
Parsley, or garden parsley is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae that is native to Greece, Morocco and the former Yugoslavia. It has been introduced and naturalized in Europe and elsewhere in the world with suitable climates, and is widely cultivated as an herb and a vegetable.

Chicken soup is a soup made from chicken, simmered in water, usually with various other ingredients. The classic chicken soup consists of a clear chicken broth, often with pieces of chicken or vegetables; common additions are pasta, noodles, dumplings, or carrots, and grains such as rice and barley. Chicken soup is commonly considered a comfort food.

The sweet potato or sweetpotato is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the bindweed or morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable. The young shoots and leaves are sometimes eaten as greens. Cultivars of the sweet potato have been bred to bear tubers with flesh and skin of various colors. Sweet potato is only distantly related to the common potato, both being in the order Solanales. Although darker sweet potatoes are often referred to as "yams" in parts of North America, the species is even more distant from the true yams, which are monocots in the order Dioscoreales.

Root vegetables are underground plant parts eaten by humans as food. In agricultural and culinary terminology, the term applies to true roots such as taproots and tuberous roots as well as non-roots such as bulbs, corms, rhizomes, and stem tubers.

A mirepoix is a mixture of diced vegetables cooked with fat for a long time on low heat without coloring or browning. The ingredients are not sautéed or otherwise hard-cooked, because the intention is to sweeten rather than caramelize them. Mirepoix is a long-standing part of French cuisine and is the flavor base for a wide variety of dishes, including stocks, soups, stews, and sauces.

The parsnip is a root vegetable closely related to carrot and parsley, all belonging to the flowering plant family Apiaceae. It is a biennial plant usually grown as an annual. Its long taproot has cream-colored skin and flesh, and, left in the ground to mature, becomes sweeter in flavor after winter frosts. In its first growing season, the plant has a rosette of pinnate, mid-green leaves. If unharvested, it produces a flowering stem topped by an umbel of small yellow flowers in its second growing season, later producing pale brown, flat, winged seeds. By this time, the stem has become woody, and the tap root inedible. Precautions should be taken when handling the stems and foliage, as parsnip sap can cause a skin rash or even blindness if exposed to sunlight after handling.

Oxalis tuberosa is a perennial herbaceous plant that overwinters as underground stem tubers. These tubers are known as uqa in Quechua, oca in Spanish, yams in New Zealand and several other alternative names. The plant was brought into cultivation in the central and southern Andes for its tubers, which are used as a root vegetable. The plant is not known in the wild, but populations of wild Oxalis species that bear smaller tubers are known from four areas of the central Andean region. Oca was introduced to Europe in 1830 as a competitor to the potato, and to New Zealand as early as 1860.

Ullucus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Basellaceae, with one species, Ullucus tuberosus, a plant grown primarily as a root vegetable, secondarily as a leaf vegetable. The name ulluco is derived from the Quechua word ulluku, but depending on the region, it has many different names. These include illaco, melloco, chungua or ruba, olluco or papalisa, or ulluma.
Northern root-knot nematode is a species of vegetable pathogens which produces tiny galls on around 550 crop and weed species. They invade root tissue after birth. Females are able to lay up to 1,000 eggs at a time in a large egg mass. By surviving harsh winters, they can survive in cold climates.
Peruvian cuisine reflects local practices and ingredients including influences mainly from the indigenous population, including the Inca, and cuisines brought by immigrants from Europe, Asia, and Africa. Without the familiar ingredients from their home countries, immigrants modified their traditional cuisines by using ingredients available in Peru.
Mirabilis expansa is a species of flowering plant cultivated as a root vegetable in the Andes, at cold, windy altitudes between 2,200 m (7,200 ft) and 3,500 m (11,500 ft). The above-ground portion dies back with frost, but the root is quite hardy. The roots can reach the size of a man's forearm, and yields can reach 50,000 kg/ha (45,000 lb/acre) given two years maturation time.

Chuño is a preserved potato product traditionally made by Quechua and Aymara communities of Bolivia and Peru, and is known in various countries of South America, including Bolivia, Peru, Chile and Northwest Argentina. It is a five-day process, obtained by exposing a bitter, frost-resistant variety of potatoes to the very low night temperatures of the Andean Altiplano, freezing them, and subsequently exposing them to the intense sunlight of the day. The word comes from Quechua ch'uñu, meaning 'frozen potato'.

Yam is the common name for some plant species in the genus Dioscorea that form edible tubers.

Sopa de mondongo is a soup that originally came from Colombia, Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic. It is made from diced tripe slow-cooked with vegetables such as bell peppers, onions, carrots, cabbage, celery, tomatoes, cilantro, garlic or root vegetables. The dish is generally prepared in former Spanish colonies in Latin America, Caribbean, and in the Philippines. The proposed etymology for mondongo is in the African Kikongo language, meaning “intestines, entrails of certain animals.

A purée is cooked food, usually vegetables, fruits or legumes, that has been ground, pressed, blended or sieved to the consistency of a creamy paste or liquid. Purées of specific foods are often known by specific names, e.g., apple sauce or hummus. The term is of French origin, where it meant in Old French purified or refined.
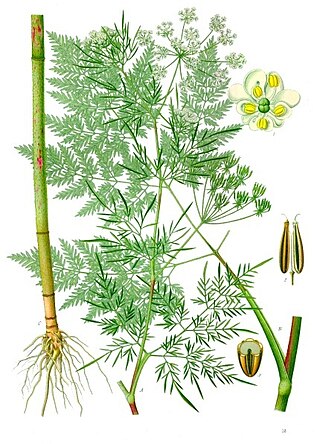
Chaerophyllum bulbosum is a species of flowering plant from the carrot family and known by several common names, including turnip-rooted chervil, tuberous-rooted chervil, bulbous chervil, and parsnip chervil. It is native to Europe and Western Asia. It was a popular vegetable in the 19th century.

Northern Irish cuisine encompasses the cooking styles, traditions and recipes associated with Northern Ireland. It has distinctive attributes of its own, but has also drawn heavily from Irish and British cuisines.

Vegetable chips are chips (crisps) that are prepared using vegetables other than potatoes. Vegetable chips may be fried, deep-fried, dehydrated, dried, or baked. Many different root vegetables or leaf vegetables may be used. Vegetable chips may be eaten as a snack food and may accompany other foods such as dips, or be used as a topping on dishes. In the United States, vegetable chips are often mass-produced, with many brands marketed to consumers.

A staple food, food staple, or simply staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for an individual or a population group, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and generally forming a significant proportion of the intake of other nutrients as well. For humans, a staple food of a specific society may be eaten as often as every day or every meal, and most people live on a diet based on just a small variety of food staples. Specific staples vary from place to place, but typically are inexpensive or readily available foods that supply one or more of the macronutrients and micronutrients needed for survival and health: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, and vitamins. Typical examples include grains, seeds, nuts and root vegetables. Among them, cereals, legumes and tubers account for about 90% of the world's food calorie intake.


















