
Ozimops planiceps is a small bat in the family Molossidae, native to Australia and Indonesia.
The lesser long-fingered bat, also known as the black clinging bat or lesser bent-winged bat, is a species of vesper bat in the family Miniopteridae. It is found in western Southern Africa, south East Africa, and parts of Central Africa. Its natural habitats are temperate forests, temperate shrubland, and caves and other subterranean habitats.

The Manavi long-fingered bat is a bat in the genus Miniopterus that occurs in east-central Madagascar. First described in 1906, this species was later included in the mainland African M. minor. A 1995 revision united populations of small Miniopterus from Madagascar and the Comoros as M. manavi, but molecular and morphological studies in 2008 and 2009 showed that this concept of M. manavi in fact included five different species. M. manavi itself was restricted to a few locations in the eastern Central Highlands and populations in the Comoros and northern and western Madagascar were allocated to different species.
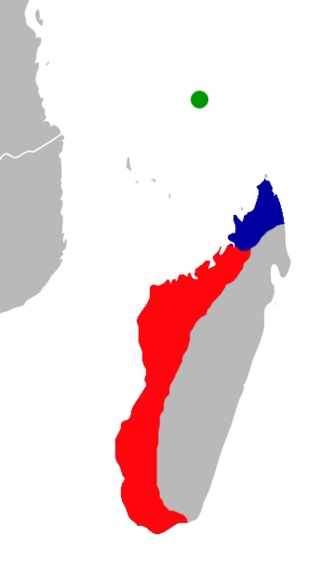
Grandidier's trident bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae endemic to Madagascar. It was formerly assigned to the genus Triaenops, but is now placed in the separate genus Paratriaenops.
Triaenops is a genus of bat in the family Rhinonycteridae. It is classified in the tribe Triaenopini, along with the closely related genus Paratriaenops and perhaps the poorly known Cloeotis. The species of Paratriaenops, which occur on Madagascar and the Seychelles, were placed in Triaenops until 2009. Triaenops currently contains the following species:

Paratriaenops furcula, also known as Trouessart's trident bat, is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is endemic to Madagascar. It was formerly assigned to the genus Triaenops, but is now placed in the separate genus Paratriaenops. A related species, Paratriaenops pauliani, occurs in the Seychelles.

Miniopterus, known as the bent-winged or long winged bats, is the sole genus of the family Miniopteridae. They are small flying insectivorous mammals, micro-bats of the order Chiroptera, with wings over twice the length of the body. The genus had been placed in its own subfamily among the vespertilionid bats, as Miniopterinae, but is now classified as its own family.

The Hipposideridae are a family of bats commonly known as the Old World leaf-nosed bats. While it has often been seen as a subfamily, Hipposiderinae, of the family Rhinolophidae, it is now more generally classified as its own family. Nevertheless, it is most closely related to Rhinolophidae within the suborder Yinpterochiroptera.

Triaenops menamena is a bat in the genus Triaenops found on Madagascar, mainly in the drier regions. It was known as Triaenops rufus until 2009, when it was discovered that that name had been incorrectly applied to the species. Triaenops rufus is a synonym of Triaenops persicus, a Middle Eastern species closely related to T. menamena— the Malagasy species had previously been placed as a subspecies of T. persicus by some authors. Triaenops menamena is mostly found in forests, but also occurs in other habitats. It often roosts in large colonies and eats insects such as butterflies and moths. Because of its wide range, common occurrence, and tolerance of habitat degradation, it is not considered to be threatened.

Miniopterus griveaudi is a bat in the genus Miniopterus found on Grande Comore and Anjouan in the Comoros and in northern and western Madagascar. First described in 1959 from Grande Comore as a subspecies of the mainland African M. minor, it was later placed with the Malagasy M. manavi. However, morphological and molecular studies published in 2008 and 2009 indicated that M. manavi as then defined contained five distinct, unrelated species, and M. griveaudi was redefined as a species occurring on both Madagascar and the Comoros.
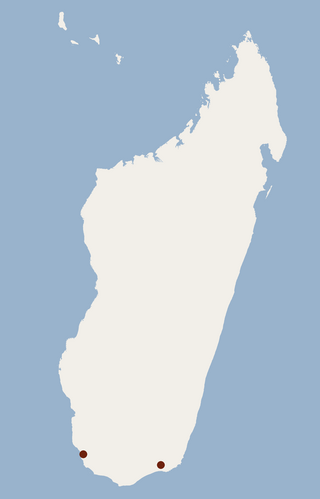
Griffith's long-fingered bat is a bat in the genus Miniopterus which occurs in southern Madagascar. M. griffithsi was previously a part of the largest family of bats, the Vespertilionidae, which consist of five subfamilies. The bat family Miniopteridae is widely distributed, ranging from the majority of sub-Saharan Africa to north Africa and Eurasia, as well as southern and southeastern Asia and Australia. Typical features of these bats include elongated third fingers, long narrow wings giving them a pointed shape when in flight, and a bent shape when folded, adding to the common name of bent-wing bats. M. griffithsi is similar to its sister species Miniopterus gleni, which lives north of the Onilahy River, while M. giffithsi lives south of it. Researchers first discovered that M. griffithsi was separate from M. gleni based on phylogeographic studies of the latter.

Paratriaenops is a genus in the bat family Hipposideridae. It is classified in the tribe Triaenopini, along with the closely related genus Triaenops and perhaps the poorly known Cloeotis. The species of Paratriaenops were placed in Triaenops until 2009. Paratriaenops currently contains the following species:

Paratriaenops pauliani is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is endemic to Aldabra Atoll of the western Seychelles, where it was found on Picard Island. It was formerly considered to be part of the species Triaenops furculus, known from Madagascar, and was initially assigned as a new species within the genus Triaenops. Later it as well as T. furculus were placed in the separate genus Paratriaenops. A related species, Paratriaenops auritus, also of Madagascar, was similarly reassigned.
Mops atsinanana is a free-tailed bat found on Madagascar. It was considered a subspecies of the little free-tailed bat until 2010. During the day, they are known to roost in man-made structures such as the roofs or attics of buildings.

The African trident bat is a species of bat found in Africa.
The Yemeni trident leaf-nosed bat is a species of bat found in the Middle East.

Rhinonycteridae is a family of bats, within to the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. The type species, the orange nose-leafed species group Rhinonicteris aurantia, is found across the north of Australia.
The Kirindy serotine is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It occurs in the central and south-central portions of western Madagascar. As of the most recent IUCN assessment in May 2016, it is of least concern.












