
Guava is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava Psidium guajava is a small tree in the myrtle family (Myrtaceae), native to Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and northern South America. The name guava is also given to some other species in the genus Psidium such as strawberry guava and to the pineapple guava, Feijoa sellowiana. In 2019, 55 million tonnes of guavas were produced worldwide, led by India with 45% of the total. Botanically, guavas are berries.

Feijoa sellowiana also known as Acca sellowiana (O.Berg) Burret, is a species of flowering plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. It is native to the highlands of southern Brazil, eastern Paraguay, Uruguay, and northern Argentina. Feijoa are also common in gardens of New Zealand. It is widely cultivated as an ornamental tree and for its fruit. Common names include feijoa, pineapple guava and guavasteen, although it is not a true guava. It is an evergreen shrub or small tree, 1–7 metres (3.3–23.0 ft) in height.

Psidium is a genus of trees and shrubs in the family Myrtaceae. It is native to warmer parts of the Western Hemisphere.

The tropical kingbird is a large tyrant flycatcher. This bird breeds from southern Arizona and the lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas in the United States through Central America, South America as far as south as central Argentina and eastern Peru, and on Trinidad and Tobago. Birds from the northernmost and southern breeding areas migrate to warmer parts of the range after breeding.
Erwinia psidii is a Gram-negative bacterium and a phytopathogen of the common guava (Psidium guajava), causing rot in branches, flowers and fruits. Recently, it was demonstrated that this species produces two acyl homoserine lactones (S-(-)-N-hexanoyl- and N-heptanoyl-homoserine lactone), widely recognized bacterial quorum sensing signaling substances, and employed in bacterial cell-to-cell communication systems.

Psidium cattleyanum , commonly known as Cattley guava, strawberry guava or cherry guava, is a small tree in the Myrtaceae (myrtle) family. The species is named in honour of English horticulturist William Cattley. Its genus name Psidium comes from the Latin psidion, or "armlet." The red-fruited variety, P. cattleyanum var. cattleyanum, is commonly known as purple guava, red cattley guava, red strawberry guava and red cherry guava. The yellow-fruited variety, P. cattleyanum var. littorale is variously known as yellow cattley guava, yellow strawberry guava, yellow cherry guava, lemon guava and in Hawaii as waiawī. Although P. cattleyanum has select economic uses, it is considered the most invasive plant in Hawaii.

Colombian cuisine is a compound of the culinary traditions of the six main regions within Colombia. Colombian cuisine varies regionally and is particularly influenced by Indigenous Colombian, Spanish, and African cuisines, with slight Arab influence in some regions. As one of the most biodiverse countries in the world, Colombia has one of the widest variety of available ingredients depending on the region.

Psidium guajava, the common guava, yellow guava, lemon guava, or apple guava is an evergreen shrub or small tree native to the Caribbean, Central America and South America. It is easily pollinated by insects; when cultivated, it is pollinated mainly by the common honey bee, Apis mellifera.

The Gambian epauletted fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Sudan, and Togo. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and savanna.
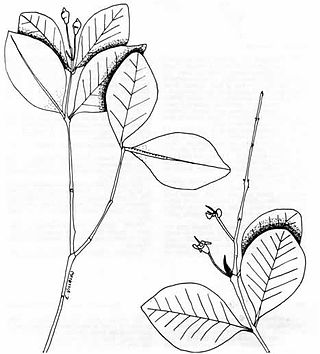
Psidium sintenisii is a species of flowering plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. It is endemic to Puerto Rico, where it is known from three or four small subpopulations, mainly within El Yunque National Forest. It grows in wet mountain forest habitat. Its common names are Sintenis' guava and hoja menuda.

Phocides polybius, the bloody spot or guava skipper, is a species of butterfly in the skipper family, Hesperiidae, that is native to the Americas. It is found from the lower Rio Grande Valley of southern Texas in the United States south through Mexico and Central America to Argentina. The species was first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1793.

Anastrepha ludens, the Mexican fruit fly or Mexfly, is a species of fly of the Anastrepha genus in the Tephritidae family. It is closely related to the Caribbean fruit fly Anastrepha suspensa, and the papaya fruit fly Anastrepha curvicauda.

Coscinoptycha improbana, the Australian guava moth, is a moth of the family Carposinidae and only member of the genus Coscinoptycha. It is native to Australia, where it is found from Eungella in Queensland down through New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania. It also occurs on Norfolk Island and has been recorded from New Zealand since 1997. The presence of this species has also been detected in New Caledonia in 2012.

Psidium guineense is a species of guava.

Muisca cuisine describes the food and preparation the Muisca elaborated. The Muisca were an advanced civilization inhabiting the central highlands of the Colombian Andes before the Spanish conquest of the Muisca in the 1530s. Their diet and cuisine consisted of many endemic flora and fauna of Colombia.

Myrteae is the largest tribe in the plant family Myrtaceae. It includes most of the species of the family that have fleshy fruits.
Psidium amplexicaule, which is commonly known as mountain guava, is a species in the family Myrtaceae that is native to the Caribbean. It is rare in a moist limestone forest at 100–600 feet altitude on north coast of Puerto Rico. This plant can also be found on islands such as St. Thomas and St. John in the United States Virgin Islands and in Tortola and Virgin Gorda of the British Virgin Islands.

Psidium galapageium, the Galápagos guava or guayabillo, is a small tree or shrub found in tropical areas, formerly endemic to the Galápagos Islands.
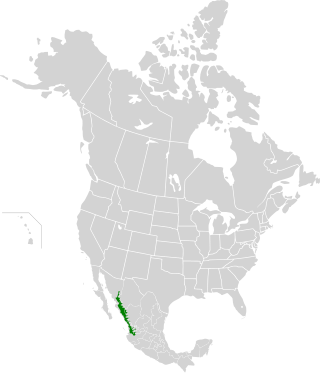
The Sinaloan dry forests is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion in western Mexico. It is the northernmost ecoregion of the Neotropical realm.
















