
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.
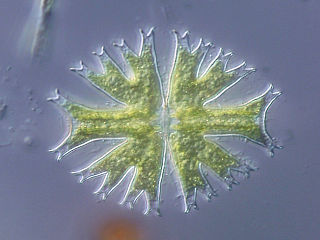
Desmidiales, commonly called the desmids, are an order in the Charophyta, a division of green algae in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Desmids consist of single-celled microscopic green algae. Because desmids are highly symmetrical, attractive, and come in a diversity of forms, they are popular subjects for microscopists, both amateur and professional.

Ankistrodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is one of the most common types of phytoplankton in freshwater habitats around the world. The name Ankistrodesmus comes from the Greek roots ankistron, meaning "cross", and desmos, meaning "bond".

Asterococcus is a genus of green algae in the order Chlamydomonadales. It is planktonic in freshwater ponds and lakes, or benthic within mires and swamps. It is a common and widespread genus, but is rarely abundant.

Chlamydocapsa is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae.

Cylindrocapsa is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats.

Desmodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae. It is the only chlorophyll-containing organism known to have caused human infections in immunocompetent individuals. All known cases involved open injuries occurring in fresh water.
Dictyochloris is a genus of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. It is the sole genus of the family Dictyochloridaceae. It is commonly found in terrestrial and subaerial habitats.

Dimorphococcus is a genus of fresh water green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae. It is found as a component of the phytoplankton of freshwater ponds, lakes, and peat bogs. It is widespread, but usually not very common.

Golenkinia is a genus of green algae first described in 1894 by Robert Chodat. The genus is named for the Russian phycologist Mikhail Iljitsch Golenkin. Golenkinia species live in fresh water and are found around the world.

Kirchneriella is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, as phytoplankton or metaphyton.

Lagerheimia is a genus of green algae in the family Oocystaceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats all over the world, although some species are rare and have only been recorded from Europe or the United States.

Planktosphaeria is a genus of Chlorophyceae of the green algae. It was first described by the phycologist Gilbert Morgan Smith in 1918, with Planktosphaeria gelatinosa as its type species. Species of Planktosphaeria are commonly found in freshwater plankton around the world.

Selenastrum is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is common in freshwater habitats around the world. Most species prefer temperate or warm-temperate waters.

Cosmarium is a large genus of desmids (Desmidiaceae), a group of green algae closely related to the land plants (Embryophyta). Members of this genus are microscopic and found in freshwater habitats around the world.

Staurodesmus is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Desmidiaceae.

Tetrastrum is a genus of green algae (Chlorophyta). It is a common component of the phytoplankton of freshwater habitats, particularly eutrophic and alkaline waters.
Deuterocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, attached to algae or detritus. It is rare and has only been recorded from Europe.

Chlorotetraedron is a genus of green algae, in the family Neochloridaceae. The name may also be written as Chlorotetraëdon. It is found as freshwater plankton or in soil.
Korshikoviella is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae.

















