In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle, transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron transforms it into a proton by the emission of an electron accompanied by an antineutrino; or, conversely a proton is converted into a neutron by the emission of a positron with a neutrino in so-called positron emission. Neither the beta particle nor its associated (anti-)neutrino exist within the nucleus prior to beta decay, but are created in the decay process. By this process, unstable atoms obtain a more stable ratio of protons to neutrons. The probability of a nuclide decaying due to beta and other forms of decay is determined by its nuclear binding energy. The binding energies of all existing nuclides form what is called the nuclear band or valley of stability. For either electron or positron emission to be energetically possible, the energy release or Q value must be positive.

The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol
n
or
n0
, which has a neutral charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons behave similarly within the nucleus, they are both referred to as nucleons. Nucleons have a mass of approximately one atomic mass unit, or dalton. Their properties and interactions are described by nuclear physics. Protons and neutrons are not elementary particles; each is composed of three quarks.

Neutron activation analysis (NAA) is a nuclear process used for determining the concentrations of elements in many materials. NAA allows discrete sampling of elements as it disregards the chemical form of a sample, and focuses solely on atomic nuclei. The method is based on neutron activation and thus requires a neutron source. The sample is bombarded with neutrons, causing its constituent elements to form radioactive isotopes. The radioactive emissions and radioactive decay paths for each element have long been studied and determined. Using this information, it is possible to study spectra of the emissions of the radioactive sample, and determine the concentrations of the various elements within it. A particular advantage of this technique is that it does not destroy the sample, and thus has been used for the analysis of works of art and historical artifacts. NAA can also be used to determine the activity of a radioactive sample.
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nuclide the decay rate, and thus the half-life (t1/2) for that collection, can be calculated from their measured decay constants. The range of the half-lives of radioactive atoms has no known limits and spans a time range of over 55 orders of magnitude.

A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation, is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and β+ decay, which produce electrons and positrons respectively.

A nuclide is a class of atoms characterized by their number of protons, Z, their number of neutrons, N, and their nuclear energy state.
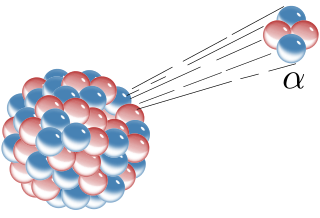
Radioactive decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha, beta, and gamma decay. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force.
Ionizing radiation, including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.

Nuclear chemistry is the sub-field of chemistry dealing with radioactivity, nuclear processes, and transformations in the nuclei of atoms, such as nuclear transmutation and nuclear properties.

Positron emission, beta plus decay, or β+ decay is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is converted into a neutron while releasing a positron and an electron neutrino. Positron emission is mediated by the weak force. The positron is a type of beta particle (β+), the other beta particle being the electron (β−) emitted from the β− decay of a nucleus.
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a synthetic derivative of a natural compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide. By virtue of its radioactive decay, it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tracing the path that the radioisotope follows from reactants to products. Radiolabeling or radiotracing is thus the radioactive form of isotopic labeling. In biological contexts, experiments that use radioisotope tracers are sometimes called radioisotope feeding experiments.

Radiopharmacology is radiochemistry applied to medicine and thus the pharmacology of radiopharmaceuticals. Radiopharmaceuticals are used in the field of nuclear medicine as radioactive tracers in medical imaging and in therapy for many diseases. Many radiopharmaceuticals use technetium-99m (Tc-99m) which has many useful properties as a gamma-emitting tracer nuclide. In the book Technetium a total of 31 different radiopharmaceuticals based on Tc-99m are listed for imaging and functional studies of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood and tumors.

Radiochemistry is the chemistry of radioactive materials, where radioactive isotopes of elements are used to study the properties and chemical reactions of non-radioactive isotopes. Much of radiochemistry deals with the use of radioactivity to study ordinary chemical reactions. This is very different from radiation chemistry where the radiation levels are kept too low to influence the chemistry.

Hydrogen (1H) has three naturally occurring isotopes, sometimes denoted 1
H
, 2
H
, and 3
H
. 1
H
and 2
H
are stable, while 3
H
has a half-life of 12.32(2) years. Heavier isotopes also exist, all of which are synthetic and have a half-life of less than one zeptosecond (10−21 s). Of these, 5
H
is the least stable, while 7
H
is the most.
Radionuclides which emit gamma radiation are valuable in a range of different industrial, scientific and medical technologies. This article lists some common gamma-emitting radionuclides of technological importance, and their properties.
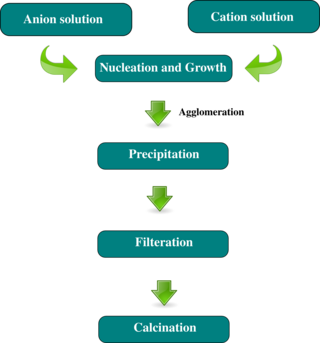
In chemistry, coprecipitation (CPT) or co-precipitation is the carrying down by a precipitate of substances normally soluble under the conditions employed. Analogously, in medicine, coprecipitation is specifically "an assay designed to purify a single antigen from a complex mixture using a specific antibody attached to a beaded support".

Isotopes are distinct nuclear species of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number and position in the periodic table, but differ in nucleon numbers due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have similar chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties.
Nuclear forensics is the investigation of nuclear materials to find evidence for the source, the trafficking, and the enrichment of the material. The material can be recovered from various sources including dust from the vicinity of a nuclear facility, or from the radioactive debris following a nuclear explosion.

A radionuclide identification device is a small, lightweight, portable gamma-ray spectrometer used for the detection and identification of radioactive substances. As RIIDs are portable, they are suitable for medical and industrial applications, fieldwork, geological surveys, first-line responders in Homeland Security, and Environmental Monitoring and Radiological Mapping along with other industries that necessitate the identification of radioactive substances..

A radioactive source is a known quantity of a radionuclide which emits ionizing radiation, typically one or more of the radiation types gamma rays, alpha particles, beta particles, and neutron radiation.