
Euphorbia helioscopia, the sun spurge or madwoman's milk, is a species of flowering plant in the spurge family Euphorbiaceae. It is a herbaceous annual plant, native to most of Europe, northern Africa, and eastward through most of Asia.

Quercus mongolica, commonly known as Mongolian oak, is a species of oak native to Japan, China, Korea, Mongolia, and Siberia. The species can grow to be 30 metres tall.
A hydrolysable tannin or pyrogallol-type tannin is a type of tannin that, on heating with hydrochloric or sulfuric acids, yields gallic or ellagic acids.

Glucogallin is chemical compound formed from gallic acid and β-D-glucose. It can be found in oaks species like the North American white oak, European red oak and Amla fruit.

Stenophyllanin A is an ellagitannin. It can be found in Cowania mexicana, Coleogyne ramosissima and Quercus stenophylla.
The Flavono-ellagitannins or complex tannins are a class of tannins formed from the complexation of an ellagitannin with a flavonoid. Flavono-ellagitannins can be found in Quercus mongolica var. grosseserrata.

Punigluconin is an ellagitannin, a polyphenol compound. It is found in the bark of Punica granatum (pomegranate) and in Emblica officinalis. It is a molecule having a hexahydroxydiphenic acid group and two gallic acids attached to a gluconic acid core.
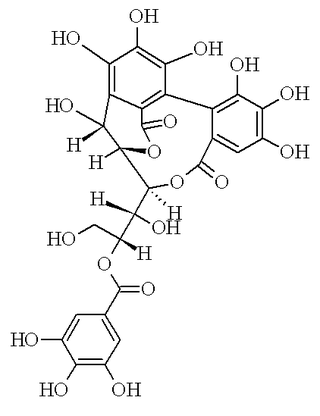
Punicacortein A is an ellagitannin, a polyphenol compound. It is found in the bark of Punica granatum (pomegranate) and in Osbeckia chinensis.
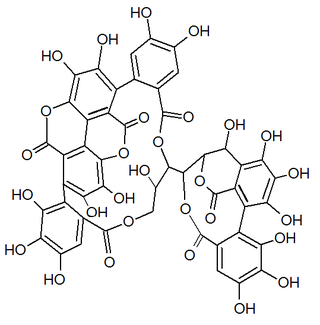
Punicacortein C is an ellagitannin, a phenolic compound. It is found in the bark of Punica granatum (pomegranate). The molecule contains a gallagic acid component.

Punicacortein D is an ellagitannin, a type of phenolic compound. It is found in the bark and heartwood of Punica granatum (pomegranate). The molecule contains a gallagic acid component.

Punicacortein B is an ellagitannin, a polyphenol compound. It is found in the bark of Punica granatum (pomegranate).

Friedelin is a triterpenoid chemical compound found in Azima tetracantha, Orostachys japonica, and Quercus stenophylla. Friedelin is also found in the roots of the Cannabis plant.

Elaeocarpus sylvestris, the woodland elaeocarpus, is a tree species in the genus Elaeocarpus.
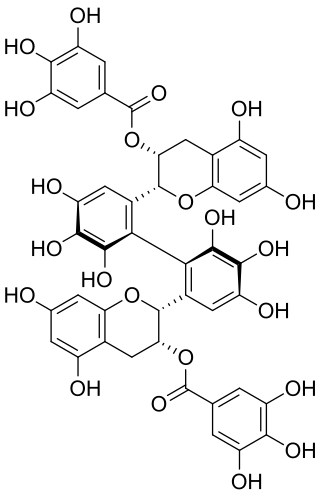
Theasinensin A is polyphenol flavonoid from black tea created during fermentation, by oxidation of epigallocatechin gallate.
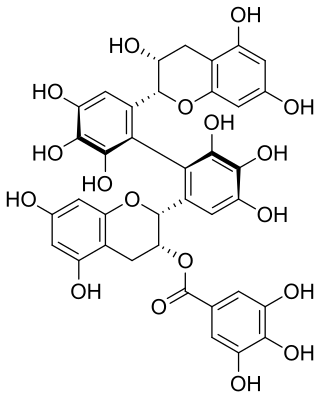
Theasinensin B is polyphenol flavonoid from black tea.

Theasinensin C is polyphenol flavonoid from black tea.
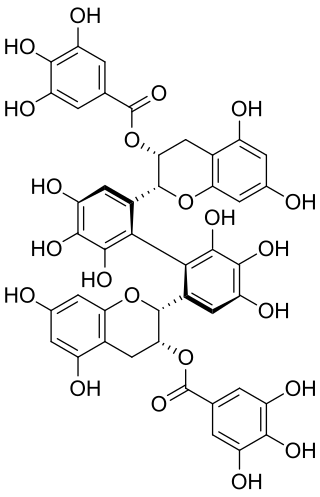
Theasinensin D is polyphenol flavonoid found in oolong tea. It's an atropisomer of theasinensin A.
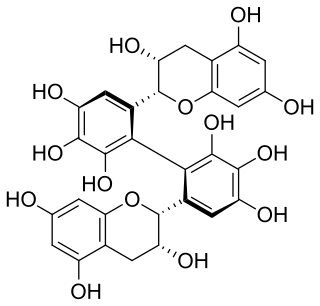
Theasinensin E is polyphenol flavonoid found in oolong tea. It's an atropisomer of theasinensin C.

Theasinensin F is polyphenol flavonoid found in oolong tea.
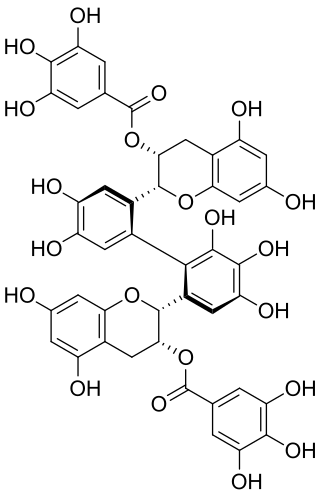
Theasinensin G is polyphenol flavonoid found in oolong tea.


















