
In biology, a nymph is the juvenile form of some invertebrates, particularly insects, which undergoes gradual metamorphosis (hemimetabolism) before reaching its adult stage. Unlike a typical larva, a nymph's overall form already resembles that of the adult, except for a lack of wings and the emergence of genitalia. In addition, while a nymph moults, it never enters a pupal stage. Instead, the final moult results in an adult insect. Nymphs undergo multiple stages of development called instars.

Plecoptera is an order of insects, commonly known as stoneflies. Some 3,500 species are described worldwide, with new species still being discovered. Stoneflies are found worldwide, except Antarctica. Stoneflies are believed to be one of the most primitive groups of Neoptera, with close relatives identified from the Carboniferous and Lower Permian geological periods, while true stoneflies are known from fossils only a bit younger. Their modern diversity, however, apparently is of Mesozoic origin.

Mayflies are aquatic insects belonging to the order Ephemeroptera. This order is part of an ancient group of insects termed the Palaeoptera, which also contains dragonflies and damselflies. Over 3,000 species of mayfly are known worldwide, grouped into over 400 genera in 42 families.

Aquatic insects or water insects live some portion of their life cycle in the water. They feed in the same ways as other insects. Some diving insects, such as predatory diving beetles, can hunt for food underwater where land-living insects cannot compete.

The caddisflies, or order Trichoptera, are a group of insects with aquatic larvae and terrestrial adults. There are approximately 14,500 described species, most of which can be divided into the suborders Integripalpia and Annulipalpia on the basis of the adult mouthparts. Integripalpian larvae construct a portable casing to protect themselves as they move around looking for food, while annulipalpian larvae make themselves a fixed retreat in which they remain, waiting for food to come to them. The affinities of the small third suborder Spicipalpia are unclear, and molecular analysis suggests it may not be monophyletic. Also called sedge-flies or rail-flies, the adults are small moth-like insects with two pairs of hairy membranous wings. They are closely related to the Lepidoptera which have scales on their wings; the two orders together form the superorder Amphiesmenoptera.

Dobsonflies are a subfamily of insects, Corydalinae, part of the Megalopteran family Corydalidae. The larvae are aquatic, living in streams, and the adults are often found along streams as well. The nine genera of dobsonflies are distributed in the Americas, Asia, and South Africa.

An artificial fly or fly lure is a type of fishing lure, usually used in the sport of fly fishing. In general, artificial flies are an imitation of aquatic insects that are natural food of the target fish species the fly fishers try to catch. Artificial flies are constructed by fly tying, in which furs, feathers, thread or any of very many other materials are tied onto a fish hook.

The Pteronarcyidae, also known as giant stoneflies or salmonflies, are a family of the order Plecoptera.

Ephemerellidae are known as the spiny crawler mayflies. They are a family of the order Ephemeroptera. There are eight genera consisting of a total 90 species. They are distributed throughout North America as well as the UK. Their habitat is lotic-erosional, they are found in all sizes of flowing streams on different types of substrates where there is reduced flow. They are even found on the shores of lakes and beaches where there is wave action present. They move by swimming and clinging, they are very well camouflaged. Most species have one generation per year. They are mostly collector-gatherers.

The Capniidae, the small winter stoneflies, are a family of insects in the stonefly order (Plecoptera). It constitutes one of the largest stonefly families, containing some 300 species distributed throughout the holarctic. Their closest relatives are the rolled-winged stoneflies (Leuctridae).

Sympetrum vicinum, the Yellow-Legged Meadowhawk is one of some fifteen North American species of autumn meadowhawk, which are members of the Odonate family Libellulidae. It grows to 26–35 mm long.
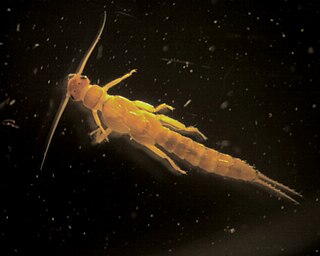
Chloroperlidae are a family of stoneflies, commonly known as green stoneflies, with more than 200 species and 22 genera. They appear green to yellow in colour, and are popularly used among fisherman as bait for trout fishing. Green stoneflies live in the benthic zone of the cold streams and rivers of five continents and four zoogeographical regions, emerging from the water to live in the riparian zone as adults. They are sensitive to pollutants, making them an indicator species for determining the quality of water bodies. Chloroperlidae are hemimetabolous, having no pupal stage, but instead hatch from eggs as nymphs and mature directly into adults. They are omnivorous, feeding on small organisms and plant particles, and become more carnivorous as they mature. The classification of Chloroperlidae is contested, with some believing that they should be considered as members of different orders, as opposed to the order Plecoptera that they currently belong to.

Progomphus borealis is a species of dragonfly in the family Gomphidae. This dragonfly species is commonly known as the gray sanddragon.

Gomphurus externus, the plains clubtail, is a species of dragonfly in the family Gomphidae.

Phanogomphus graslinellus is a species of dragonfly in the family Gomphidae. This species is commonly known as the pronghorn clubtail.

Parks' Salmonfly is a traditional dry fly imitating adults of the family of giant stoneflies or salmonflies (Pteronarcyidae). The most commonly imitated species is Pteronarcys californica or salmonfly common throughout Western North America from British Columbia to California.

Thaumatoperla alpina is a species of stonefly in the genus Thaumatoperla, and are the largest Australian stonefly. They are endemic to the Bogong High Plains area of the Victorian alps, Australia.

Salmon fly patterns are an important collection of artificial flies used by fly anglers to imitate nymphal and adult forms of Pteronarcys californica a giant stonefly or salmon fly. Salmon flies are common in high gradient, freestone rivers and streams from Western Canada throughout the Western U.S. to Mexico in the Rocky Mountains and coastal mountain ranges. Nymphs live for three to five years before adult emergence which typically occurs in late Spring or early summer. The long lifespan of the nymphal form provides year-round angling opportunities for fly anglers.

Stenoperla prasina is a species of stonefly belonging to the family Eustheniidae. This species is endemic to New Zealand and is classified as "Not Threatened" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System. It is found on the North, South and Stewart Island / Rakiura Islands as well as on Little Barrier Island. Although adults of this species are most often coloured bright green, this species can be coloured yellow. This species inhabits clean, cold, running streams and rivers with stony bottoms within native bush. It is a known indicator of water quality. The larvae eat plant detritus and other aquatic insects while the adult insects feed on sooty mould fungi as well as other plant matter. The adults of this species are a known food source for New Zealand long tailed bats. Adults have been dissected and have been found to have been carrying Nematomorpha and trematode parasites. The New Zealand Department of Conservation classifies this species as "Not Threatened". In 2022 a specimen of this species was the 5 millionth specimen to be digitised in the Natural History Museum, London collection.

Eusthenia spectabilis is a very large species of stonefly in the family of giant stoneflies, Eustheniidae. At 4 cm (1.6 in) Eusthenia spectabilis is the largest member of the genus and emerges later than other similar species.
























