Genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

The mackerel, tuna, and bonito family, Scombridae, includes many of the most important and familiar food fishes. The family consists of 51 species in 15 genera and two subfamilies. All species are in the subfamily Scombrinae, except the butterfly kingfish, which is the sole member of subfamily Gasterochismatinae.
The Chiroteuthidae are a family of deep-sea squid, generally small to medium in size, rather soft and gelatinous, and slow moving. They are found in most temperate and tropical oceans, but are known primarily from the North Atlantic, North Pacific, and Indo-Pacific. The family is represented by approximately 12 species and four subspecies in four genera, two of which are monotypic. They are sometimes known collectively as whip-lash squid, but this common name is also applied to the Mastigoteuthidae, which are sometimes treated as a subfamily (Mastigoteuthinae) of Chiroteuthidae.

Tube-dwelling anemones or ceriantharians look very similar to sea anemones but belong to an entirely different subclass of anthozoans. They are solitary, living buried in soft sediments. Tube anemones live inside and can withdraw into tubes, which are composed of a fibrous material made from secreted mucus and threads of nematocyst-like organelles known as ptychocysts. Within the tubes of these ceriantharians, more than one polyp is present, which is an exceptional trait because species that create tube systems usually contain only one polyp per tube. Ceriantharians were formerly classified in the taxon Ceriantipatharia along with the black corals but have since been moved to their own subclass, Ceriantharia.

The Valvatida are an order of starfish in the class Asteroidea, which contains 695 species in 172 genera in 17 families.

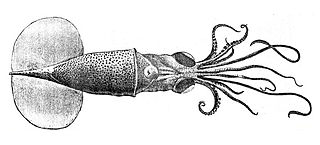
Chiroteuthis veranii, commonly known as the long-armed squid, is a species of chiroteuthid squid. It grows to a mantle length of 12.5 cm and a total length of 130 cm.

Neritidae, common name the nerites, is a taxonomic family of small to medium-sized saltwater and freshwater snails which have a gill and a distinctive operculum.

Santanachelys gaffneyi is an extinct species of sea turtle. It is the only species in the genus Santanachelys, which itself is a member of the extinct family Protostegidae. The species was first described from a 20-centimeter long fossil specimen unearthed in 1998 from the Santana Formation of eastern Brazil. From the rock layer from which it was excavated, it was determined that the specimen was from the Early Cretaceous period. It is therefore one of the oldest known sea turtles. It was even recorded as the oldest sea turtle in Encyclopædia Britannica, but a new fossil named Desmatochelyspadillai in 2015 is estimated to be as old as 120 million years.

Dunkleosteidae is an extinct family of arthrodire placoderms. The gigantic apex predator Dunkleosteus terrelli is the best known member of this group. While they were previously thought to be close relatives of the genus Dinichthys and grouped together in the family Dinichthyidae, more recent studies have shown that the two taxa represent two very distinct clades within Arthrodira. The reappraisal of Kiangyousteus lead to a restructuring of the family, with the inclusions of the benthic, aberrant Heterosteus as the sister taxon of Dunkleosteus, and the Late Emsian Xiangshuiosteus as the sister taxon of Eastmanosteus calliaspis, and the removal of Westralichthys from the family

The false ark shells (Cucullaea) are a small genus of marine bivalve molluscs related to the ark clams. The genus is the only member of the family Cucullaeidae.

Turbinellidae are a family of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the clade Neogastropoda. Members of this family are predators.

Corallimorpharia is an order of marine cnidarians closely related to stony or reef building corals (Scleractinia). They occur in both temperate and tropical climates, although they are mostly tropical. Temperate forms tend to be very robust, with wide and long columns, whereas tropical forms tend to have very short columns with a wide oral disc and very short tentacles. The tentacles are usually arranged in rows radiating from the mouth. Many species occur together in large groups, although there are recorded instances of individuals. In many respects, they resemble the stony corals, except for the absence of a stony skeleton. Morphological and molecular evidence suggests that they are very closely related to stony corals.

Odostomia is the most speciose genus of minute sea snails, pyramidellid gastropod mollusks. This genus is placed in the family Pyramidellidae in the subfamily Odostomiinae. There are several hundred species in this diverse genus

Chiroteuthis is a genus of chiroteuthid squid, comprising two subgenera. The hectocotylus is absent from all members of the genus; instead, a penis extending from the mantle opening is utilised. The genus is characterised by enlarged, lidded photophores present at the end of the tentacular club. Arms IV are both the longest and thickest, their membranes acting as sheaths to the retractable tentacles.
Planctoteuthis danae, or Dana's Chiroteutid squid is a species of chiroteuthid squid. It is distinguished from further members of Planctoteuthis by a fin length greater than half of the mantle. During the paralarval stage, the species occurs in depths of 200–300 m, progressing to 200–800 m at 10-15mm ML; larger specimens have been captured from 700 m to in excess of 1000 m. The type locality of P. danae is in the Gulf of Panama, and it has also been recorded from the eastern Pacific Ocean and North Atlantic Ocean.

Corallimorphus is a genus of colonial anthozoans similar in appearance to sea anemones and in body format to scleractinian stony corals. These animals are cnidarians in the family Corallimorphidae. Members of the genus live off the Pacific coast of the US.

Favia is a genus of reef-building stony corals in the family Mussidae. Members of the genus are massive or thickly encrusting colonial corals, either dome-shaped or flat, and a few are foliaceous. There is a great diversity of form even among individuals of the same species. The corallites project slightly above the surface of the coral and each has its own wall. In most species, the corallites are plocoid and in some, monocentric. The septa and costae linked to the corallite wall are well developed and covered by fine teeth. The polyps only extend and feed during the night. Each one has a small number of tapering tentacles which often have a darker coloured tip; these are called stinger tentacles, or sweeper tentacles. They use these to sweep the water to see if any other coral is in its area; if so, then they begin to sting the other coral. This is commonly known as coral war. Each coral is trying to make sure it has enough room around it so it can continue to grow and have more surface area for its offspring. The columella is parietal and spongy, and there are vesicles on both the endotheca and exotheca. Members of this genus are widespread in both the Atlantic Ocean and the Indo-Pacific.

Caryophyllia is a genus of solitary corals in the family Caryophylliidae. Members of this genus are azooxanthellate and are found in the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea at depths down to 2,670 metres (8,760 ft).
Perkinsozoa is a proposed phylum of intracellular parasites in the superphylum Alveolata, which was suggested to account for the genus Perkinsus and other protist species that do not fit into existing Alveolata phyla.

Cichliformes is an order of fishes. Its members were previously classified under the order Perciformes, but now many authorities consider it to be an independent order within the subseries Ovalentaria.
















