
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male or female. Cycads vary in size from having trunks only a few centimeters to several meters tall. They typically grow slowly and have long lifespans. Because of their superficial resemblance to palms or ferns, they are sometimes mistaken for them, but they are not closely related to either group. Cycads are gymnosperms (naked-seeded), meaning their unfertilized seeds are open to the air to be directly fertilized by pollination, as contrasted with angiosperms, which have enclosed seeds with more complex fertilization arrangements. Cycads have very specialized pollinators, usually a specific species of beetle. Both male and female cycads bear cones (strobili), somewhat similar to conifer cones.

Chelidae is one of three living families of the turtle suborder Pleurodira, and are commonly called Austro-South American side-neck turtles. The family is distributed in Australia, New Guinea, parts of Indonesia, and throughout most of South America. It is a large family of turtles with a significant fossil history dating back to the Cretaceous. The family is entirely Gondwanan in origin, with no members found outside Gondwana, either in the present day or as a fossil.

The Zamiaceae are a family of cycads that are superficially palm or fern-like. They are divided into two subfamilies with eight genera and about 150 species in the tropical and subtropical regions of Africa, Australia and North and South America.

Lardizabalaceae is a family of flowering plants.
Amazonsaurus is a genus of diplodocoid sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Period of what is now South America. It would have been a large-bodied quadrupedal herbivore with a long neck and whiplash tail. Although more derived diplodocoids were some of the longest animals ever to exist, Amazonsaurus was probably not more than 12 meters (40 ft) long. Gregory S. Paul estimated in 2010 its weight at 5000 kg.
Loricosaurus is a genus of sauropod represented by a single species. It is a titanosaurian that lived near the end of the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 71 million years ago in the early Maastrichtian. Found in the province of Neuquen, Argentina in the Allen Formation. Due to the presence of armour, at first it was thought that it was an ankylosaur, but today it is considered to be the armour of a titanosaur.

Patagonykus is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of Argentina. This alvarezsauroid was discovered in exposures of the Portezuelo Formation (Turonian-Coniacian) of the Rio Neuquén Subgroup in the Neuquén Basin, Neuquen Province of Patagonia, Argentina. The holotype consists of an incomplete but well-preserved skeleton, lacking a skull, but including many vertebrae, the coracoids, a partial forelimb, pelvic girdle, and hindlimbs. Patagonykus has been classed with the Alvarezsauridae, a family which includes such taxa as the Mongolian Mononykus and the Argentinian Alvarezsaurus. In 2010 Gregory S. Paul estimated its length at 1 meter and its weight at 3.5 kg.
Mendozasaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur. It was a member of Titanosauria, which were massive sauropods that were common on the southern landmasses during the Cretaceous. It is represented by several partial skeletons from a single locality within the Coniacian Sierra Barrosa Formation in the south of Mendoza Province, northern Neuquén Basin, Argentina. The type species, Mendozasaurus neguyelap, was described by Argentine paleontologist Bernardo Javier González Riga in 2003. Mendozasaurus is the first dinosaur named from Mendoza Province, Argentina, for which it was named.

Noasaurus is a genus of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaur genus from the late Campanian-Maastrichtian of Argentina. The type and only species is N. leali.

Ligabuesaurus is a genus of somphospondylan sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous that lived in what is now Argentina. The type species, Ligabuesaurus leanzai, was described by Jose Bonaparte, Gonzalez Riga, and Sebastián Apesteguía in 2006, based on a partial skeleton with skull, holotype MCF-PHV-233. The generic name, Ligabuesaurus, honors Giancarlo Ligabue, while the specific name, leanzai, honors the geologist Dr. Héctor A. Leanza, who discovered the skeleton in the Lohan Cura Formation. In 2022, a second skeleton was referred, specimen MCF-PHV-228. A third skeleton was recovered but not referred due to a lack of overlapping material. The three skeletons were excavated between 1998 and 2000.
Zapalasaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur described by Leonardo Salgado, Ismar de Souza Carvalho and Alberto Garrido in 2006. It was named after the city of Zapala, which is approximately 80 kilometres (50 mi) away from where the holotype was discovered. The type species, Zapalasaurus bonapartei, was found in the La Amarga Formation of the Neuquén Basin, Neuquén Province, Argentina. It was a diplodocoid, a long-necked herbivore, and it lived during the Early Cretaceous. The authors conclude from examining the skeleton that "The record of Zapalasaurus bonapartei shows that, at least in the Neuquén Basin, basal diplodocoids were more diverse than previously thought." Zapalasaurus is assumed to have a long neck which would have been developed for feeding adaption, allowing its neck to swing in an arc like shape. This would allow Zapalasaurus to browse a wide variety of plants and greens without having to walk very far.

Sulcusuchus is a genus of polycotylid plesiosaur from the Late Campanian to Early Maastrichtian of Argentina.
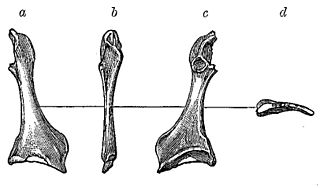
Cimolopteryx is a prehistoric bird genus from the Late Cretaceous Period. It is currently thought to contain only a single species, Cimolopteryx rara. The only specimen confidently attributed to C. rara was found in the Lance Formation of Wyoming, dating to the end of the Maastrichtian age, which ended about 66 million years ago. The dubious species "Cimolopteryx" maxima has been described from both the Lance Formation and the Hell Creek Formation of Montana. The humeral end of a left coracoid from the Frenchman Formation of southern Saskatchewan has also been attributed to the genus.
Ceramornis is a genus of ornithuran dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous. It lived shortly before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event in the Maastrichtian, some 66 million years ago (mya). Its remains were found in the Lull 2 location, a Lance Formation site in Niobrara County, Wyoming. A single species is known, Ceramornis major, and even that only from a proximal piece of coracoid. This is specimen UCMP V53957, which was collected by a University of California team in 1958.

Palintropus is a prehistoric bird genus from the Late Cretaceous. A single species has been named based on a proximal coracoid from the Lance Formation of Wyoming, dated to the latest Maastrichtian, 66 million years ago. Coracoids and a proximal scapula of two unnamed species from the upper Campanian Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, dating to between 76.5 and 75 million years ago, are also known.
Notoemys is an extinct genus of platychelyid turtle known from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of the Americas.
Barcinosuchus is an extinct genus of carnivorous metasuchian from the early Cretaceous period. It is a peirosaurid which lived during the early Cretaceous period in what is now Chubut Province, Argentina. It is known from the holotype MPEF-PV 3095, which consists of skull, mandible, and postcranial remains. The specimen recovered from the lower part of the Cerro Castaño Member of the Cerro Barcino Formation. Barcinosuchus was named by Martín Leardi and Diego Pol in 2009 and the type species is Barcinosuchus gradilis.
Comahuesaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur of the family Rebbachisauridae. It was found in the Lohan Cura Formation, in Argentina and lived during the Early Cretaceous, Aptian to Albian. The type species is C. windhauseni, named by Carballido and colleagues in 2012. It had originally been assigned to Limaysaurus by Salgado et al. (2004), but was later assigned its own genus based on the presence of diagnostic characters in the caudal centra, pubis and ischium.
Martín Daniel Ezcurra is an Argentine palaeontologist naming many extinct genera such as Aerotitan, Lophostropheus and Powellvenator.
Lamarqueavis is an extinct genus of ornithuran dinosaurs from the family Cimolopterygidae known from Late Cretaceous-aged rocks from Argentina, Canada, and the United States. The type species, L. australis, was named in 2010 and is based on the holotype MML 207, a partial right coracoid found in the Allen Formation, Argentina. Two other species, L. minima, based on the holotype UCMP 53976, a right coracoid found in the Lance Formation, Wyoming, and L. petra, based on the holotype AMNH 21911, a left coracoid also found in the Lance Formation, Wyoming, were transferred over from Cimolopteryx to Lamarqueavis in 2010. A third unnamed species is known from the Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, Canada.









