The Rodrigues day gecko, also known commonly as the Rodrigues blue-dotted day gecko, is an extinct species of day gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species was endemic to the island of Rodrigues, where it typically inhabited forests and dwelt in trees. The Rodrigues day gecko fed on insects and nectar.

Newton's parakeet, also known as the Rodrigues parakeet or Rodrigues ring-necked parakeet, is an extinct species of parrot that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues in the western Indian Ocean. Several of its features diverged from related species, indicating long-term isolation on Rodrigues and subsequent adaptation. The rose-ringed parakeet of the same genus is a close relative and probable ancestor. Newton's parakeet may itself have been ancestral to the endemic parakeets of nearby Mauritius and Réunion.

The Rodrigues solitaire is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Rodrigues, east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. Genetically within the family of pigeons and doves, it was most closely related to the also extinct dodo of the nearby island Mauritius, the two forming the subfamily Raphinae. The Nicobar pigeon is their closest living genetic relative.

The pink pigeon is a species of pigeon in the family Columbidae endemic to Mauritius. The pink pigeon nearly became extinct in the 1970s and the 1990s and is still very rare. It is the only Mascarene pigeon that has not become extinct. It was on the brink of extinction in 1991 when only 10 individuals remained, but its numbers have increased due to the efforts of the Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust since 1977. While the population remains at below 500 birds as of 2011, the IUCN downlisted the species from Critically endangered to Endangered on the IUCN Red List in 2000, and then downlisted it again to Vulnerable in 2018.

The broad-billed parrot or raven parrot is a large extinct parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It was endemic to the Mascarene island of Mauritius. The species was first referred to as the "Indian raven" in Dutch ships' journals from 1598 onwards. Only a few brief contemporary descriptions and three depictions are known. It was first scientifically described from a subfossil mandible in 1866, but this was not linked to the old accounts until the rediscovery of a detailed 1601 sketch that matched both the subfossils and the accounts. It is unclear what other species it was most closely related to, but it has been classified as a member of the tribe Psittaculini, along with other Mascarene parrots. It had similarities with the Rodrigues parrot, and may have been closely related.
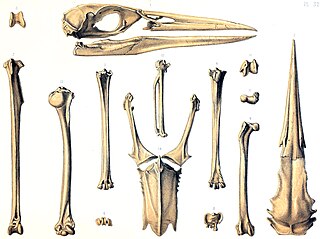
The Rodrigues night heron is an extinct species of heron that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues in the Indian Ocean. The species was first mentioned as "bitterns" in two accounts from 1691–1693 and 1725–1726, and these were correlated with subfossil remains found and described in the latter part of the 19th century. The bones showed that the bird was a heron, first named Ardea megacephala in 1873, but moved to the night heron genus Nycticorax in 1879 after more remains were described. The specific name megacephala is Greek for "great-headed". Two related extinct species from the other Mascarene islands have also been identified from accounts and remains: the Mauritius night heron and the Réunion night heron.

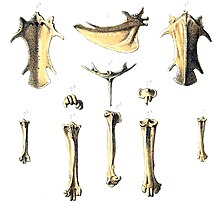
The Rodrigues rail, also known as Leguat's gelinote or Leguat's rail, is an extinct species of the rail family that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues. The bird was first documented from life by two accounts from 1691–93 and 1725–26. Subfossil remains were later discovered and correlated with the old accounts in 1874, and the species was named E. leguati in Leguat's honour. It is generally kept in its own genus, Erythromachus, but has sometimes been assigned to the genus Aphanapteryx along with its close relative the red rail of Mauritius; their relationship with other rails is unclear.

The red rail is an extinct species of rail that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Mauritius, east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. It had a close relative on Rodrigues island, the likewise extinct Rodrigues rail, with which it is sometimes considered congeneric, but their relationship with other rails is unclear. Rails often evolve flightlessness when adapting to isolated islands, free of mammalian predators, and that was also the case for this species. The red rail was a little larger than a chicken and had reddish, hairlike plumage, with dark legs and a long, curved beak. The wings were small, and its legs were slender for a bird of its size. It was similar to the Rodrigues rail, but was larger, and had proportionally shorter wings. It has been compared to a kiwi or a limpkin in appearance and behaviour.

The Réunion pink pigeon is an extinct subspecies of pigeon that formerly lived on the Mascarene island of Réunion. It is known from the description of a rusty-red pigeon given by Dubois in 1674 and a single subfossil humerus that agrees with that of the pink pigeon of Mauritius in generic characteristics, except being slightly longer. Also, Dubois' reference to the bill being red at the base and the eyes being surrounded by a red ring suggest that this species was closely allied to the Mauritius taxon. Dubois' description was as follows:
wild pigeons, everywhere full with them, some with slaty-coloured feathering [Alectroenas?], the others russet-red [N. duboisi]. They are a little larger than the European pigeons, and have larger bills, red at the end close to the head, the eyes ringed with the colour of fire, like pheasants. There is a season when they are so fat that one can no longer see their cloaca [croupion]. They are very good tasting. Wood-pigeons and turtle-doves, as one sees in Europe and as good.

The Rodrigues parrot or Leguat's parrot is an extinct species of parrot that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues. The species is known from subfossil bones and from mentions in contemporary accounts. It is unclear to which other species it is most closely related, but it is classified as a member of the tribe Psittaculini, along with other Mascarene parrots. The Rodrigues parrot bore similarities to the broad-billed parrot of Mauritius, and may have been related. Two additional species have been assigned to its genus, based on descriptions of parrots from the other Mascarene islands, but their identities and validity have been debated.

The Rodrigues scops owl, also known as Rodrigues owl, Rodrigues lizard owl, Leguat's owl, or Rodrigues little owl, was a small owl. It lived on the Mascarene island of Rodrigues, but it is nowadays extinct. It is part of the three Mascarene owls, formerly classified in the genus Mascarenotus, although they are now classified in the genus Otus. Like many of the Mascarene land-birds, the genus was a distinct relative to South-East Asian taxa, in this case apparently being a descendant of the direct ancestor of the Oriental scops owl. This insular scops owl had evolved gigantism, becoming twice as large and four times heavier than its continental ancestor.

The Mauritius blue pigeon is an extinct species of blue pigeon formerly endemic to the Mascarene island of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean east of Madagascar. It has two extinct relatives from the Mascarenes and three extant ones from other islands. It is the type species of the genus of blue pigeons, Alectroenas. It had white hackles around the head, neck and breast and blue plumage on the body, and it was red on the tail and the bare parts of the head. These colours were thought similar to those of the Dutch flag, a resemblance reflected in its French common name, Pigeon Hollandais. The juveniles may have been partially green. It was 30 cm (12 in) long and larger and more robust than any other blue pigeon species. It fed on fruits, nuts, and molluscs, and was once widespread in the forests of Mauritius.

The Rodrigues starling is an extinct species of starling that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues. Its closest relatives were the Mauritius starling and the hoopoe starling from nearby islands; all three are extinct and appear to be of Southeast Asian origin. The bird was only reported by French sailor Julien Tafforet, who was marooned on the island from 1725 to 1726. Tafforet observed it on the offshore islet of Île Gombrani. Subfossil remains found on the mainland were described in 1879, and were suggested to belong to the bird mentioned by Tafforet. There was much confusion about the bird and its taxonomic relations throughout the 20th century.

The blue pigeons are a genus, Alectroenas, of birds in the dove and pigeon family Columbidae. They are native to islands in the western Indian Ocean.

The Malagasy turtle dove or Madagascar turtle dove is a bird species in the pigeon and dove family, Columbidae.

Nesoenas is a bird genus in the pigeon and dove family, Columbidae. It is often included with the typical turtle-doves in Streptopelia or the typical pigeons (Columba). By those who accepted it, it was usually treated as monotypic, containing only the pink pigeon of Mauritius.

The Mascarene grey parakeet, Mauritius grey parrot, or Thirioux's grey parrot, is an extinct species of parrot which was endemic to the Mascarene Islands of Mauritius and Réunion in the western Indian Ocean. It has been classified as a member of the tribe Psittaculini, along with other parrots from the Islands.
The Rodrigues blue pigeon is an extinct species of blue pigeon which was endemic to Rodrigues. It is known only from the holotype tarsometatarsus collected in 2005, associated with remains of a Rodrigues night heron and a Rodrigues rail. A femur described in 1879 but now lost may also have belonged to the species. It was not specifically mentioned by contemporary writers, and it is therefore unknown when it became extinct.

The Mauritian turtle dove is an extinct species of the pigeon genus Nesoenas which was endemic to Mauritius. The holotype is a right tarsometatarsus collected in 2008 in southeastern Mauritius. It became extinct around 1730 because of overhunting, predation by rats, and deforestation.