Related Research Articles

Transport in New Zealand, with its mountainous topography and a relatively small population mostly located near its long coastline, has always faced many challenges. Before Europeans arrived, Māori either walked or used watercraft on rivers or along the coasts. Later on, European shipping and railways revolutionised the way of transporting goods and people, before being themselves overtaken by road and air, which are nowadays the dominant forms of transport. However, bulk freight still continues to be transported by coastal shipping and by rail transport, and there are attempts to (re)introduce public transport as a major transport mode in the larger population centres.
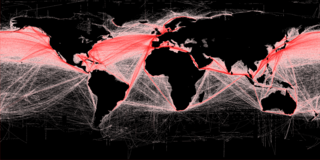
Freight transport, also referred as freight forwarding, is the physical process of transporting commodities and merchandise goods and cargo. The term shipping originally referred to transport by sea but in American English, it has been extended to refer to transport by land or air as well. "Logistics", a term borrowed from the military environment, is also used in the same sense.

Highways in Australia are generally high capacity roads managed by state and territory government agencies, though Australia's federal government contributes funding for important links between capital cities and major regional centres. Prior to European settlement, the earliest needs for trade and travel were met by narrow bush tracks, used by tribes of Indigenous Australians. The formal construction of roads began in 1788, after the founding of the colony of New South Wales, and a network of three major roads across the colony emerged by the 1820s. Similar road networks were established in the other colonies of Australia. Road construction programs in the early 19th century were generally underfunded, as they were dependent on government budgets, loans, and tolls; while there was a huge increase in road usage, due to the Australian gold rushes. Local government authorities, often known as Road Boards, were therefore established to be primarily responsible for funding and undertaking road construction and maintenance. The early 1900s saw both the increasingly widespread use of motorised transportation, and the creation of state road authorities in each state, between 1913 and 1926. These authorities managed each state's road network, with the main arterial roads controlled and maintained by the state, and other roads remaining the responsibility of local governments. The federal government became involved in road funding in the 1920s, distributing funding to the states. The depression of the 1930s slowed the funding and development of the major road network until the onset on World War II. Supply roads leading to the north of the country were considered vital, resulting in the construction of Barkly, Stuart, and Eyre Highways.

The Department for Transport (DfT) is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for the English transport network and a limited number of transport matters in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland that have not been devolved. The department is run by the Secretary of State for Transport, currently Mark Harper.

The Port of Hong Kong, located by the South China Sea, is a deepwater seaport dominated by trade in containerised manufactured products, and to a lesser extent raw materials and passengers. A key factor in the economic development of Hong Kong, the natural shelter and deep waters of Victoria Harbour provide ideal conditions for berthing and the handling of all types of vessels. It is one of the busiest ports in the world, in the three categories of shipping movements, cargo handled and passengers carried. This makes Hong Kong a Large-Port Metropolis.

Australian Maritime Safety Authority (AMSA) is an Australian statutory authority responsible for the regulation and safety oversight of Australia's shipping fleet and management of Australia's international maritime obligations. The authority has jurisdiction over Australia's exclusive economic zone which covers an area of 11,000,000 square kilometres (4,200,000 sq mi). AMSA maintains Australia's shipping registries: the general and the international shipping registers.

Transport in Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria, Australia, consists of several interlinking modes. Melbourne is a hub for intercity, intracity and regional travel. Road-based transport accounts for most trips across many parts of the city, facilitated by Australia's largest freeway network. Public transport, including the world's largest tram network, trains and buses, also forms a key part of the transport system. Other dominant modes include walking, cycling and commercial-passenger vehicle services such as taxis.
The flag state of a merchant vessel is the jurisdiction under whose laws the vessel is registered or licensed, and is deemed the nationality of the vessel. A merchant vessel must be registered and can only be registered in one jurisdiction, but may change the jurisdiction in which it is registered. The flag state has the authority and responsibility to enforce regulations over vessels registered under its flag, including those relating to inspection, certification, and issuance of safety and pollution prevention documents. As a ship operates under the laws of its flag state, these laws are applicable if the ship is involved in an admiralty case.
Gavan McDonell is an Australian civil engineer, economist and political sociologist in the fields of national infrastructure policy reform, international development and academic education for advanced sustainability studies.

The Minister for Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Local Government in the Government of Australia is a position currently held by Catherine King following the swearing in of the full Albanese ministry on 1 June 2022.
Transport law is the area of law dealing with transport. The laws can apply very broadly at a transport system level or more narrowly to transport things or activities within that system such as vehicles, things and behaviours. Transport law is generally found in two main areas:
The National Transport Commission (NTC), previously known as the National Road Transport Commission, is an Australian statutory body created to develop regulatory and operational reform for road, rail and intermodal transport.

The Transport Integration Act 2010 is a law enacted by the Parliament of the State of Victoria, Australia. The Act is the prime transport statute in Victoria, having replaced major parts of the Transport Act 1983, which was renamed as the Transport Act 1983.

The Department of Transport (DOT) was the government agency responsible for the coordination, integration and regulation of the transport system in the State of Victoria, Australia. The department generated planning, policy, and legislation for transport in Victoria. As a result, the department drove the integration of Victoria's transport land and water transport systems and the delivery of public transport, road and port services and associated activities across the State. The department's stated mission was "Building a safer, fairer and greener transport system for all Victorians to create a more prosperous and connected community."

The Director of Public Transport was the head of the Public Transport Division (PTD) of the Victorian Department of Transport. PTD was the government agency responsible for promoting, providing, coordinating and regulating public transport in the state of Victoria, Australia between August 1999 and June 2013. The Director of Public Transport was created as a statutory office supported by staff of the Department of Transport.
The Chief Investigator, Transport Safety is the independent Government agency responsible for investigation of safety-related trends and incidents in the rail, bus and marine industries in the State of Victoria, Australia.
The Port of Hastings Development Authority is an authority of the Government of Victoria, Australia. The authority is responsible for the development and management of the port of Hastings located in Western Port Bay approximately 72 kilometres to the south east of Melbourne. The port is expected to be developed by the authority as a major new container port in competition with the Port of Melbourne, Australia's busiest container port.
The Danish Maritime Authority is the agency of the Danish Government responsible for regulating and administrating Danish maritime affairs. The Danish Maritime Authority (DMA) is part of the Ministry of Industry, Business, and Financial Affairs. The Agency consists of the central authority and eight vision offices, including the office in Nuuk and the Centre for Maritime Health on Fanø. Its headquarters are in Korsør.
Transport in South Australia is provided by a mix of road, rail, sea and air transport. The capital city of Adelaide is the centre to transport in the state. With its population of 1.4 million people, it has the majority of the state's 1.7 million inhabitants. Adelaide has the state's major airport and sea port.

The Department of Infrastructure and Regional Development was an Australian Government department that existed between September 2013 and December 2017. Matters dealt with by the department included: infrastructure planning and coordination; transport safety; land transport; civil aviation and airports; maritime transport including shipping; administration of Australian territories; constitutional development of the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory; regional programs; regional development; local government matters; and regional policy.
References
- ↑ Ports Australia, About Us
- 1 2 "Ports". infrastructure.gov.au. Retrieved 3 November 2017.
- ↑ "Ports Australia". www.weareports.com.au. Retrieved 3 November 2017.