Prosopis alba is a South American tree species that grows in central Argentina, the Gran Chaco ecoregion, and part of the Argentine Mesopotamia, as well as Bolivia, Paraguay, and Peru. It is known as algarrobo blanco in Spanish. Spanish settlers gave it that name because of its similarity to the European carob tree. Other common names come from Guaraní, including ibopé and igopé.

Prosopis nigra is a South American leguminous tree species that inhabits the Gran Chaco ecoregion, in Argentina and Paraguay. It is known as algarrobo negro in Spanish, which means "black carob tree". It is also variously called algarrobo dulce, algarrobo morado and algarrobo amarillo.

Jerdon's bush lark or Jerdon's lark is a species of lark in the family Alaudidae found in south Asia. This was formerly considered as a subspecies of Mirafra assamica and termed as the Madras bushlark. Two other species in the complex include Mirafra marionae and Mirafra microptera. Jerdon's bush lark is typically very pale on the underside

The savanna nightjar is a species of nightjar found in South and Southeast Asia. Eight subspecies are recognised: C. a. monticolus, C. a. amoyensis, C. a. stictomus, C. a. affinis, C. a. timorensis, C. a. griseatus, C. a. mindanensis and C. a. propinquus. Its habitat is open forest and areas with scrub. Its length is about 25 cm (9.8 in). The upperparts are brownish-grey and vermiculated, with pale brown speckles. The underparts are brown, with bars. The savanna nightjar is nocturnal. Its call is a loud, repetitive chweep, mainly given in flight. The IUCN Red List has assessed the species to be of least concern because it has a large range and its population trend is stable.
Prosopis abbreviata, commonly known as the algarrobillo espinoso, is a species of flowering plant in the pea family, Fabaceae, that is endemic to Argentina. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Prosopis caldenia, commonly known as the caldén, is a species of flowering tree in the family Fabaceae, The tree is endemic to subtropical regions of Argentina. It thrives in sandy and arid soil and resists drought, developing an extremely deep root system. The leaves of this tree are pinnately compound, deciduous, alternate and small. Its foliage is tortuous, with conical spines arranged in pairs at the nodes.

Prosopis kuntzei is a South American leguminous tree species that inhabits the westernmost Gran Chaco forests covering areas of Argentina, Bolivia, and Paraguay, where it acts as natural component. It has also been able to colonize the nearby pasture sabanas. It is commonly referred to as itín, palo mataco, carandá or barba de tigre. It is adapted to arid climate, but can also survive flooded ground for a long time.

Prosopis laevigata, commonly known as smooth mesquite, is a species of flowering tree in the pea family, Fabaceae, that is native to Mexico, Bolivia, Peru, and north-western Argentina. In Mexico, the species is found in the nation's the central highlands, the lowlands of southern Tamaulipas, and in parts of Oaxaca, Morelos, Puebla, and Chiapas. It grows on a variety of sites on hillslides, in depressions, and along floodplains. It has been spotted growing in the Middle East as well.

Pritchardia affinis, the Hawai'i pritchardia, is a species of palm tree that is endemic to the Hawaiian Islands. Wild populations currently exist on the leeward side of the Island of Hawaiʻi. It was most likely cultivated by Native Hawaiians, so its exact native range is uncertain. P. affinis reaches a height of 10–25 m (33–82 ft). It is threatened by rats and pigs, which damage the trees and eat the seeds before they can grow. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States. Its fruit was reportedly the preferred food of the now-extinct ula-ai-hawane—a niche that has been seemingly filled by the introduced lavender waxbill.
Pristimantis affinis is an endangered species of frog in the family Craugastoridae. It is endemic to Colombia. Its natural habitats are tropical high-altitude shrubland and grassland. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The black-chested jay is a species of bird in the family Corvidae.

The brown-rumped bunting is a species of bird in the family Emberizidae found in Africa from Senegal to Sudan and Uganda. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests.

The intermediate horseshoe bat is a bat species of the family Rhinolophidae that is very widespread throughout much of the Indian subcontinent, southern and central China and Southeast Asia.
Shorea affinis is a plant species in the family Dipterocarpaceae endemic to Sri Lanka.

Stemonoporus affinis is a species of plant in the family Dipterocarpaceae. It is endemic to Sri Lanka.
Vatica affinis is a species of plant in the family Dipterocarpaceae. It is endemic to Sri Lanka. It is a Critically endangered species threatened by habitat loss.
Weinmannia affinis is a species of plant in the family Cunoniaceae. It is endemic to Fiji.
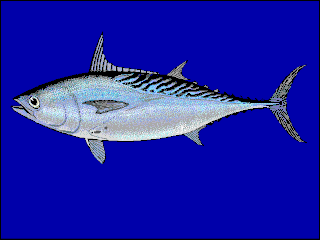
Euthynnus affinis, the mackerel tuna, little tuna, wavyback skipjack tuna, kawakawa, or tongkol is a species of ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae, or mackerel family. It belongs to the tribe Thunnini, better known as the tunas. This is an Indo-Pacific species which is found from the Red Sea to French Polynesia.
Engaeus affinis is a species of crayfish in the family Parastacidae. It is endemic to Australia.

Prosopis africana is a flowering plant species in the genus Fabaceae. It is found in Africa. Its common names include African mesquite, iron tree, gele (Malinke) or somb tree.