
The Lamiaceae or Labiatae are a family of flowering plants commonly known as the mint, deadnettle, or sage family. Many of the plants are aromatic in all parts and include widely used culinary herbs like basil, mint, rosemary, sage, savory, marjoram, oregano, hyssop, thyme, lavender, and perilla, as well as other medicinal herbs such as catnip, salvia, bee balm, wild dagga, and oriental motherwort. Some species are shrubs, trees, or, rarely, vines. Many members of the family are widely cultivated, not only for their aromatic qualities, but also their ease of cultivation, since they are readily propagated by stem cuttings. Besides those grown for their edible leaves, some are grown for decorative foliage. Others are grown for seed, such as Salvia hispanica (chia), or for their edible tubers, such as Plectranthus edulis, P. esculentus, P. rotundifolius, and Stachys affinis. Many are also grown ornamentally, notably coleus, Plectranthus, and many Salvia species and hybrids.

Salvia rosmarinus, commonly known as rosemary, is a shrub with fragrant, evergreen, needle-like leaves and white, pink, purple, or blue flowers. It is native to the Mediterranean region, as well as Portugal and Spain. Until 2017, it was known by the scientific name Rosmarinus officinalis, now a synonym.

Rosmarinus is a small taxonomic clade of woody, perennial herbs with fragrant evergreen needle-like leaves in the family Lamiaceae, native to the Mediterranean Basin.

Salvia officinalis, the common sage or sage, is a perennial, evergreen subshrub, with woody stems, grayish leaves, and blue to purplish flowers. It is a member of the mint family Lamiaceae and native to the Mediterranean region, though it has been naturalized in many places throughout the world. It has a long history of medicinal and culinary use, and in modern times it has been used as an ornamental garden plant. The common name "sage" is also used for closely related species and cultivars.

A subshrub or undershrub is either a small shrub or a perennial that is largely herbaceous but slightly woody at the base. The term is often interchangeable with "bush".
Rosemary is the common name for the herb Salvia rosmarinus.
In biological nomenclature, a nomen novum, new replacement name is a scientific name that is created specifically to replace another scientific name, but only when this other name cannot be used for technical, nomenclatural reasons. It does not apply when a name is changed for taxonomic reasons. It is frequently abbreviated, e.g.nomen nov., nom. nov..
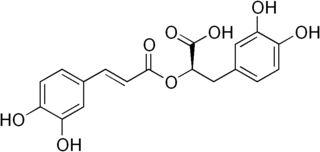
Rosmarinic acid, named after rosemary, is a polyphenol constituent of many culinary herbs, including rosemary, perilla, sage, mint, and basil.

The red-tailed squirrel is a species of tree squirrel distributed from southern Central America to northern South America.

Salvia divinorum is a species of plant in the sage genus Salvia, known for its transient psychoactive properties when its leaves, or extracts made from the leaves, are administered by smoking, chewing, or drinking. The leaves contain the potent compound salvinorin A and can induce a dissociative state and hallucinations.

Chrysolina americana, common name rosemary beetle, is a species of beetle belonging to the family Chrysomelidae.

Salvia is the largest genus of plants in the sage family Lamiaceae, with nearly 1,000 species of shrubs, herbaceous perennials, and annuals. Within the Lamiaceae, Salvia is part of the tribe Mentheae within the subfamily Nepetoideae. One of several genera, commonly referred to as sage, it includes two widely used herbs, Salvia officinalis and Salvia rosmarinus.

Taxodone is a naturally occurring diterpenoid found in Taxodium distichum, Rosmarinus officinalis (rosemary), several salvia species and other plants, along with its oxidized rearrangement product, taxodione. Taxodone and taxodione exhibit anticancer, antibacterial, antioxidant, antifungal, insecticide, and antifeedant activities.
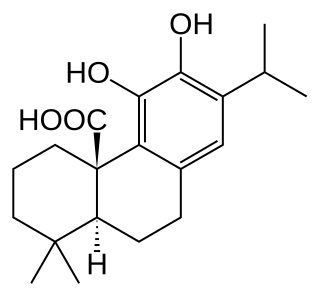
Carnosic acid is a natural benzenediol abietane diterpene found in rosemary and common sage. Dried leaves of rosemary and sage contain 1.5 to 2.5% carnosic acid.

Osmia latreillei is a species of mason bee belonging to the family Megachilidae subfamily Megachilinae.

Carnosol is a phenolic diterpene found in the herbs rosemary and Mountain desert sage.

Salvia jordanii is a species of Salvia from Spain, Morocco, Algeria, and Libya. It was formerly in a much smaller genus Rosmarinus, but was moved into Salvia based on DNA evidence.

The Monachil River is a river in the province of Granada, Spain. It is a tributary of the Genil. The river receives its name from the municipality Monachil, which the river passes through.















