
The Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone is an American twin-row, supercharged, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine with 18 cylinders displacing nearly 3,350 cubic inches (54.9 L). Power ranged from 2,200 to 3,700 hp, depending on model. Developed before World War II, the R-3350's design required a long time to mature, and was still experiencing problems with reliability when used to power the Boeing B-29 Superfortress.

The Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major is an American 28-cylinder four-row radial piston aircraft engine designed and built during World War II. At 4,362.5 cu in (71.5 L), it is the largest-displacement aviation piston engine to be mass-produced in the United States, and at 4,300 hp (3,200 kW) the most powerful. First run in 1944, it was the last of the Pratt & Whitney Wasp family, and the culmination of its maker's piston engine technology.

The Stinson Reliant is a popular single-engine four- to five-seat high-wing monoplane manufactured by the Stinson Aircraft Division of the Aviation Manufacturing Corporation of Wayne, Michigan.

The Lycoming XR-7755 was the largest piston aircraft engine ever built in the United States, with 36 cylinders totaling about 7,750 in3 (127 L) of displacement and a power output of 5,000 horsepower (3,700 kilowatts). It was originally intended to be used in the "European bomber" that eventually emerged as the Convair B-36. Only two examples were built before the project was terminated in 1946.

The Warner Scarab is an American seven-cylinder radial aircraft engine, that was manufactured by the Warner Aircraft Corporation of Detroit, Michigan in 1928 through to the early 1940s. In military service the engine was designated R-420.

The Continental R-670 was a seven-cylinder four-stroke radial aircraft engine produced by Continental displacing 668 cubic inches and a dry weight of 465 lb (211 kg). Horsepower varied from 210 to 240 at 2,200 rpm. The engine was the successor to Continental's first radial engine, the 170 hp Continental A-70. This engine was used on many aircraft in the 1930s and 1940s. The R-670 was widely used in the PT-17 Stearman primary training aircraft of the U.S. military.

The Franklin O-335 was an American air-cooled aircraft engine of the 1940s. The engine was of six-cylinder, horizontally-opposed layout and displaced 335 cu in (5.5 L). The power output of later variants was 225 hp (168 kW).

The Alfa Romeo 115 is an Italian six-cylinder air-cooled inverted inline engine for aircraft use, mainly for training and light planes, based on the de Havilland Gipsy Six engine. Production totalled approximately 1,600 units. Derivatives of the 115 include the -1, bis, ter and Alfa Romeo 116.

The Jacobs R-755 is a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft manufactured in the United States by the Jacobs Aircraft Engine Company.

The Wright R-760 Whirlwind was a series of seven-cylinder air-cooled radial aircraft engines built by the Wright Aeronautical division of Curtiss-Wright. These engines had a displacement of 756 in³ (12.4 L) and power ratings of 225-350 hp (168-261 kW).

The Wright R-2160 Tornado was an experimental 42-cylinder, 7-cylinder per row, 6-row liquid-cooled inline radial aircraft engine. It was proposed in 1940 with 2,350 hp (1,752 kW) for experimental aircraft such as the Lockheed XP-58 Chain Lightning, Vultee XP-68 Tornado, and the Republic XP-69.

The Kinner B-5 was a popular five cylinder American radial engine for light general and sport aircraft of the 1930s.

The ENMASA Beta was a Spanish air-cooled radial engine of the 1950s. A copy of the American Wright R-1820 Cyclone, the Beta was the powerplant of a number of post Spanish Civil War aircraft, including the Spanish version of the Junkers Ju 52 transport, the CASA C-202 Halcón and the Hispano HA-100 trainer.
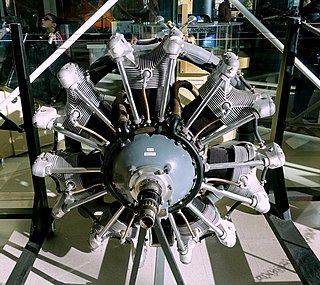
The Jacobs R-915 or Jacobs L-6 is a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft manufactured in the United States, production started in 1936.

The Alvis Pelides was an unflown British air-cooled radial aero engine first developed in 1936. The Pelides Major was a projected but unbuilt development as were the Alcides, Alcides Major and the Maeonides Major, the Alvis aircraft engine range taking their names from Greek mythology.
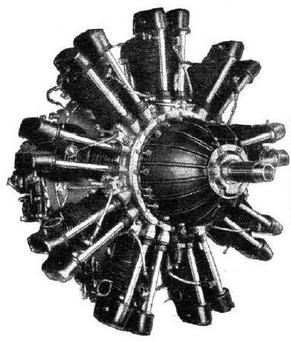
The Wolseley Aries III or A.R.9 was a British nine-cylinder, air-cooled radial aero engine that first ran in 1933, it was designed and built by Wolseley Motors. Intended for the military trainer aircraft market few were produced as Wolseley withdrew from the aero engine market in 1936.

The Avia Rk.17 was a 9-cylinder radial aircraft engine, developed from the 7-cylinder Avia Rk.12, with a rated output of 270 kW (360 hp). The Rk.17 was one of Avia's own designs and was built in Czechoslovakia in the 1930s.
The Wright R-4090 Cyclone 22 was an American experimental radial piston engine designed and built in prototype form by Wright Aeronautical during the 1940s.

The Guiberson A-1020 is a four-stroke diesel radial engine developed for use in aircraft and tanks.

The Fiat A.70 was an air cooled radial engine with seven cylinders developed by the Italian engineering company Fiat Aviazione in the 1930s. The engine powered a number of Italian light competition and prototype aircraft.


















