
Diplarrena is a genus of flowering plants in the family Iridaceae. The two species are endemic to Australia. The name is from Greek diploos ("double") and arren ("male"); plants in the genus have only two functional stamens, while all other Iridaceae have three. The name is often misspelled Diplarrhena, an error that began with George Bentham's Flora Australiensis in 1873.

Conospermum stoechadis, commonly known as common smokebush, is a shrub endemic to Western Australia.
Amphibolis antarctica is a species of flowering plant in the family Cymodoceaceae. It is referred to by the common names wire weed or sea nymph, and is a seagrass found in coastal waters of southern and western Australia.

Gahnia filum, the chaffy saw-sedge, is a tussock-forming perennial in the family Cyperaceae, endemic to Australia. It grows to between 60 and 110 cm in height.

Brachyscome ciliaris, commonly known as variable daisy, is a small bushy perennial herb with a prominent flower, which occurs throughout most of temperate Australia

Bulbine semibarbata, commonly known as leek lily, native leek or wild onion, is a species of annual herb native to Australia.

Daucus glochidiatus, commonly known as Australian carrot, Austral carrot or native carrot, is a species of herb in the flowering plant family Apiaceae. It is native to Australia and New Zealand.

Eragrostis dielsii, commonly known as mallee lovegrass, is a species of grass in the family Poaceae that is endemic to Australia.

Nicotiana occidentalis, commonly known as native tobacco, is a short-lived herb native to Australia.

Euchiton sphaericus, the star cudweed or tropical creeping cudweed, is a herb native to Australia, New Zealand, New Caledonia, Taiwan, Java, and Philippines. It has become naturalized in a few places in the United States.
Plantago debilis is a species of herb native to Australia. Common names include shade plantain and weak plantain.
Senecio glossanthus is an annual herb native to Australia. In Western Australia it is commonly known as slender groundsel.

Trichodesma zeylanicum, commonly known as Northern bluebell, camel bush or cattle bush, is a herb or shrub native to Australia.

Podotheca is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Gnaphalieae within the family Asteraceae. All species are endemic to Western Australia, except for Podotheca angustifolia which occurs across the south of Australia.
Leptorhynchos is a genus of annual or perennial herbs in the family Asteraceae. All species are endemic to Australia. These include:
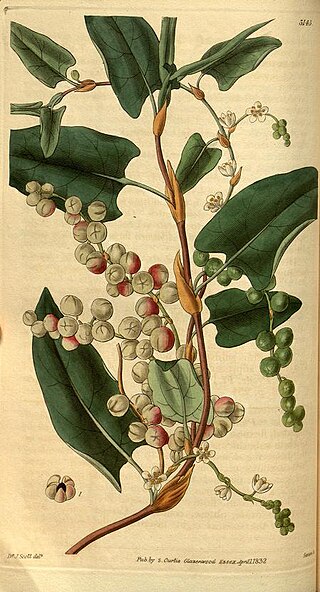
Muehlenbeckia adpressa, commonly known as climbing lignum, is a prostrate or climbing plant, native to Australia. It has thin red-brown stems up to 1 metre in length. The leaves are 1.5–6 centimetres (0.59–2.36 in) long and 1.5–3.5 centimetres (0.59–1.38 in) wide. It occurs in coastal areas of Western Australia, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and New South Wales.

Coronidium scorpioides, commonly known as the button everlasting, is a perennial herbaceous shrub in the family Asteraceae found in Australia. Previously known as Helichrysum scorpioides, it was placed in the newly described genus Coronidium in 2008.

Gratiola peruviana, commonly known as austral brooklime, is a small perennial herb in the family Plantaginaceae. The species is native to South America and Australasia. It grows to between 10 and 30 centimetres high and has pink or white tubular flowers with red-purple stripes inside. These are followed by ovoid capsules that are up to 7mm long. The stem-clasping ovate leaves are arranged in opposite pairs and have shallowly toothed edges.

Coprosma hirtella is a shrub in the family Rubiaceae. It is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It grows to about 2 metres high and has leaves that are between 15 and 50 mm long and 10 to 25 mm wide. Plants have male and female flower clusters that appear between August and April. These are followed by orange to reddish fruits that are 7 to 8 mm in diameter.

Pterostylis plumosa, commonly known as the bearded greenhood or plumed greenhood is a species of orchid in the family Orchidaceae which is endemic to south-eastern Australia and possibly New Zealand. Its labellum or lip is long and thin, bordered with golden hairs, giving it the name "bearded".
















