
Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores, and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, Vandellia cirrhosa. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus Corydoras, are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, but others are crepuscular or diurnal.

The Cetopsidae are a small family of catfishes, commonly called the whale catfishes.

The stream catfishes comprise the family Akysidae of catfishes.
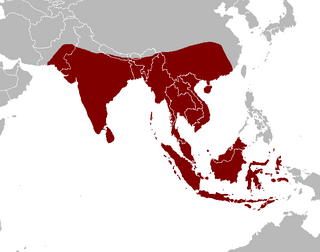
The shark catfishes form the family Pangasiidae. They are found in fresh and brackish waters across southern Asia, from Pakistan to Borneo. Among the 30-odd members of this family is the plant-eating, endangered Mekong giant catfish Pangasianodon gigas, one of the largest known freshwater fish. Several species are the basis of productive aquaculture industries in Vietnam's Mekong Delta.

The Ariidae or ariid catfish are a family of catfish that mainly live in marine waters with many freshwater and brackish water species. They are found worldwide in tropical to warm temperate zones. The family includes about 143 species.

The Bagridae are a family of catfish that are native to Africa (Bagrus) and Asia from Japan to Borneo. It includes about 245 species. These fish are commonly known as naked catfishes or bagrid catfishes.

Siluridae is the nominate family of catfishes in the order Siluriformes. About 105 living species of silurids are placed in 12 or 14 genera.

Horabagrus is a genus of catfish in the family Horabagridae endemic to rivers in the Western Ghats in Kerala and Karnataka, India. H. brachysoma is an important food fish and members of this genus can be found in the aquarium trade.

Erethistes is a genus of South Asian river catfishes.

Helogenes is a genus of whale catfish found in tropical South America.

Bagarius is an Asian genus of catfishes of the family Sisoridae. It includes five to six extant species and potentially one extinct fossil species, B. gigas.

Ailia is a genus of catfish in the family Ailiidae native to Asia. It is called "Kajoli" or "Bahpati" in Assamese and contributes to a major catch in Brahmaputra River. It is a surface to mid water fish that is found commonly near the shoals.

Entomocorus is a genus of catfishes of the family Auchenipteridae.
Siluranodon auritus is the only species in the genus Siluranodon of the catfish family Schilbeidae.

Synodontis guttatus is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Niger River basin of Nigeria. It was first described by German ichthyologist Albert Günther in 1865, from the Niger River. The species name guttatus is the Latin word for "spotted", referring to the spots appearing on the fins and body of the fish.

Pareutropius debauwi is a species that belong to the Order Actinopterygii, ray-finned fishes, and can be placed in the Schilbeidae family, Schilbid catfishes. This family includes 9 genera and 46 species. The common name for Pareutropius debauwi is the African glass catfish.

Ailia punctata, also known as the Jamuna ailia is a species of catfish in the family Ailiidae native to Bangladesh, India and Pakistan. The species is heavily fished and other threats include habitat loss, pollution and introduced species but the exact effects are unknown. This species grows to a length of 10.0 centimetres (3.9 in) TL.

Pseudeutropius is a genus of catfishes conventionally placed in the family Schilbeidae but recent work has suggested it be placed in the newer family Horabagridae, the genus is native to Asia.

Horabagridae is a proposed family of catfishes containing three genera, Horabagrus, Platytropius and Pseudeutropius. Horobagrus has been more usually assigned to the family Bagridae and sometimes it has been suggested it is closer to the Schilbeidae which is where the other two genera have been more conventionally placed.

Ailiidae is a family of catfishes native to Asia. These fishes usually have dorsal fins with a short base and a spine, but Ailia lack a dorsal fin altogether.

















