
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows. The word comes from the Latin arcus, meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In modern times, it is mainly a competitive sport and recreational activity. A person who practices archery is typically called an archer, bowman, or toxophilite.

An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers called fletchings mounted near the rear, and a slot at the rear end called a nock for engaging the bowstring. A container or bag carrying additional arrows for convenient reloading is called a quiver.

In modern archery, a compound bow is a bow that uses a levering system, usually of cables and pulleys, to bend the limbs. The compound bow was first developed in 1966 by Holless Wilbur Allen in North Kansas City, Missouri, and a US patent was granted in 1969. Compound bows are widely used in target practice and hunting.

Kyūdō is the Japanese martial art of archery. Kyūdō is based on kyūjutsu, which originated with the samurai class of feudal Japan. In 1919, the name of kyūjutsu was officially changed to kyūdō, and following the example of other martial arts that have been systematizing for educational purposes, kyūdō also reorganized and integrated various forms of shooting that had been used up until then. Many practitioners may refer to themselves as yumihiki (弓引き), or 'ones who draw the bow'. Kyūdō is practised by over a hundred thousand people worldwide. The bow they use is called a yumi (弓). It has an asymmetrical shape and length of more than 2.0 metres, and its use is characterized by the archer gripping the lower third of the bow stave to shoot.
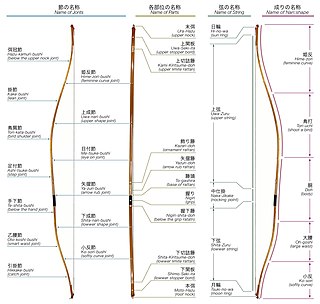
Yumi is the Japanese term for a bow. As used in English, yumi refers more specifically to traditional Japanese asymmetrical bows, and includes the longer daikyū and the shorter hankyū used in the practice of kyūdō and kyūjutsu, or Japanese archery.

The bow and arrow is a ranged weapon system consisting of an elastic launching device (bow) and long-shafted projectiles (arrows). Humans used bows and arrows for hunting and aggression long before recorded history, and the practice was common to many prehistoric cultures. They were important weapons of war from ancient history until the early modern period, where they were rendered increasingly obsolete by the development of the more powerful and accurate firearms. Today, bows and arrows are mostly used for hunting and sports.

Fletching is the fin-shaped aerodynamic stabilization device attached on arrows, bolts, darts, or javelins, and are typically made from light semi-flexible materials such as feathers or bark. Each piece of such fin is a fletch, also known as a flight or feather. A fletcher is a person who attaches fletchings to the shaft of arrows, fletchers were traditionally associated with the Worshipful Company of Fletchers, a guild in the City of London.
In archery, a finger tab or archer tab is a small leather or synthetic patch that protects an archer's fingers from the bowstring. It is strapped or otherwise attached to an archer's hand. In summertime, tabs are far more comfortable than gloves and can more conveniently use thicker material. They are also less expensive and easier to fit, and are the normal finger-protection used with recurve bows.

A strap, sometimes also called strop, is an elongated flap or ribbon, usually of leather or other flexible materials.

The Mongol bow is a type of recurved composite bow historically used in Mongolia, and by the horse archers of the Mongol Empire. "Mongol bow" can refer to two types of bow. From the 17th century onward, most of the traditional bows in Mongolia were replaced with the similar Manchu bow which is primarily distinguished by larger siyahs and the presence of prominent string bridges.

Turkish archery is a tradition of archery which became highly developed in the Ottoman Empire, although its origins date back to the Eurasian Steppe in the second millennium BC.

Archery, or the use of bow and arrows, was probably developed in Africa by the later Middle Stone Age. It is documented as part of warfare and hunting from the classical period until the end of the 19th century, when it was made obsolete by the invention and spread of repeating firearms.
A bow draw in archery is the method or technique of pulling back the bowstring to store energy for the bow to shoot an arrow. The most common method in modern target archery is the Mediterranean draw, which has long been the usual method in European archery. Other methods include the pinch draw and the Mongolian or "thumb" draw. In traditional archery practice outside Western Europe the variations of the thumb draw are by far the most dominant draw types, with the Mediterranean draw restricted to the Olympic style of target archery.
This is a list of archery terms, including both the equipment and the practice. A brief description for each word or phrase is also included.

In archery, a recurve bow is one of the main shapes a bow can take, with limbs that curve away from the archer when unstrung. A recurve bow stores more energy and delivers energy more efficiently than the equivalent straight-limbed bow, giving a greater amount of energy and speed to the arrow. A recurve will permit a shorter bow than the simple straight limb bow for given arrow energy, and this form was often preferred by archers in environments where long weapons could be cumbersome, such as in brush and forest terrain, or while on horseback.

Mounted archery is a form of archery that involves shooting arrows while on horseback. A horse archer is a person who does mounted archery. Archery has occasionally been used from the backs of other riding animals. In large open areas, mounted archery was a highly successful technique for hunting, for protecting herds, and for war. It was a defining characteristic of the Eurasian nomads during antiquity and the medieval period, as well as the Iranian peoples such as the Alans, Sarmatians, Cimmerians, Scythians, Massagetae, Parthians, and Persians in Antiquity, and by the Hungarians, Mongols, Chinese, and Turkic peoples during the Middle Ages. The expansion of these cultures have had a great influence on other geographical regions including Eastern Europe, West Asia, and East Asia. In East Asia, horse archery came to be particularly honored in the samurai tradition of Japan, where horse archery is called Yabusame.

In archery, a release aid, mechanical release, or release is a device that helps to fire arrows more precisely, by using a trigger to release the bowstring, rather than the archer's fingers. It is used to make the release of the bowstring quicker and reducing the amount of torque put onto the bowstring from the archer's fingers.

Yazutsu or Yadzutsu is a type of arrow quiver used in kyūdō, Japanese archery, using the Japanese longbow, the Yumi. It is generally cylindrical in shape, and zippered at the top, and appears something like a cylindrical holder of plans.
Arab archery is the traditional style of archery practiced by the Arab people of the West Asia and North Africa from ancient to modern times.
Traditional Inuit hunters lack the more elastic timbers used to make bows in temperate and tropical parts of the world. Using sinew cords for the back of the bow, and spruce timber or antler for the belly, however, they build very effective weapons. When hunting polar bears, the bows used are powerful enough, if they do not hit bone, to penetrate completely through the body of the bear.























