
Orycteropus is a genus of mammals in the family Orycteropodidae within Tubulidentata. The genus is known from Late Miocene to recent of Africa.

Rajiformes is one of the four orders in the superorder Batoidea, flattened cartilaginous fishes related to sharks. Rajiforms are distinguished by the presence of greatly enlarged pectoral fins, which reach as far forward as the sides of the head, with a generally flattened body. The undulatory pectoral fin motion diagnostic to this taxon is known as rajiform locomotion. The eyes and spiracles are located on the upper surface of the head and the gill slits are on the underside of the body. Most species give birth to live young, although some lay eggs enclosed in a horny capsule.
In biology, a homonym is a name for a taxon that is identical in spelling to another such name, that belongs to a different taxon.

Sclerorhynchus is an extinct genus of ganopristid sclerorhynchoid that lived during the Late Cretaceous. The genus Ganopristis is considered a junior synonym of Sclerorhynchus. It was a widespread genus, with fossils found in the Middle East, North Africa, Europe, and North America. While it had a long rostrum with large denticles similar to sawfishes and sawsharks, its closest living relatives are actually skates. Complete specimens of S. atavus show that its fin arrangement was similar to skates, with the pectoral and pelvic fins touching, both dorsal fins located behind the pelvic fins, and a reduced caudal fin.

Schizorhiza is an extinct genus of schizorhizid sclerorhynchoid that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It contains one valid species, Schizorhiza stromeri. It lived from the Campanian to Maastrichtian, and its fossils have been found in Africa, the Middle East, North America, and South America.

Ischyrhiza is an extinct genus of sclerorhynchoid ray from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Maastrichtian).

The Kem Kem Group is a geological group in the Kem Kem region of eastern Morocco, whose strata date back to the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous. Its strata are subdivided into two geological formations, with the lower Ifezouane Formation and the upper Aoufous Formation used for the strata on the eastern side of the Atlas Mountains (Tinghir), with the Gara Sbaa Formation and Douira Formation used in the southern Tafilalt region. It is exposed on an escarpment along the Algeria–Morocco border.

Saurocephalus is an extinct genus of ray-finned fishes within the family Saurodontidae. The genus was first described in 1824 and contains six or seven species, including the type species S. lanciformis. Saurocephalus first appeared during the early Valanginian and continued on to the Maastrichtian, where it nearly went extinct. However, the recent discovery of S. lanciformis remains from the earliest Paleocene indicates that it just barely survived into the Cenozoic. This would make it the last surviving ichthyodectiform.

Wadi Harrana is a seasonal stream (wadi) in the eastern Jordanian Badia, about sixty kilometers southeast of the city of Amman. It runs eastwards from the edge of the Jordanian Highlands to the Azraq oasis.

Gigantatypus is an extinct late Maastrichtian sea turtle that lived in the southern regions of the Tethys Ocean about 100–120 kilometres (62–75 mi) off the north eastern margins of Cretaceous Africa immediately before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction events . Fossil remains of Gigantatypus are so far only represented in sediments from the Muwaqqar Chalk-Marl Formation of Jordan. Estimated at over 3.5 metres (11 ft) in length, members of this genus reached remarkably large proportions equivalent to that of or possibly even exceeding Archelon Wieland, 1896, considered as the largest marine turtles to ever roam the oceans of the world. Although Gigantatypus apparently did not survive the K/T boundary, which also was the fate of other gigantic marine turtles such as protostegids, other genera of Cheloniidae, though significantly smaller, survived the mass extinction and continued on until the present day.
Harranahynchus is an extinct genus of schizorhizid sawskate that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It contains one valid species, Harranahynchus minutadens. It is known from relatively complete cranial and body fossils found in the Muwaqqar Chalk Marl Formation of Jordan, dating back to the late Maastrichtian. Its rostral denticles are extremely small and are arranged in batteries like its close relative Schizorhiza. It has an estimated length of around 2 m (6.6 ft).

Nyctosauridae is a family of specialized soaring pterosaurs of the late Cretaceous Period of North America, Africa, and possibly other continents including South America. It was named in 1889 by Henry Alleyne Nicholson and Richard Lydekker.

Cryodraco is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. They are found in the Southern Ocean. While C. antarcticus has minor commercial importance, C. atkinsoni and C. pappenheimi are of no interest to commercial fisheries.

Sclerorhynchoidei is an extinct suborder of rajiform rays that had long rostra with large denticles similar to sawfishes and sawsharks. This feature was convergently evolved, recently proposed as 'pristification', and their closest living relatives are actually skates. While they are often called "sawfishes", sawskates is a more accurate common name proposed in 2021 for sclerorhynchoids, which has been subsequently used by other researchers.

The Globidensini or Globidentatini are a tribe of mosasaurine mosasaurs, a diverse group of Late Cretaceous marine squamates. Members of the tribe, known as "globidensins" or "globidensine mosasaurs", have been recovered from North America, Europe, Africa and Asia. The tribe contains the genera Globidens, Carinodens, Igdamanosaurus, Harranasaurus and Xenodens. Features of the maxilla and digits make the placement of Carinodens and Xenodens in the tribe uncertain; some researchers have suggested that they may be more appropriately placed in the Mosasaurini.

Travunioidea is a superfamily of armoured harvestmen in the order Opiliones. There are 4 families and around 75 described species in Travunioidea.

Cryptomastridae is a family of armoured harvestmen in the order Opiliones. There are two genera and four described species in Cryptomastridae, found in Oregon and Idaho.
Ganopristidae is an extinct family of cartilaginous fish from the Cretaceous belonging to the suborder Sclerorhynchoidei. While the name Sclerorhynchidae is often used for this family, it is a junior synonym of Ganopristidae. This family contains the genera Libanopristis, Micropristis, and Sclerorhynchus. The type genus Ganopristis is considered to be a junior synonym of Sclerorhynchus.
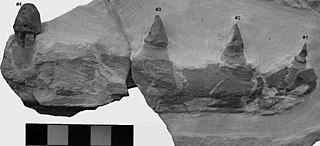
Harranasaurus is an extinct genus of globidensin mosasaur from Jordan. The genus contains one known species, H. khuludae from the Muwaqqar Chalk Marl Formation of Jordan.















