| Posthodiplostomum | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Trematoda |
| Order: | Diplostomida |
| Family: | Diplostomidae |
| Genus: | Posthodiplostomum Dubois, 1936 |
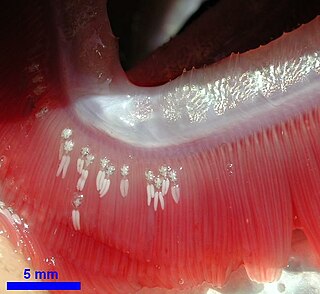
Posthodiplostomum is a genus of flatworms belonging to the family Diplostomidae. [1]
The species of this genus are found in Europe, Australia and Northern America. [1]
As of May 2024 [update] , a total of 36 species are recognized by the Global Biodiversity Information Facility: [1]
- Posthodiplostomum anterovarium (Dronen, 1985)
- Posthodiplostomum australe Dubois, 1937
- Posthodiplostomum biellipticum Dubois, 1958
- Posthodiplostomum botauri Vidyarthi, 1938
- Posthodiplostomum brevicaudatum (von Nordmann, 1832)
- Posthodiplostomum centrarchi Hoffman, 1958
- Posthodiplostomum cuticola (von Nordmann, 1832)
- Posthodiplostomum erickgreenei Achatz, Chermak, Cromwell & Tkach, 2021
- Posthodiplostomum eurypygae Achatz, Chermak, Bell, Fecchio & Tkach, 2021
- Posthodiplostomum giganteum Dubois, 1988
- Posthodiplostomum grande (Diesing, 1850)
- Posthodiplostomum grayii (Verma, 1936)
- Posthodiplostomum huesingi Odening, 1962
- Posthodiplostomum ixobrychi (Lung, 1966)
- Posthodiplostomum kinselli Achatz, Chermak, Martens, Pulis & Tkach, 2021
- Posthodiplostomum larai (Refuerzo & Garcia, 1937)
- Posthodiplostomum linguaeforme Pearson & Dubois, 1985
- Posthodiplostomum macrocotyle Dubois, 1937
- Posthodiplostomum mehtai Gupta & Mishra, 1974
- Posthodiplostomum microsicya Dubois, 1936
- Posthodiplostomum mignum Boero, Led & Brandetti, 1972
- Posthodiplostomum milvi Fotedar & Bambroo, 1965
- Posthodiplostomum minimum (MacCallum, 1921)
- Posthodiplostomum nanum Dubois, 1937
- Posthodiplostomum obesum (Lutz, 1928)
- Posthodiplostomum oblongum Dubois, 1937
- Posthodiplostomum opisthosicya Dubois, 1969
- Posthodiplostomum orchilongum Noble, 1936
- Posthodiplostomum pacificum Achatz, Chermak, Kent & Tkach, 2021
- Posthodiplostomum podicipitis (Yamaguti, 1939)
- Posthodiplostomum pricei (Krull, 1934)
- Posthodiplostomum prosostomum Dubois & Rausch, 1948
- Posthodiplostomum ptychocheilus (Faust, 1917)
- Posthodiplostomum recurvirostrae Achatz, Chermak & Tkach, 2021
- Posthodiplostomum scardinii (Shulman, 1952)
- Posthodiplostomum skrjabini Sadychov, 1967