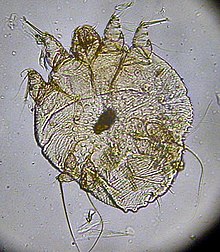
Scabies is a contagious skin infestation by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the skin. In a first-ever infection, the infected person usually develops symptoms within two to six weeks. During a second infection, symptoms may begin within 24 hours. These symptoms can be present across most of the body or just certain areas such as the wrists, between fingers, or along the waistline. The head may be affected, but this is typically only in young children. The itch is often worse at night. Scratching may cause skin breakdown and an additional bacterial infection in the skin.

Babesiosis or piroplasmosis is a malaria-like parasitic disease caused by infection with a eukaryotic parasite in the order Piroplasmida, typically a Babesia or Theileria, in the phylum Apicomplexa. Human babesiosis transmission via tick bite is most common in the Northeastern and Midwestern United States and parts of Europe, and sporadic throughout the rest of the world. It occurs in warm weather. People can get infected with Babesia parasites by the bite of an infected tick, by getting a blood transfusion from an infected donor of blood products, or by congenital transmission . Ticks transmit the human strain of babesiosis, so it often presents with other tick-borne illnesses such as Lyme disease. After trypanosomes, Babesia is thought to be the second-most common blood parasite of mammals. They can have major adverse effects on the health of domestic animals in areas without severe winters. In cattle the disease is known as Texas cattle fever or redwater.

Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question but by their way of life. This means it forms a synthesis of other disciplines, and draws on techniques from fields such as cell biology, bioinformatics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, genetics, evolution and ecology.
Veterinary parasitology is a branch of veterinary medicine that deals with the study of morphology, life-cycle, pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and control of eukaryotic invertebrates of the kingdom Animalia and the taxon Protozoa that depend upon other invertebrates and higher vertebrates for their propagation, nutrition, and metabolism without necessarily causing the death of their hosts. Modern parasitology focuses on responses of animal hosts to parasitic invasion. Parasites of domestic animals,, as well as wildlife animals are considered. Data obtained from parasitological research in animals helps in veterinary practice and improves animal breeding. The major goal of veterinary parasitology is to protect animals and improve their health, but because a number of animal parasites are transmitted to humans, veterinary parasitology is also important for public health.

Sarcoptes scabiei or the itch mite is a parasitic mite that burrows into skin and causes scabies. The mite is found in all parts of the world. Humans are not the only mammals that can become infected. Other mammals, such as wild and domesticated dogs and cats as well as ungulates, wild boars, bovids, wombats, koalas, and great apes are affected.
Acariasis is an infestation with mites.

The Acariformes, also known as the Actinotrichida, are the more diverse of the two superorders of mites. Over 32,000 described species are found in 351 families, with an estimated total of 440,000 to 929,000 species, including undescribed species.

The discipline of medical entomology, or public health entomology, and also veterinary entomology is focused upon insects and arthropods that impact human health. Veterinary entomology is included in this category, because many animal diseases can "jump species" and become a human health threat, for example, bovine encephalitis. Medical entomology also includes scientific research on the behavior, ecology, and epidemiology of arthropod disease vectors, and involves a tremendous outreach to the public, including local and state officials and other stake holders in the interest of public safety.

Theileria is a genus of parasites that belongs to the phylum Apicomplexa, and is closely related to Plasmodium. Two Theileria species, T. annulata and T. parva, are important cattle parasites. T. annulata causes tropical theileriosis and T. parva causes East Coast fever. Theileria species are transmitted by ticks. The genomes of T. orientalis Shintoku, Theileria equi WA, Theileria annulata Ankara and Theileria parva Muguga have been sequenced and published.
Human parasites include various protozoa and worms.
Suis, a Latin adjective referring to the pig, may refer to:

Mites that infest and parasitize domestic animals cause disease and loss of production. Mites are small invertebrates, most of which are free living but some are parasitic. Mites are similar to ticks and both comprise the order Acari in the phylum Arthropoda. Mites are highly varied and their classification is complex; a simple grouping is used in this introductory article. Vernacular terms to describe diseases caused by mites include scab, mange, and scabies. Mites and ticks have substantially different biology from, and are classed separately from, insects. Mites of domestic animals cause important types of skin disease, and some mites infest other organs. Diagnosis of mite infestations can be difficult because of the small size of most mites, but understanding how mites are adapted to feed within the structure of the skin is useful.
Flystrike in sheep is a myiasis condition, in which domestic sheep are infected by one of several species of flies which are external parasites of sheep. Sheep are particularly susceptible to flystrike because their thick wool, if sufficiently contaminated with urine and faecal material, can provide effective breeding ground for maggots even in the relative absence of wounds.

Mites are small crawling animals related to ticks and spiders. Most mites are free-living and harmless. Other mites are parasitic, and those that infest livestock animals cause many diseases that are widespread, reduce production and profit for farmers, and are expensive to control.
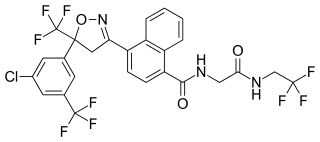
Afoxolaner (INN) is an insecticide and acaricide that belongs to the isoxazoline chemical compound group.

Notoedric mange, also referred to as Feline scabies, is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by an ectoparasitic and skin burrowing mite Notoedres cati. N. cati is primarily a parasite of felids, but it can also infest rodents, lagomorphs, and occasionally also dogs and foxes. This skin disease also has zoonotic potential. Infestation is also called acariasis, which refers to a rash that is caused by mites.
Imidacloprid/moxidectin, sold under the brand names Advantage Multi for Dogs and Advantage Multi for Cats among others, is a medicine for dogs and cats to treat heartworm, fleas, sarcoptic mange, intestinal parasites and ear mites.