
The Salicaceae are the willow family of flowering plants. The traditional family included the willows, poplars. Genetic studies summarized by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) have greatly expanded the circumscription of the family to contain 56 genera and about 1220 species, including the tropical Scyphostegiaceae and many of the former Flacourtiaceae.

Botrychium is a genus of ferns, seedless vascular plants in the family Ophioglossaceae. Botrychium species are known as moonworts. They are small, with fleshy roots, and reproduce by spores shed into the air. One part of the leaf, the trophophore, is sterile and fernlike; the other, the sporophore, is fertile and carries the clusters of sporangia or spore cases. Some species only occasionally emerge above ground and gain most of their nourishment from an association with mycorrhizal fungi.
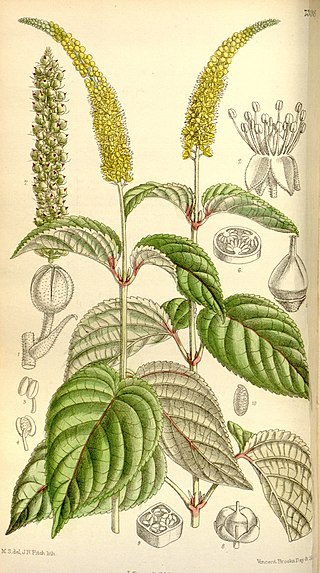
Abatia is a genus of about ten species of Central and South American trees in the family Salicaceae. Previously, it was treated in the family Flacourtiaceae, or tribe Abatieae of the family Passifloraceae or Samydaceae by G. Bentham & J.D. Hooker and Hutchinson.

Richard Spruce was an English botanist specializing in bryology. One of the great Victorian botanical explorers, Spruce spent 15 years exploring the Amazon from the Andes to its mouth, and was one of the very first Europeans to observe many of the places where he collected specimens. Spruce discovered and named a number of new plant species, and corresponded with some of the leading botanists of the nineteenth century.

Antidesma is a genus of tropical plant in the family Phyllanthaceae formally described by Linnaeus in 1753. It is native to tropical Africa, S + E + SE Asia, Australia, and various oceanic islands. The greatest diversity occurs in Southeast Asia.
Achariaceae is a family of flowering plants consisting of 31 genera and about 155 species of tropical herbs, shrubs, and trees. The APG IV system has greatly expanded the scope of the family by including many genera previously classified in Flacourtiaceae. Molecular data strongly support the inclusion of this family in the order Malpighiales.

Crotonogyne is a shrub of the spurge family (Euphorbiaceae) first described as a genus in 1864. It is native to western and central Africa. It is dioecious.
Manniophyton is a genus of lianas of the spurge family (Euphorbiaceae) described as a genus in 1864. It contains only one known species, Manniophyton fulvum, native to tropical western and central Africa from Guinea to Angola. It is dioecious.

Johann Müller was a Swiss botanist who was a specialist in lichens. He published under the name Johannes Müller Argoviensis to distinguish himself from other naturalists with similar names.

Macrohasseltia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It consists of one species of tree: Macrohasseltia macroterantha, which is native to Central America. Formerly placed in the heterogeneous family Flacourtiaceae, Macrohasseltia is now classified in Salicaceae, along with close relatives Bennettiodendron, Carrierea, Idesia, Itoa, Olmediella, Poliothyrsis, and even the willows (Salix) and cottonwoods (Populus) themselves.

Pausandra is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described in 1870. It is native to Central America and South America.
- Pausandra fordiiSecco - Amapá, French Guiana
- Pausandra hirsutaLanj. - Peru, Brazil, Bolivia (Pando), Colombia (Amazonas)
- Pausandra macropetalaDucke - Brazil, Peru (Loreto), Venezuela (Amazonas)
- Pausandra macrostachyaDucke - Pará
- Pausandra martiniBaill. - French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana, Colombia, Venezuela, Peru, Brazil
- Pausandra megalophyllaMüll.Arg. - Rio de Janeiro
- Pausandra morisiana(Casar.) Radlk. - Brazil
- Pausandra trianae(Müll.Arg.) Baill. - widespread from Honduras to Bolivia
Ophiobotrys zenkeri is a species of flowering plant in the family Salicaceae. It is a tree native to tropical Africa from Ivory Coast to Gabon and is the only member of the genus Ophiobotrys. Formerly classified in the Flacourtiaceae, phylogenetic analyses based on DNA data indicate that this species, along with its close relatives in the Asian genera Osmelia and Pseudosmelia, are better placed in a broadly circumscribed Salicaceae. Ophiobotrys differs from its close relatives in having 5 sepals, 5(-6) stamens, one divided style, and terminal inflorescences.
Mallotus floribundus is a tree in the family Euphorbiaceae, in the Stylanthus section, native to Southeast Asia, Wallaceae, New Guinea and the Solomon Islands.

Symphyotrichum spathulatum is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae native to western North America including northwestern Mexico. Commonly known as western mountain aster, it is a perennial, herbaceous plant that may reach 20 to 80 centimeters tall. Its flowers, which open in July and August, have violet ray florets and yellow disk florets.

Phyllobotryon spathulatum is a species of tree in the family Salicaceae native to Cameroon, Gabon, and Nigeria.

Camptocarpus semihastatus is a species of plant in the Apocynaceae family. It is native to Madagascar. Jens Klackenberg, the botanist who formally described the species named it after the distinct coronal lobes of its flowers that resemble half the head of a spear.

Condylocarpon amazonicum is a species of plant in the Apocynaceae family. It is native to Bolivia, Brazil, Suriname, and Venezuela. Friedrich Markgraf, the botanist who first formally described the species, using the basionym Anechites amazonicus, named it after the area near the Amazon River in Pará Brazil where the specimen he examined was collected by Adolpho Ducke.

Condylocarpon pubiflorum is a species of plant in the Apocynaceae family. It is native to Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Peru and Venezuela. Johannes Müller Argoviensis, the botanist who first formally described the species, named it after an invalid nomen nudum, Hortsmania pubiflora, previously offered by George Bentham.
Cryptolepis delagoensis is a species of plant in the Apocynaceae family. It is native to Mozambique and South Africa. Rudolf Schlechter, the botanist who first formally described the species, named it after the location where the specimen he examined was found near Maputo Bay which was then called Delagoa Bay.
Phyllobathelium is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Strigulaceae. It comprises eight species of foliicolous (leaf-dwelling, crustose lichens.
















