
The BMW 132 was a nine-cylinder radial aircraft engine produced by BMW starting in 1933.
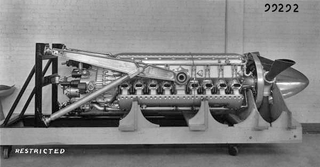
The Chrysler XIV-2220 was an experimental 2,500 hp, 2,220 cubic inch liquid-cooled inverted-V-16 aircraft engine designed by Chrysler starting in 1940. Although several aircraft designs had considered using it, by the time it was ready for use in 1945 the war was already over. Only a few engines were built during the program, and it retained its 'X' designation the entire time as the XIV-2220, later XI-2220. The IV-2220 is historically important as it was Chrysler's first hemi, a design that would re-appear for many years later and is now a Chrysler trademark.

The Lycoming XR-7755 was the largest piston aircraft engine ever built in the United States, with 36 cylinders totaling about 7,750 in³ (127 L) of displacement and a power output of 5,000 horsepower (3,700 kilowatts). It was originally intended to be used in the "European bomber" that eventually emerged as the Convair B-36. Only two examples were built before the project was terminated in 1946.

The Allison V-3420 was a large experimental piston aircraft engine, designed in 1937 by the American Allison Engine Company.

The Armstrong Siddeley Mongoose is a British five-cylinder radial aero engine produced by Armstrong Siddeley. Developed in the mid-1920s it was used in the Hawker Tomtit trainer and Parnall Peto seaplane amongst others. With a displacement of 540 cubic inches (9 litres) the Mongoose had a maximum power output of 155 horsepower (115 kilowatts).

The Warner Scarab is an American seven-cylinder radial aircraft engine, that was manufactured by the Warner Aircraft Corporation of Detroit, Michigan in 1928 through to the early 1940s. In military service the engine was designated R-420.

The Continental R-670 was a seven-cylinder four-cycle radial aircraft engine produced by Continental displacing 668 cubic inches and a dry weight of 465 lb (211 kg). Horsepower varied from 210 to 240 at 2,200 rpm. The engine was the successor to Continental's first radial engine, the 170 hp Continental A-70. This engine was used on many aircraft in the 1930s and 1940s. The R-670 was widely used in the PT-17 Stearman primary training aircraft of the U.S. military.

The LeBlond radial engines, later produced under the name Ken-Royce, were a family of 3-cylinder, 5-cylinder and 7-cylinder, air-cooled radial engines for aircraft, built in the 1930s by the LeBlond Aircraft Engine Corporation until the operation was sold to Rearwin Airplanes in 1937 and renamed Ken-Royce Engines.

The Shvetsov ASh-62 is a nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine produced in the Soviet Union. A version of this engine is produced in Poland as the ASz-62 and the People's Republic of China as the HS-5.

The Fiat A.74 was a two-row, fourteen-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine produced in Italy in the 1930s as a powerplant for aircraft. It was used in some of Italy's most important aircraft of World War II.

The Wright R-2160 Tornado was an experimental 42-cylinder, 7-cylinder per row, 6-row liquid-cooled inline radial aircraft engine. It was proposed in 1940 with 2,350 hp (1,752 kW) for experimental aircraft such as the Lockheed XP-58 Chain Lightning, Vultee XP-68 Tornado, and the Republic XP-69.

The Kinner R-5 is an American five cylinder radial engine for light general and sport aircraft of the 1930s.

The Shvetsov ASh-21 is a seven-cylinder single-row air-cooled radial aero engine.
The Shvetsov ASh-73 was an 18-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine produced between 1947 and 1957 in the Soviet Union. It was primarily used as the powerplant for the Tupolev Tu-4 heavy bomber, a copy of the American Boeing B-29 Superfortress.

The Alvis Pelides was an unflown British air-cooled radial aero engine first developed in 1936. The Pelides Major was a projected but unbuilt development as were the Alcides, Alcides Major and the Maeonides Major, the Alvis aircraft engine range taking their names from Greek mythology.
The Kinner C-5 was an American five cylinder radial engine for small general and sport aircraft of the 1930s.

The Curtiss H-1640 Chieftain was an unusual American 12-cylinder radial aero engine designed and built by the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company in the mid-1920s.

The Wolseley 60 hp or Type C was a British liquid-cooled V-8 aero engine that first ran in 1910, it was designed and built by Wolseley Motors. The engine featured water-cooled exhaust ports and employed a 20 lb (9 kg) flywheel. During an official four-hour test the engine produced an average of 55 horsepower. A larger capacity variant known as the 80 hp or Type B used an internal camshaft and propeller reduction gear.
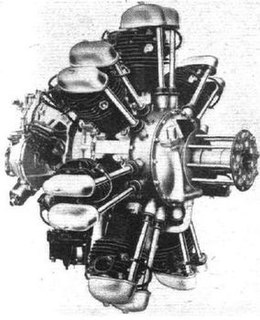
The Wolseley Aquarius I or A.R.7 was a British seven-cylinder, air-cooled radial aero engine that first ran in 1933, it was designed and built by Wolseley Motors. Intended for the military trainer aircraft market few were produced, as Wolseley withdrew from the aero engine market in 1936.

The Aeromarine B-90 is an aircraft engine built by the Aeromarine Plane and Motor Company in 1915. Aeromarine made two series of V-8 engines. The B series was developed by Joseph Boland and the L series by Charles F. Willard.


















