Related Research Articles
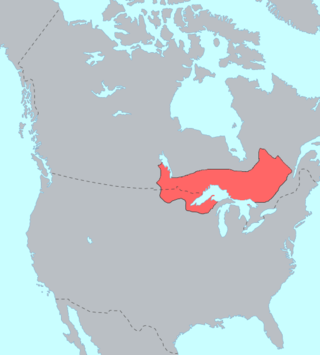
The Ojibwe are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland covers much of the Great Lakes region and the northern plains, extending into the subarctic and throughout the northeastern woodlands. The Ojibwe, being Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands and of the subarctic, are known by several names, including Ojibway or Chippewa. As a large ethnic group, several distinct nations also consider themselves Ojibwe, including the Saulteaux, Nipissings, and Oji-Cree.

The Saulteaux, otherwise known as the Plains Ojibwe, are a First Nations band government in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia, Canada. They are a branch of the Ojibwe who pushed west. They formed a mixed culture of woodlands and plains Indigenous customs and traditions.
Yellow Quill First Nation (formerly Nut Lake Band of Saulteaux) is a Saulteaux First Nation band government in Saskatchewan, Canada. Their reserve is twenty kilometres northwest of Kelvington. The Yellow Quill First Nation is a signatory of Treaty No. 4, which was signed by Chief Yellow-quill on August 24, 1876.

Garden River First Nation, also known as Ketegaunseebee, is an Ojibwa band located at Garden River 14 near Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Canada.

The Couchiching First Nation is a Saulteaux First Nation band government in the Canadian province of Ontario, who live on the Couchiching 16A and Agency 1 reserves in the Rainy River District near Fort Frances.
Nigigoonsiminikaaning First Nation, formerly known as the Nicickousemenecaning First Nation and as the Red Gut First Nation, is a Saulteaux First Nation band government who inhabit the banks of Rainy Lake of the Rainy River District in Northwestern Ontario, Canada. As of January, 2008, the First Nation had a population of 290 registered people. As of 2017, it has approximately 130 on-reserve members.
Lac La Croix First Nation is a Saulteaux First Nation band government who reside in the Rainy River District of northwestern Ontario, Canada, along the Ontario-Minnesota border. It is approximately 200 km northwest of Thunder Bay, Ontario. As of January 2008, the First Nation had a registered population of 398 people, of which their on-Reserve population was 273.
Wabaseemoong Independent Nations or more fully as the Wabaseemoong Independent Nations of One Man Lake, Swan Lake and Whitedog, is an Ojibway First Nation band government who reside 120 km northwest of Kenora, Ontario and 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) east of the Ontario-Manitoba border of northwestern Ontario, Canada. As of December 2018, the First Nation had a population of 2,000 registered people, of which their on-Reserve population was 1200 registered members and approximately 100 non-Band members.
Skownan First Nation is a Saulteaux (Ojibwe) First Nations band government whose reserve community, Waterhen 45, is located 288 km north of Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, on the south shore of Waterhen Lake, between Lake Winnipeg and Lake Winnipegosis. As of May, 2015, the First Nation had 1,464 registered members, of which 750 lived on-reserve.

The Kinistin Saulteaux Nation is a Saulteaux band government in Saskatchewan. Their reserve is 39 kilometres (24 mi) southeast of Melfort. The Kinistin Saulteaux Nation is a signatory of Treaty No. 4, which was signed by Chief Yellow-quill on August 24, 1876.
The Naicatchewenin First Nation, also known as the Anishinaabeg of Nagaajiwanaang and formerly known as Northwest Bay First Nation, inhabited a region in Ontario that was cited in the Northwest Angle Treaty of 1873, also known as Treaty 3. Nagaajiwanaang is located approximately 60 kilometres (37 mi) northwest of Fort Frances, with the community of Devlin 50 kilometres (31 mi) to the south on Highway 11. The city of Thunder Bay lies 420 kilometres (260 mi) to the east and Winnipeg is 450 kilometres (280 mi) to the northwest.

Rainy Lake and River Bands of Saulteaux are Saulteaux (Ojibwe) group located in Northwestern Ontario and northern Minnesota, along and about the Rainy Lake and the Rainy River, known in Ojibwe as Gojijiing.

Seine River First Nation, previously known as the Rivière la Seine Band, is an Ojibwe First Nation reserve located roughly 300 kilometres (190 mi) west of Thunder Bay, Ontario. As of November 2011, the First Nation had a total registered population of 725, of which 327 lived on their own reserve.
Mitaanjigamiing First Nation, formerly known as Stanjikoming First Nation, is an Ojibwe First Nation band government who inhabit 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) north of Fort Frances, Ontario, along the shores of Stanjikoming Bay of Rainy Lake. As of November, 2011, the First Nation had a total registered population of 142, of which 99 lived on their own reserve.

The Cote First Nation is a Saulteaux First Nations band government in Kamsack, Saskatchewan. This Saulteaux reserve is connected to the Keeseekoose First Nation and only a couple of miles from the Key First Nation. Their land is situated just south of the boreal forest in the aspen parkland ecosystem of Canada. The Ojibwe of this region of Saskatchewan and Manitoba were both hunters of the plains bison and hunters of the forests which were more abundant during the 19th century. They also fished the endless lakes and other waterways in the land. They seldom went hungry as a result of the large bison herds. However, by the 1870s, commercial hunting had reduced the bison to near extinction and the Ojibwe of Saskatchewan and Manitoba began to suffer from famine.
Big Grassy First Nation is an Ojibwe or Ontario Saulteaux First Nation band government located in Rainy River District, Ontario near Morson, Ontario.
Ojibways of Onigaming First Nation is an Ojibwe or Ontario Saulteaux First Nation located in Kenora District, Ontario near Nestor Falls, Ontario. Together with the Big Grassy First Nation, Ojibways of Onigaming First Nation is a successor apparent to the former Assabaska Band of Saulteaux. Total registered population in February, 2012, was 737, of which the on-reserve population was 445. The First Nation is a member of the Anishinabeg of Kabapikotawangag Resource Council, a regional tribal council that is a member of the Grand Council of Treaty 3.
Saulteaux First Nation is a Saulteaux Anishinaabe First Nation band government, whose reserves are located near Cochin, Saskatchewan. In February 2012, the First Nation had a total of 1,225 registered members, of whom 604 lived on their own reserve.

The Kay-Nah-Chi-Wah-Nung Historical Centre, or Manitou Mounds, is Canada's premier concentration of ancient burial mounds. Manitou Mounds National Historic Site, as it was once called, is a vast network of 30 village sites and 15 ancient burial mounds constructed from approximately 5000 BP during the Archaic Period, to 360 BP; it is one of the "most significant centres of early habitation and ceremonial burial in Canada." It is located on a river stretch known as Long Sault Rapids on the north side of Rainy River, approximately 54 kilometres east of Fort Frances, in the Rainy River District of Northwestern Ontario, Canada off highway 11. It was designated as a National Historic Site of Canada in 1969.
The Batchewana First Nation is an Ojibwe First Nation in northern Ontario. Their traditional lands run along the eastern shore of Lake Superior, from Batchawana Bay to Whitefish Island. They were reserved this land in the 1850 Robinson Huron Treaty, but surrendered most of it under the 1859 Pennefather Treaty. Through purchase and land claims, it has reclaimed some territories, including Goulais Bay 15A, Obadjiwan 15E, Rankin Location 15D and Whitefish Island.
References
48°39′18″N93°54′25″W / 48.65500°N 93.90694°W
