
Adelaide is the capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the fifth-most populous city of Australia. The demonym Adelaidean is used to denote the city and the residents of Adelaide.

The Australian Labor Party (ALP), also simply known as Labor and historically spelt Labour, is the major centre-left political party in Australia, one of two major parties in Australian politics, along with the centre-right Liberal Party of Australia. It has been in Opposition in the federal parliament since the 2013 election. The ALP is a federal party, with political branches in each state and territory. They are currently in government in Victoria, Queensland, Western Australia, the Australian Capital Territory, and the Northern Territory. The Labor Party is the oldest political party in Australia.

The British & Irish Lions is a rugby union team selected from players eligible for the national teams of England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland. The Lions are a Test side and most often select players who have already played for their national team, but they can pick uncapped players who are eligible to any one of the four unions. The team currently tours every four years, with these rotating between Australia, New Zealand and South Africa in order. The most recent Test series, the 2017 series against New Zealand, was drawn 1–1.

New South Wales is a state on the east coast of Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria to the south, and South Australia to the west. Its coast borders the Coral and Tasman Seas to the east. The Australian Capital Territory is an enclave within the state. New South Wales' state capital is Sydney, which is also Australia's most populous city. In June 2020, the population of New South Wales was over 8.1 million, making it Australia's most populous state. Just under two-thirds of the state's population, 5.3 million, live in the Greater Sydney area. The demonym for inhabitants of New South Wales is New South Welshmen.

South Australia is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of 983,482 square kilometres (379,725 sq mi), it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, and fifth largest by population. It has a total of 1.77 million people, and its population is the second most highly centralised in Australia, after Western Australia, with more than 77 percent of South Australians living in the capital, Adelaide, or its environs. Other population centres in the state are relatively small; Mount Gambier, the second largest centre, has a population of 28,684.

Sydney is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Port Jackson and extends about 70 km (43.5 mi) on its periphery towards the Blue Mountains to the west, Hawkesbury to the north, the Royal National Park to the south and Macarthur to the south-west. Sydney is made up of 658 suburbs, spread across 33 local government areas. Informally there are at least 15 regions. Residents of the city are known as "Sydneysiders". As of June 2020, Sydney's estimated metropolitan population was 5,367,206, meaning the city is home to approximately 66% of the state's population.

Tasmania is an island state of Australia. It is located 240 km (150 mi) to the south of the Australian mainland, separated by Bass Strait. The state encompasses the main island of Tasmania, the 26th-largest island in the world, and the surrounding 1000 islands. The state has a population of about 541,000 people as of September 2020. The state capital and largest city is Hobart, with around 40 percent of the population living in the Greater Hobart area.

Wombats are short-legged, muscular quadrupedal marsupials that are native to Australia. They are about 1 m (40 in) in length with small, stubby tails and weigh between 20 and 35 kg. There are three extant species and they are all members of the family Vombatidae. They are adaptable and habitat tolerant, and are found in forested, mountainous, and heathland areas of southern and eastern Australia, including Tasmania, as well as an isolated patch of about 300 ha in Epping Forest National Park in central Queensland.

Brisbane is the capital of and most populous city in the Australian state of Queensland, and the third-most populous city in Australia. Brisbane's metropolitan area has a population around 2.6 million, and it lies at the centre of the South East Queensland metropolitan region, which encompasses a population around 3.8 million. The Brisbane central business district is situated inside a peninsula of the Brisbane River, about 15 km (9 mi) from its mouth at Moreton Bay, a bay of the Coral Sea. The metropolitan area extends in all directions along the hilly floodplain of the Brisbane River Valley between Moreton Bay and the Taylor and D'Aguilar mountain ranges. It sprawls across several of Australia's most populous local government areas (LGAs)—most centrally the City of Brisbane, the most populous LGA in the nation. The demonym of Brisbane is "Brisbanite", while common nicknames include "Brissy" and "River City".

Super Rugby is a men's professional rugby union club competition currently involving teams from Australia and New Zealand. It previously included teams from South Africa, Argentina, and Japan. Building on various Southern Hemisphere competitions dating back to the South Pacific Championship in 1986, with teams from a number of southern nations, the Super Rugby started as the Super 12 in the 1996 season with 12 teams from 3 nations: Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. The Super 12 was established by SANZAR after the sport became professional in 1995. At its peak the tournament featured the top players from nations representing 16 of the 24 top-three finishes in the history of the Rugby World Cup, and is widely regarded as rugby union's strongest provincial competition. After the COVID-19 pandemic forced the competition to split into three, the reformed competition in 2021 and beyond will only include Australian and New Zealand clubs.

In Australia, electoral districts for the Australian House of Representatives are called divisions or more commonly referred to as electorates or seats. There are currently 151 single-member electorates for the Australian House of Representatives.

Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Islands. The term Indigenous Australians refers to Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders collectively. It is generally used when both groups are included in the topic being addressed. Torres Strait Islanders are ethnically and culturally distinct, despite extensive cultural exchange with some of the Aboriginal groups. The Torres Strait Islands are mostly part of Queensland but have a separate governmental status.

The states and territories of Australia are the regional governments in Australia, distinct from the federal government and local governments. States are self-administered regions with their own constitutions, legislature, police services, departments, and certain civil authorities, that administer and deliver most public policies and programmes. Territories administer local policies and programmes much like states, but are constitutionally and financially subordinate to the federal government.

Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia's population of nearly 26 million, in an area of 7,617,930 square kilometres (2,941,300 sq mi), is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Canberra is the nation's capital, while the largest city is Sydney, and other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide.

The Australia national soccer team represents Australia in international men's soccer. Officially nicknamed the Socceroos, the team is controlled by the governing body for soccer in Australia, Football Australia, which is currently a member of the Asian Football Confederation (AFC) and the regional ASEAN Football Federation (AFF) since leaving the Oceania Football Confederation (OFC) in 2006.

Lands administrative divisions of Australia are the cadastral divisions of Australia for the purposes of identification of land to ensure security of land ownership. Most states term these divisions as counties, parishes, hundreds, and other terms. The eastern states of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania were divided into counties and parishes in the 19th century, although the Tasmanian counties were renamed land districts in the 20th century. Parts of South Australia (south-east) and Western Australia (south-west) were similarly divided into counties, and there were also five counties in a small part of the Northern Territory. However South Australia has subdivisions of hundreds instead of parishes, along with the Northern Territory, which was part of South Australia when the hundreds were proclaimed. There were also formerly hundreds in Tasmania. There have been at least 600 counties, 544 hundreds and at least 15,692 parishes in Australia, but there are none of these units for most of the sparsely inhabited central and western parts of the country.

Postcodes in Australia are used to more efficiently sort and route mail within the Australian postal system. Postcodes in Australia have four digits and are placed at the end of the Australian address, before the country. Postcodes were introduced in Australia in 1967 by the Postmaster-General's Department and are now managed by Australia Post, Australia's national postal service. Postcodes are published in booklets available from post offices or online from the Australia Post website.

A continent is one of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven regions are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. Variations with fewer continents may merge some of these, for example some systems include Eurasia or America as single continents.
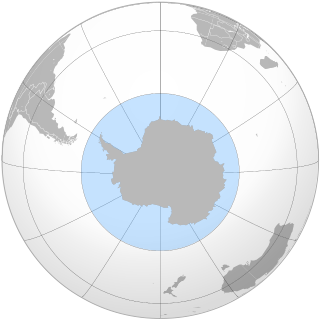
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. As such, it is regarded as the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. Over the past 30 years, the Southern Ocean has been subject to rapid climate change, which has led to changes in the marine ecosystem.


















