
Micropterus is a genus of North American freshwater fish collectively known as the black bass, which belong to the sunfish family Centrarchidae of order Centrarchiformes. They are sometimes erroneously called "black trout", but the name trout more correctly refers to certain potamodromous members of the family Salmonidae.

Pollock or pollack is the common name used for either of the two species of North Atlantic marine fish in the genus Pollachius. Pollachius pollachius is referred to as "pollock" in North America, Ireland and the United Kingdom, while Pollachius virens is usually known as saithe or coley in Great Britain and Ireland. Other names for P. pollachius include the Atlantic pollock, European pollock, lieu jaune, and lythe or lithe; while P. virens is also known as Boston blue, silver bill, or saithe.

The Squaliformes are an order of sharks that includes about 126 species in seven families.

The flagtails are a family (Kuhliidae) of centrarchiform ray-finned fish of the Indo-Pacific area. The family consists of about 12 species in one genus, Kuhlia. Most are euryhaline and often found in brackish water, but the genus also includes species restricted to marine or fresh water.

Carpet sharks are sharks classified in the order Orectolobiformes. Sometimes the common name "carpet shark" is used interchangeably with "wobbegong", which is the common name of sharks in the family Orectolobidae. Carpet sharks have five gill slits, two spineless dorsal fins, and a small mouth that does not extend past the eyes. Many species have barbels.

Nycteris comprises a genus of bats commonly called slit-faced or hollow-faced bats. They are grouped in the family Nycteridae. The bats are found in East Malaysia, Indonesia, and many parts of Africa.

Sander is a genus of predatory ray-finned fish in the family Percidae, which also includes the perches, ruffes, and darters. They are also known as "pike-perch" because of their resemblance to fish in the unrelated Esocidae (pike) family. They are the only genus in the monotypic tribe Luciopercini, which is one of two tribes in the subfamily Luciopercinae.

Notothenioidei is one of 19 suborders of the order Perciformes. The group is found mainly in Antarctic and Subantarctic waters, with some species ranging north to southern Australia and southern South America. Notothenioids constitute approximately 90% of the fish biomass in the continental shelf waters surrounding Antarctica.
The Pseudotriakidae are a small family of ground sharks, belonging to the order Carcharhiniformes, containing the false catsharks and gollumsharks. It contains the only ground shark species that exhibit intrauterine oophagy, in which developing fetuses are nourished by eggs produced by their mother.

Jack mackerels or saurels are marine ray-finned fish in the genus Trachurus of the family Carangidae. The name of the genus derives from the Greek words trachys ("rough") and oura ("tail"). Some species, such as T. murphyi, are harvested in purse seine nets, and overfishing has sometimes occurred.

Rivulus is a genus of small freshwater fish in the Cyprinodontiformes family Rivulidae. It was traditionally considered to be the largest genus in its family; however, the genus's size is currently in dispute. Wilson J. E. Costa split this genus into several new genera in 2004 and 2011, leaving only a few Greater Antillean species in Rivulus itself. Despite being moved to other genera, some of the species retain the common name "rivulus", like the well-known mangrove rivulus. Shortly after the review by Costa, another review authored by J.H. Huber refuted the split, moving the proposed genera back in Rivulus and again making the genus the largest in the family Aplocheilidae.

Nothobranchiidae are a family of bony fishes containing roughly 300 species, also known as African rivulines. They are small killifish, usually measuring about 5 centimetres (2.0 in). They are limited to Africa, living in fresh water but being also somewhat salt-tolerant. They are also found in muddy or brackish water. Some species are kept as aquarium pets. They have frilly fins and many are brightly colored. They were formerly included in the family Aplocheilidae ; a return to that broader family has recently been suggested.

An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water.
Enteromius seymouri is a species of cyprinid fish in the genus Enteromius which is endemic to Malawi.

Aphyosemion is a genus of African rivulines endemic as the name indicates to Africa. Many of these species are popular aquarium fish.
Pronothobranchius kiyawensis is a species of killifish from the family Nothobranchiidae which is native to western Africa where it occurs in the drainage basin of Lake Chad.
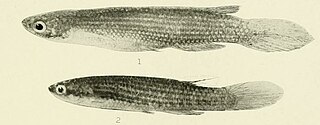
Anablepsoides is a genus of killifish in the family Rivulidae native to tropical South America and the Lesser Antilles. The majority are from the Amazon and Orinoco basins, as well as freshwater systems in the Guiana Shield, but a few species are from northern Venezuela, northeastern Brazil and the Lesser Antilles. Although largely restricted to lowlands, a few species occur in the lower East Andean foothills. They are mostly found in shallow fresh water swamps, streams, edges of rivers, ponds and pools, but a few may occur in brackish estuaries. They are able to jump over land and breathe air for short periods, allowing them to access isolated waters inhabited by few or no other fish. Several Anablepsoides species have small distributions and some are seriously threatened by habitat loss; the entire known range of A. xinguensis is in the area flooded by the Belo Monte Dam.

Laimosemion is a genus of fish in the family Rivulidae from the Amazon basin and basins in the Guiana Shield in tropical South America. They mostly inhabit small streams, creeks, swamps and pools in lowlands, but locally occur to an altitude of 1,300 m (4,300 ft).

Moema is a genus of fish in the family Rivulidae. These annual killifish are mostly restricted to the Amazon basin in Bolivia, Brazil and Peru, but a few inhabit the upper Essequibo basin in Guyana, upper Orinoco basin in Venezuela and upper Paraguay basin in Brazil. They inhabit temporary waters, such as swamps or ponds, in primary forests. Once the water disappears, the adults die, but the eggs that have been laid in the bottom remain, only hatching after 3–10 months when the water returns. They rapidly reach adult size, but generally only live a few months after hatching, although captives can live longer.
Papiliolebias is a genus of fish in the family Rivulidae. These annual killifish are endemic to seasonal pools in the Paraguay and upper Madeira river basins in northwestern Argentina, central and southeastern Bolivia, and western Paraguay.















