
The Malpighiales comprise one of the largest orders of flowering plants, containing about 36 families and more than 16,000 species, about 7.8% of the eudicots. The order is very diverse, containing plants as different as the willow, violet, poinsettia, manchineel, rafflesia and coca plant, and are hard to recognize except with molecular phylogenetic evidence. It is not part of any of the classification systems based only on plant morphology. Molecular clock calculations estimate the origin of stem group Malpighiales at around 100 million years ago (Mya) and the origin of crown group Malpighiales at about 90 Mya.

The Salicaceae are the willow family of flowering plants. The traditional family included the willows, poplars, aspens, and cottonwoods. Genetic studies summarized by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) have greatly expanded the circumscription of the family to contain 56 genera and about 1220 species, including the tropical Scyphostegiaceae and many of the former Flacourtiaceae.

The Flacourtiaceae is a defunct family of flowering plants whose former members have been scattered to various families, mostly to the Achariaceae and Salicaceae. It was so vaguely defined that hardly anything seemed out of place there and it became a dumping ground for odd and anomalous genera, gradually making the family even more heterogeneous. In 1975, Hermann Sleumer noted that "Flacourtiaceae as a family is a fiction; only the tribes are homogeneous."
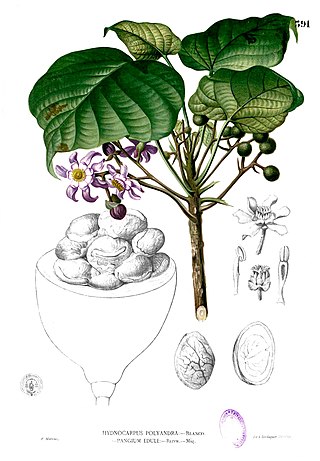
Achariaceae is a family of flowering plants consisting of 31 genera and about 155 species of tropical herbs, shrubs, and trees. The APG IV system has greatly expanded the scope of the family by including many genera previously classified in Flacourtiaceae. Molecular data strongly support the inclusion of this family in the order Malpighiales.

Samydaceae is a family of tropical and subtropical woody plants, its best known genus being Casearia. It has always been of uncertain placement, in the past usually being submerged in the family Flacourtiaceae.
Dipentodon is a genus of flowering plants in the family Dipentodontaceae. Its only species, Dipentodon sinicus, is a small, deciduous tree native to southern China, northern Myanmar, and northern India. It has been little studied and until recently its affinities remained obscure.

Macrohasseltia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It consists of one species of tree: Macrohasseltia macroterantha, which is native to Central America. Formerly placed in the heterogeneous family Flacourtiaceae, Macrohasseltia is now classified in Salicaceae, along with close relatives Bennettiodendron, Carrierea, Idesia, Itoa, Olmediella, Poliothyrsis, and even the willows (Salix) and cottonwoods (Populus) themselves.

Olmediella is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It consists of one species of trees: Olmediella betschleriana, which is native to Central America. Formerly placed in the heterogeneous family Flacourtiaceae, Olmediella is now classified in Salicaceae, along with close relatives Bennettiodendron, Carrierea, Idesia, Itoa, Macrohasseltia, Poliothyrsis, and even the willows (Salix) and cottonwoods (Populus) themselves.
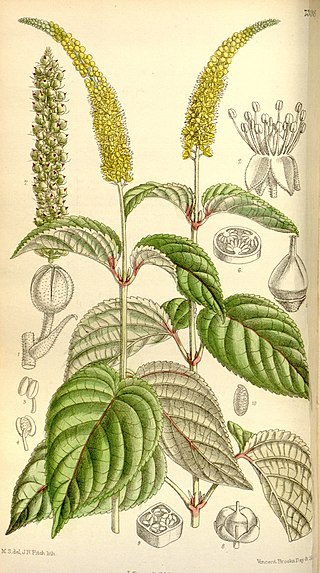
Aphaerema was formerly a genus of flowering plants in the Flacourtiaceae, consisting of one species of small shrubs, Aphaerema spicata, which is native to Brazil and Argentina. Later studies indicated that Aphaerema should be classified in the willow family, Salicaceae, and combined with the genus Abatia. Because the name Abatia spicata was already used, the species was given the new name Abatia angeliana, in honor of Brazilian botanist João Angely. Aphaerema is one of the few groups of Salicaceae with opposite leaves.
Hasseltiopsis is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It consists of one species of trees: Hasseltiopsis dioica, which is native to Central America. Formerly placed in the heterogeneous family Flacourtiaceae, Hasseltiopsis is now classified in Salicaceae, along with close relatives Prockia, Pineda, Neosprucea, and Banara.
Ahernia is a genus of a single species, Ahernia glandulosa, a tree in the family Achariaceae, native to Hainan and Luzon island of the Philippines. Previously it was treated in the family Flacourtiaceae before being placed in Achariaceae. Ahernia is closely related to the American genera Hasseltia, Macrothumia, and Pleuranthodendron, but differs in its axillary racemes and more numerous (10–15) petals. Ahernia glandulosa is found in low elevation primary forests and is known in the Tagalog language as butun or sanglai. It grows 8–15 m (26–49 ft) tall.
Irenodendron is a genus of three species of shrubs and trees in the willow family Salicaceae native to northern South America. These species were previously treated as a section of the genus Laetia in the family Flacourtiaceae, but the genus Laetia and its relatives were moved to the Salicaceae based on analyses of DNA data. Irenodendron was later hypothesized to be more closely related to the genera Ryania, Trichostephanus, and Piparea due to the presence of an apically divided style, and wood with dark heartwood and large rays; it differs from those genera in having cup-shaped bracts under the flowers and in lacking staminodes.
Dianyuea turbinata is a species of shrub endemic to the Tongbiguan Nature Preserve in Yunnan province of China. Originally described in the genus Flacourtia based on limited material, this unusual species is now recognized as the sole member of the genus Dianyuea, and is the only other member of subfamily Scyphostegioideae of Salicaceae. In addition to phylogenetic analyses of DNA data, the species's basal placentation, connate stamen filaments, and seeds with arilloid appendages indicate that this species is related to Scyphostegia, a monotypic genus which is now placed in a broadly circumscribed Salicaceae.

Osmelia is a genus of flowering plants in the willow family, Salicaceae. Osmelia includes four species of trees native to Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia. Osmelia is closely related to the monotypic Pseudosmelia of Morotai and Halmahera of the Indonesian Maluku Islands and to the monotypic Ophiobotrys from west and west-central tropical Africa.
Zuelania guidonia is a species of shrub or tree native to the West Indies, Central America, and northern South America and is the only member of the genus Zuelania. Formerly classified in the Flacourtiaceae, phylogenetic analyses based on DNA data indicate that this species, along with its close relatives in Casearia, Samyda, Hecatostemon, and Laetia, are better placed in a broadly circumscribed Salicaceae. Zuelania differs from its close relatives in having a large, subsessile stigma.
Ophiobotrys zenkeri is a species of flowering plant in the family Salicaceae. It is a tree native to tropical Africa from Ivory Coast to Gabon and is the only member of the genus Ophiobotrys. Formerly classified in the Flacourtiaceae, phylogenetic analyses based on DNA data indicate that this species, along with its close relatives in the Asian genera Osmelia and Pseudosmelia, are better placed in a broadly circumscribed Salicaceae. Ophiobotrys differs from its close relatives in having 5 sepals, 5(-6) stamens, one divided style, and terminal inflorescences.
Pseudosmelia moluccana is a species of shrub or small tree native to Morotai and Halmahera of the Indonesian Maluku Islands and is the only member of the genus Pseudosmelia. Formerly classified in the Flacourtiaceae, phylogenetic analyses based on DNA data indicate that this species, along with its close relatives in the Asian genus Osmelia and the African genus Ophiobotrys, are better placed in a broadly circumscribed Salicaceae. Pseudosmelia differs from its close relatives in having thick, truncate staminodes and large, spindle-shaped fruits with numerous seeds.

Macrothumia is a genus in the willow family Salicaceae with a single species Macrothumia kuhlmannii. It is a tree native to the states of Bahia, Espírito Santo, and Minas Gerais in Brazil. Formerly classified in the genus Banara in the family Flacourtiaceae, phylogenetic analyses based on DNA data indicate that this species, along with its close relatives in Ahernia, Hasseltia, and Pleuranthodendron are better placed in a broadly circumscribed Salicaceae. Macrothumia differs from its close relatives in having a congested fascicle- or umbel-like inflorescence and a large fruit. The genus name is derived from the Greek word μακροθυμία, which means long-suffering and enduring patience.
Tetrathylacium is a genus of two species of shrubs and small trees in the family Salicaceae native to the southern Central America and northern South America. Previously it was treated in the family Flacourtiaceae but was moved along with its close relatives to the Salicaceae based on analyses of DNA data. Tetrathylacium is rather unique in the Samydaceae in having tightly arranged panicles of spikes, four sepals and stamens, and non-arillate seeds. The stems are often inhabited by ants, and T. macrophyllum is suspected to have locust pollination.
Hecatostemon completus is a species of shrub or tree native to northeastern South America and is the only member of the genus Hecatostemon.









