
Flemish Brabant is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Hainaut and East Flanders. Flemish Brabant also surrounds the Brussels-Capital Region. Its capital is Leuven. It has an area of 2,118 km2 (818 sq mi) which is divided into two administrative districts containing 65 municipalities. As of January 2024, Flemish Brabant had a population of over 1.19 million.

Belgium is a federal state comprising three communities and three regions that are based on four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the subdivisions together make up the entire country; in other words, the types overlap.
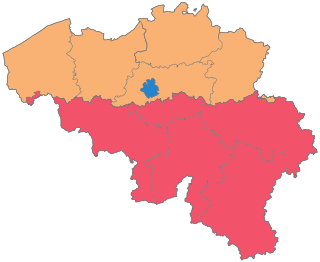
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province, nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration.

Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde is a judicial arrondissement encompassing the bilingual—French and Dutch—Brussels-Capital Region, which coincides with the administrative arrondissement of Brussels-Capital and the surrounding Dutch-speaking area of Halle-Vilvoorde, which in turn coincides with the administrative arrondissement of Halle-Vilvoorde. Halle-Vilvoorde contains several municipalities with language facilities, i.e. municipalities where French-speaking people form a considerable part of the population and therefore have special language rights. The arrondissment is the location of a tribunal of first instance, enterprise tribunal and a labour tribunal.

Elections in Belgium are organised for legislative bodies only, and not for executive functions. Direct elections take place for the European Parliament, the Chamber of Representatives, the Parliaments of the Regions, the Parliaments of the Communities, the provincial councils, the municipal councils and the councils of Districts of Antwerp. Voting is mandatory in federal elections, and all elections use proportional representation which in general requires coalition governments.

The Belgian provincial, municipal and district elections of 2006 took place on Sunday 8 October 2006. The electors have elected the municipal councillors of 589 cities and towns as well as the ten provincial councils. The voters in the town of Antwerp have also been able to vote for the city's district councils. In seven Flemish municipalities with a special language statute and in the Walloon municipality of Comines-Warneton the aldermen and the members of the OCMW/CPAS council have also been directly elected.

Federal elections were held in Belgium on 10 June 2007. Voters went to the polls in order to elect new members for the Chamber of Representatives and Senate.

Olivier D. A. Gh. Maingain is a Belgian francophone politician and former president of DéFI.

The Union of Francophones is a political party in Belgium that participates as electoral lists in regional, provincial, and municipal elections in the Flemish Province of Flemish Brabant. As its name suggests, its primary target is the French-speaking community of Flemish Brabant and particularly those who live in the officially Dutch-speaking area Halle-Vilvoorde including the now predominantly French-speaking municipalities with language facilities in the Brussels Periphery. Its main goal is to provide both constitutional exemptions for and privileges to Francophones living in Dutch-speaking Flanders, for example by annexing the municipalities with language facilities to the officially bilingual Brussels-Capital Region.

State reform, in the context of Belgium, is the ongoing process of seeking and finding constitutional and legal solutions to the problems and tensions in the different segments of the Belgian population, mostly between the Dutch-speakers of Flanders and the French-speakers of Wallonia. In general, Belgium has evolved from a unitary state to a federal state with communities, regions, and language areas.

An election of the delegation from Belgium to the European Parliament was held on Sunday, 7 June 2009. The elections were on the same day as regional elections to the Flemish Parliament, Walloon Parliament, Brussels Parliament and the Parliament of the German-speaking Community.
Regional elections were held in Belgium on 7 June 2009 to choose representatives in the regional parliaments of Flanders, Wallonia, Brussels and the German-speaking Community of Belgium. These elections were held on the same day as the European elections.
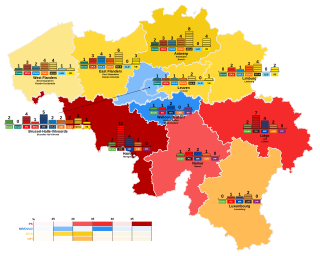
Federal elections were held in Belgium on 13 June 2010, during the midst of the 2007-11 Belgian political crisis. After the fall of the previous Leterme II Government over the withdrawal of Open Flemish Liberals and Democrats from the government the King dissolved the legislature and called new elections. The New Flemish Alliance, led by Bart De Wever, emerged as the plurality party with 27 seats, just one more than the francophone Socialist Party, led by Elio Di Rupo, which was the largest party in the Wallonia region and Brussels. It took a world record 541 days until a government was formed, resulting in a government led by Di Rupo.

Dave Sinardet is a Belgian political scientist, author and columnist.

The Belgian provincial, municipal and district elections of 2012 took place on 14 October. As with the previous 2006 elections, these are no longer organised by the Belgian federal state but instead by the respective regions:
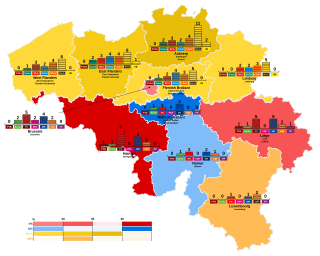
Federal elections were held in Belgium on 25 May 2014. All 150 members of the Chamber of Representatives were elected, whereas the Senate was no longer directly elected following the 2011–2012 state reform. These were the first elections held under King Philippe's reign.
Regional elections were held in Belgium on 25 May 2014 to choose representatives for the Flemish Parliament, Walloon Parliament, Brussels Parliament and the Parliament of the German-speaking Community. These elections were held on the same day as the 2014 European elections as well as the 2014 Belgian federal election.

The 2019 Belgian regional elections took place on Sunday 26 May, the same day as the 2019 European Parliament election as well as the Belgian federal election.
The 2024 Belgian regional elections were held on Sunday 9 June, the same day as the 2024 European Parliament election as well as the Belgian federal election.

















