
Ravana was a ancient mythological king of the island of Lanka, and the chief antagonist in the Hindu epic Ramayana. In the Ramayana, Ravana is described as the eldest son of sage Vishrava and Kaikasi. He abducted Prince Rama's wife, Sita, and took her to his kingdom of Lanka, where he held her in the Ashoka Vatika. Rama, with the support of vanara King Sugriva and his army of vanaras, launched an invasion against Ravana in Lanka. Ravana was subsequently slain, and Rama rescued his beloved wife Sita.

Rākshasa are a race of usually malevolent beings prominently featured in Hindu mythology. They reside on Earth but possess supernatural powers, which they usually use for evil acts such as disrupting Vedic sacrifices or eating humans.

Adam's Bridge, also known as Rama's Bridge or Rama Setu, is a chain of natural limestone shoals between Pamban Island, also known as Rameswaram Island, off the south-eastern coast of Tamil Nadu, India, and Mannar Island, off the north-western coast of Sri Lanka. Geological evidence suggests that the bridge was formerly a land connection between India and Sri Lanka.

Lanka is the name given in Hindu epics to the island fortress capital of the legendary asura king Ravana in the epics of the Ramayana and the Mahabharata. The fortress was situated on a plateau between three mountain peaks known as the Trikuta Mountains. The ancient city of Lankapura is said to have been burnt down by Hanuman. After its king, Ravana was killed by Rama with the help of Ravana's brother Vibhishana, the latter was crowned king of Lankapura. His descendants were said to still rule the kingdom during the period of the Pandavas. According to the Mahabharata, the Pandava Sahadeva visited this kingdom during his southern military campaign for the rajasuya of Yudhishthira. The palaces of Ravana were said to be guarded by four-tusked elephants.
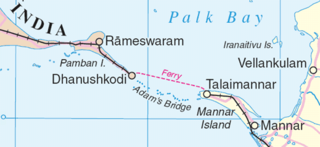
The Palk Strait is a strait between the Tamil Nadu state of India and the Jaffna District of the Northern Province of the island nation of Sri Lanka. It connects the Bay of Bengal in the northeast with Palk Bay in the southwest. It is 40 to 85 miles wide and 85 miles long. Several rivers flow into it, including the Vaigai River of Tamil Nadu. The strait is named after Robert Palk, who was a governor of Madras (1755–1763) during the Company Raj period.

Nuwara Eliya is a city in the hill country of the Central Province, Sri Lanka. Its name means "city on the plain " or "city of light". The city is the administrative capital of Nuwara Eliya District, with a picturesque landscape and temperate climate. It is at an altitude of 1,868 m (6,128 ft) and is considered to be the most important location for tea production in Sri Lanka. The city is overlooked by Pidurutalagala, the tallest mountain in Sri Lanka. Nuwara Eliya is known for its temperate, cool climate – the coolest area in Sri Lanka.

Yala (යාල) National Park is the most visited and second largest national park in Sri Lanka, bordering the Indian Ocean. The park consists of five blocks, three of which are now open to the public. There are also two adjoining parks, Kumana National Park or 'Yala East' and Lunugamvehera National Park. The blocks have individual names, such as Palatupana. It is situated in the southeastern region of the country, in the Southern Province and Uva Province. The park covers 979 square kilometres (378 sq mi) and is located about 300 kilometres (190 mi) from Colombo. Yala was designated as a wildlife sanctuary in 1900, along with Wilpattu, designated in 1938, as the first two designated national parks in Sri Lanka. The park is best known for its variety of wildlife and is important conservation of Sri Lankan elephants, Sri Lankan leopards and aquatic birds.

Vibhishana is the younger brother of Ravana, the King of Lanka, in the ancient Indian epic Ramayana. Though a rakshasa himself, Vibhishana turned his back on Ravana, and defected to Rama's side, owing to his dharma. After Rama defeated Ravana, the former crowned Prince Vibhishana as the King of Lanka before returning to Ayodhya.

Sita, also known as Siya, Janaki, Maithili, Vaidehi, and Bhumija, is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic Ramayana. Sita is the consort of Rama, the avatar of god Vishnu, and is regarded as an avatar of goddess Lakshmi. She is the chief goddess of the Rama-centric Hindu traditions and is known as the goddess of beauty and devotion. Sita is known for her dedication, self-sacrifice, courage, and purity.

Hinduism is one of Sri Lanka's oldest religions, with temples dating back over 2,000 years. As of 2011, Hindus made up 12.6% of the Sri Lankan population. They are almost exclusively Tamils, except for small immigrant communities from India and Pakistan.

Murdeshwar is a town in Uttara Kannada district in the state of Karnataka, India, It is famous for the world's third tallest Shiva statue, the town lies on the coast of the Laccadive Sea and is also famous for the Murudeshwara Temple. The town has a railway station on the Mangalore–Mumbai Konkan railway route.

Kalasuri Arisen Ahubudu was a Sri Lankan writer, orator, scholar, playwright, teacher (Guru), Sinhala lyricist, author and poet. He is a member of the Hela Havula. He has received three government awards for literary works, the title of Kalasuri from the Government of Sri Lanka, and the Sarasaviya Awards film award for best composer. As a composer, he is especially noted for writing music performed by W.D. Amaradeva, such as Gilem Obe Guna.
The wildlife of Sri Lanka includes its flora and fauna and their natural habitats. Sri Lanka has one of the highest rates of biological endemism.

Adam's Peak is a 2,243 m (7,359 ft) tall conical sacred mountain located in central Sri Lanka. It is well known for the Sri Pada, a 1.8 m rock formation near the summit whose name is also used for the mountain itself. In Buddhist tradition the print is held to be the footprint of the Buddha, in Sri Lankan Hindu tradition that of Hanuman or Shiva, and in some Islamic and Christian traditions that of Adam or St. Thomas.

Hakgala Strict Nature Reserve is one of the three strict nature reserves in Sri Lanka, the only one in the wet zone. The reserve is an important although isolated cloud forest which supports a number of faunal species including some endemics. The area was designated a strict nature reserve on 25 February 1938. The reserve is adjacent to and contiguous with the Hakgala Botanical Garden which was founded in 1860.

Dinesh Subasinghe is a Sri Lankan composer, violinist, and music producer. He composed Karuna Nadee, a Buddhist oratorio, and re-introduced a lost, ancient musical instrument known as the ravanahatha to Sri Lanka. He is also a film and television composer whose works integrate western and eastern classical music with electronic music, Buddhist music, folk music, traditional orchestral arrangements, and world music genres. From 2002 to 2009 he led the pop classical band, Dee R Cee Members.
Ravana Desam or Ravan Desam is a 2013 Indian Tamil-language film written and directed by Ajay Nuthakki. The film is based on the refugees missing during the 2009 Sri Lankan Civil War.

Ella is a small town in the Badulla District of Uva Province, Sri Lanka governed by an Urban Council. It is approximately 200 kilometres (120 mi) east of Colombo and is situated at an elevation of 1,041 metres (3,415 ft) above sea level. The area has a rich bio-diversity, dense with numerous varieties of flora and fauna. Ella is surrounded by hills covered with cloud forests and tea plantations. The town has a cooler climate than surrounding lowlands, due to its elevation. The Ella Gap allows views across the southern plains of Sri Lanka.

Aspidura ravanai, commonly known as Ravana's rough-sided snake is a species of colubrid snake endemic to Sri Lanka.

















