
Lavandula is a genus of 47 known species of flowering plants in the mint family, Lamiaceae. It is native to the Old World and is found from Cape Verde and the Canary Islands, Europe across to northern and eastern Africa, the Mediterranean, southwest Asia, China to southeast India. Many members of the genus are cultivated extensively in temperate climates as ornamental plants for garden and landscape use, for use as culinary herbs, and also commercially for the extraction of essential oils. The most widely cultivated species, Lavandula angustifolia, is often referred to as lavender, and there is a color named for the shade of the flowers of this species.

Lemon balm, balm, common balm, or balm mint, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the mint family Lamiaceae and native to south-central Europe, the Mediterranean Basin, Iran, and Central Asia, but now naturalized in the Americas and elsewhere.

Oregano is a flowering plant in the mint family (Lamiaceae). It is native to temperate Western and Southwestern Eurasia and the Mediterranean region.

Anise, also called aniseed, is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae native to the eastern Mediterranean region and Southwest Asia.

An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile chemical compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils, aetherolea, or simply as the oil of the plant from which they were extracted, such as oil of clove. An essential oil is "essential" in the sense that it contains the "essence of" the plant's fragrance—the characteristic fragrance of the plant from which it is derived. The term essential used here does not mean indispensable as with the terms essential amino acid or essential fatty acid which are so called since they are nutritionally required by a given living organism. In contrast to fatty oils, essential oils typically evaporate completely without leaving a stain or residue.

Ajwain, ajowan, or Trachyspermum ammi—also known as ajowan caraway, bishop's weed, or carom—is an annual herb in the family Apiaceae. Both the leaves and the seed‑like fruit of the plant are consumed by humans. The name "bishop's weed" also is a common name for other plants. The "seed" is often confused with lovage "seed".

Salvia officinalis is a perennial, evergreen subshrub, with woody stems, grayish leaves, and blue to purplish flowers. It is a member of the mint family Lamiaceae and native to the Mediterranean region, though it has naturalized in many places throughout the world. It has a long history of medicinal and culinary use, and in modern times as an ornamental garden plant. The common name "sage" is also used for a number of related and unrelated species.

Vitex agnus-castus, also called vitex, chaste tree, chasteberry, Abraham's balm, lilac chastetree, or monk's pepper, is a native of the Mediterranean region. It is one of the few temperate-zone species of Vitex, which is on the whole a genus of tropical and sub-tropical flowering plants. Theophrastus mentioned the shrub several times, as agnos (άγνος) in Enquiry into Plants. It has been long believed to be an anaphrodisiac – leading to its name as chaste tree – but its effectiveness for such action remains unproven.

Glebionis segetum is a species of the genus Glebionis, probably native only to the eastern Mediterranean region but now naturalized in western and northern Europe as well as China and parts of North America. Common names include corn marigold and corn daisy.

Tansy is a perennial, herbaceous flowering plant of the aster family, native to temperate Europe and Asia. It has been introduced to other parts of the world, including North America, and in some areas has become invasive. It is also known as common tansy, bitter buttons, cow bitter, or golden buttons. The Latin name vulgare means "common".

Eugenia uniflora, with common names pitanga, Suriname cherry, Brazilian cherry, Cayenne cherry, or Cerisier Carré is a plant in the family Myrtaceae, native to tropical South America’s east coast, ranging from Suriname, French Guiana to southern Brazil, as well as parts of Paraguay, Argentina and Uruguay. Known as pitanga throughout Brazil and Uruguay, or ñangapirí in surrounding countries, the plant is relatively pest resistant, easy to grow and high in antioxidants. The tree is also grown in the West Indies, specifically in Haiti, where it is known as Cerisier Carré, as is in French Guiana. The Suriname cherry is often used in gardens as a hedge or screen. The tree was introduced to Bermuda for ornamental purposes but is now out of control and listed as an invasive species. In Suriname this cherry is known as Monkimonki Kersie, also Montjimontji Kersie. The tree has also been introduced to Florida.

Oenothera biennis is a species of Oenothera native to eastern and central North America, from Newfoundland west to Alberta, southeast to Florida, and southwest to Texas, and widely naturalized elsewhere in temperate and subtropical regions. Evening primrose oil is produced from the plant.

Cinnamomum tamala, Indian bay leaf', also known as ತಮಾಲ (Tamaala) in Kannada(ಕನ್ನಡ), மரப்பட்டை இலை in தமிழ்(Tamizh), tejpat, tejapatta, Malabar leaf, Indian bark, Indian cassia, or malabathrum, is a tree in the Lauraceae family that is native to India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and China. It can grow up to 20 m (66 ft) tall. Its leaves have a clove-like aroma with a hint of peppery taste, they are used for culinary and medicinal purposes. It is thought to have been one of the major sources of the medicinal plant leaves known in classic and medieval times as malabathrum.
Eucalyptus oil is the generic name for distilled oil from the leaf of Eucalyptus, a genus of the plant family Myrtaceae native to Australia and cultivated worldwide. Eucalyptus oil has a history of wide application, as a pharmaceutical, antiseptic, repellent, flavouring, fragrance and industrial uses. The leaves of selected Eucalyptus species are steam distilled to extract eucalyptus oil.

Juniperus phoenicea, the Phoenicean juniper or Arâr, is a juniper found throughout the Mediterranean region, from Morocco and Portugal east to Italy, Turkey and Egypt, south on the mountains of Lebanon, the Palestine region and in western Saudi Arabia near the Red Sea, and also on Madeira and the Canary Islands. It mostly grows at low altitudes close to the coast, but reaches 2,400 metres (7,900 ft) altitude in the south of its range in the Atlas Mountains. It is the vegetable symbol of the island of El Hierro.

Perilla frutescens, commonly called perilla or Korean perilla, is a species of Perilla in the mint family Lamiaceae. It is an annual plant native to Southeast Asia and Indian highlands, and is traditionally grown in the Korean peninsula, Southern China, Japan and India as a crop. An edible plant, perilla is a very attractive plant for the garden and attracts butterflies. It is an aromatic plant with a strong minty smell. Various perilla varieties are traditionally used by local people, the leaves are used as a vegetable and the seeds supply nutritious cooking oil. A variety of this plant, P. frutescens var. crispa or "shiso", is widely grown and is one of the most popular garnishes in Japan, used as an antidote for fish and crab meat allergy or as a food colorant. In the United States, perilla is a weed pest, toxic to cattle after ingestion.

Cymbopogon citratus, commonly known as lemon grass, is a tropical plant from South Asia and introduced to Southeast Asia.

Cymbopogon martinii is a species of grass in the genus Cymbopogon (lemongrasses) native to India and Indochina, but widely cultivated in many places for its aromatic oil. It is best known by the common name palmarosa as it smells sweet and rose-like. Other common names include Indian geranium, gingergrass, rosha, and rosha grass.
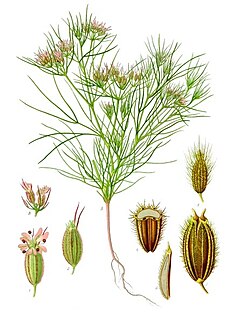
Cumin is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, native to a territory including the Middle East and stretching east to India. Its seeds – each one contained within a fruit, which is dried – are used in the cuisines of many cultures in both whole and ground form. Although cumin is thought to have uses in traditional medicine, there is no high-quality evidence that it is safe or effective as a therapeutic agent.



















