
The Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone is an American twin-row, supercharged, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine with 18 cylinders displacing nearly 3,350 cubic inches (54.9 L). Power ranged from 2,200 to 3,700 hp, depending on model. Developed before World War II, the R-3350's design required a long time to mature, and was still experiencing problems with reliability when used to power the Boeing B-29 Superfortress.

The Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major is an American 28-cylinder four-row radial piston aircraft engine designed and built during World War II. At 4,362.5 cu in (71.5 L), it is the largest-displacement aviation piston engine to be mass-produced in the United States, and at 4,300 hp (3,200 kW) the most powerful. First run in 1944, it was the last of the Pratt & Whitney Wasp family, and the culmination of its maker's piston engine technology.

The hyper engine was a 1930s study project by the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) to develop a high-performance aircraft engine that would be equal to or better than the aircraft and engines then under development in Europe. The project goal was to produce an engine that was capable of delivering 1 hp/in3 (46 kW/L) of engine displacement for a weight of less than 1 lb/hp delivered. The ultimate design goal was an increased power-to-weight ratio suitable for long-range airliners and bombers.

The Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp is an American twin-row, 18-cylinder, air-cooled radial aircraft engine with a displacement of 2,800 cu in (46 L), and is part of the long-lived Wasp family of engines.

The Curtiss-Wright XP-55 Ascender is a 1940s United States prototype fighter aircraft built by Curtiss-Wright. Along with the Vultee XP-54 and Northrop XP-56, it resulted from United States Army Air Corps proposal R-40C issued on 27 November 1939 for aircraft with improved performance, armament, and pilot visibility over existing fighters; it specifically allowed for unconventional aircraft designs. An unusual design for its time, it had a canard configuration with a rear-mounted engine, and two vertical tails at end of swept wings. Because of its pusher design, it was satirically referred to as the "Ass-ender". Like the XP-54, the Ascender was designed for the 1,800 hp Pratt & Whitney X-1800 24-Cylinder H-engine, but was redesigned after that engine project was canceled. It was also the first Curtiss fighter aircraft to use tricycle landing gear.
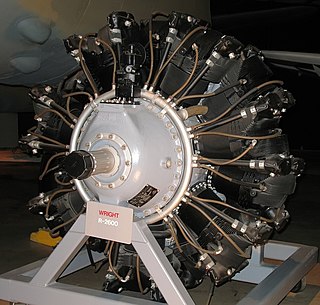
The Wright R-2600 Cyclone 14 is an American radial engine developed by Curtiss-Wright and widely used in aircraft in the 1930s and 1940s.

The Wright R-1820 Cyclone 9 is an American radial engine developed by Curtiss-Wright, widely used on aircraft in the 1930s through 1950s. It was produced under license in France as the Hispano-Suiza 9V or Hispano-Wright 9V, and in the Soviet Union as the Shvetsov M-25.

Wright Cyclone was the name given to a family of air-cooled radial piston engines designed by the Wright Aeronautical Corporation and used in numerous American aircraft in the 1930s, 1940s and 1950s.

The Pratt & Whitney Wasp was the civilian name of a family of air-cooled radial piston engines developed in the 1920s, 1930s and 1940s.

The Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp is an aircraft engine of the reciprocating type that was widely used in American aircraft from the 1920s onward. It was the Pratt & Whitney aircraft company's first engine, and the first of the famed Wasp series. It was a single-row, nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial design, and displaced 1,344 cubic inches (22 L); bore and stroke were both 5.75 in (146 mm). A total of 34,966 engines were produced.

The Pratt & Whitney R-1535 Twin Wasp Junior is an American aircraft engine developed in the 1930s. The engine was introduced in 1932 as a 14-cylinder version of the 9-cylinder R-985, and was a two-row, air-cooled radial design. Displacement was 1,535 cu in (25.2 L); bore and stroke were both 5+3⁄16 in (132 mm).

The Lockheed XP-58 Chain Lightning was an American long-range fighter developed during World War II. Although derived from the successful P-38 Lightning, the XP-58 was plagued by technical problems with its engines that eventually led to the project's cancellation.

The Vultee XP-54 Swoose Goose was a prototype fighter built by the Vultee Aircraft Company for the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF).

The Rolls-Royce Eagle Mk XXII is a British 24-cylinder, sleeve valve, H-block aero engine of 46 litre displacement. It was designed and built in the early-1940s by Rolls-Royce Limited and first ran in 1944. It was liquid-cooled, of flat H configuration with two crankshafts and was capable of 3,200 horsepower at 18 psi boost.

The Allison V-3420 was a large experimental piston aircraft engine, designed in 1937 by the American Allison Engine Company.

The Pratt & Whitney R-2000 Twin Wasp is an American radial engine developed in 1942 to power military aircraft. It is one of the Pratt & Whitney Wasp series of Radial engines.

The Pratt & Whitney R-2180-E Twin Wasp E was a radial aircraft engine developed in the United States by Pratt & Whitney. It had two rows of seven cylinders each. Its only production application was on the post-World War II Saab 90 Scandia airliner.
The Pratt & Whitney XH-3130 was an H-block aircraft engine project developed for the United States Navy in the late 1930s. The design was later enlarged as the XH-3730), but the project was canceled in 1940 in favor of Pratt & Whitney developing the R-4360 Wasp Major air-cooled radial engine.
The Pratt & Whitney R-2060 Yellow Jacket was a liquid-cooled aircraft engine project developed for the United States Army in the early 1930s. The engine had five banks of four in-line cylinders, and displaced 2,060 cubic inches. Designed to produce 1,000 hp, the engine produced 1,116 hp on its final run after 35 hours of testing. The engine was cancelled in favor of continuing development of Pratt & Whitney's air-cooled R-1830 Twin Wasp radial engine.
The Lycoming XH-2470 was an H engine for aircraft designed and developed by Lycoming Engines in the 1930s. Although the engine was flown in an aircraft, it was not fitted to any aircraft selected for production. It was derived from the Lycoming O-1230 engine.

















