growing to 2.5 m (8 ft), it is an evergreen shrub. It is widely cultivated as an ornamental for its architectural qualities, and has reportedly become established in warmer climates in the wild in various parts of the world.

Anemone hepatica, the common hepatica, liverwort, kidneywort, or pennywort, is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, native to woodland in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. This herbaceous perennial grows from a rhizome.

Mentha longifolia var. asiatica is known by the common name Asian mint. It is a variety of the mint species Mentha longifolia. It has also been treated as the separate species, Mentha asiatica and Mentha vagans.

Phlomis fruticosa, the Jerusalem sage, is a species of flowering plant in the sage family Lamiaceae, native to Albania, Cyprus, Greece, Italy, Turkey, and countries of the former Yugoslavia.
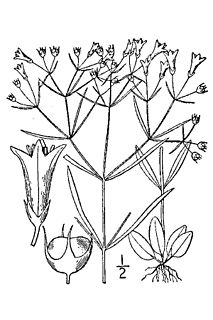
Houstonia longifolia, commonly known as long-leaved bluet or longleaf summer bluet, is a perennial plant in the family Rubiaceae. It can be found throughout most of the Eastern United States and Canada. It has been reported from every state east of the Mississippi River except Delaware, plus North Dakota, Minnesota, Missouri, Arkansas and Oklahoma, with isolated populations in Kansas and Texas. Also, all Canadian provinces from Quebec to Alberta. It prefers upland woods in poor, dry, often sandy soil, blooming from June to August.

Physalis longifolia, known by the common names common groundcherry, longleaf groundcherry, and wild tomatillo, is a species of flowering plant in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. It is native to North America, where it is native to eastern Canada, much of the continental United States, and northern Mexico. It has also been noted as an introduced species in other regions, including parts of the United States outside its native range. In some areas, such as California, it is an occasional noxious weed.

Lomandra longifolia, commonly known as spiny-head mat-rush, spiky-headed mat-rush or basket grass, is a perennial, rhizomatous herb found throughout eastern Australia. The leaves are 40 cm to 80 cm long, and generally have a leaf of about 8 mm to 12 mm wide. It grows in a variety of soil types and is frost, heat and drought tolerant. Labillardiere described Lomandra longifolia from a specimen collected in Tasmania.

Lumnitzera is an Indo-West Pacific mangrove genus in the family Combretaceae. An English common name is black mangrove. Lumnitzera, named after the German botanist, Stephan Lumnitzer (1750-1806), occurs in mangroves from East Africa to the Western Pacific, and northern Australia.

Symphyotrichum lanceolatum is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae native to North America. Common names include lance-leaved aster, panicled aster, and white panicled aster. It is a perennial, herbaceous plant that may reach 1.5 meters tall or more, sometimes approaching 2 meters. It has a stout rhizome and can spread to form a clonal colony. The species is currently divided into five varieties of plants which have minor differences in appearance and vary in chromosome counts as well as distribution, with some overlap.

Lomatia arborescens, commonly known as smooth lomatia or tree lomatia, is a shrub or small tree that grows at high altitudes, in and near rainforests. It is found north from the Barrington Tops area in eastern Australia.

Phlomis chrysophylla, the golden-leaved Jerusalem sage, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae, native to south west Asia. It is an evergreen shrub growing to 1 m (3 ft) tall by 1.2 m (4 ft) wide, with woolly-textured, sage-like leaves that turn lime green with age, and yellow flowers carried in the leaf axils in early summer.

Phlomis russeliana, the Turkish sage, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae, native to Turkey and Syria in south west Asia. It is often confused with the closely related P. samia, and wrongly marketed as Phlomis viscosa. Growing to 1 m (3.3 ft) tall, it is a herbaceous perennial with hairy, erect stems. The textured, grey-green, sage-like leaves are arrow shaped, and point downwards. In summer, whorls of green buds develop in the leaf axils at regular intervals up each vertical stem, giving a distinctive tiered effect. The buds open to globose clusters of dull yellow hooded flowers.

Dianella longifolia, commonly known as blueberry lily, pale flax lily or smooth flax lily, or blue flax-lily, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asphodelaceae and is endemic to non-arid areas of Australia. It is a tufted, rhizomatous, perennial herb with grass-like leaves, pale blue, white or greenish flowers that have pale yellow anthers, and shiny, pale blue berries.

Phlomis bourgaei, the puckered gray-green Turkish phlomis, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae, native to East Aegean Islands to South West Turkey.


















