
The Cryptobranchidae are a family of fully aquatic salamanders commonly known as the giant salamanders. They include the largest living amphibians. The family is native to China, Japan, and the eastern United States. They constitute one of two living families within the Cryptobranchoidea, one of two main divisions of living salamanders, the other being the Asiatic salamanders belonging to the family Hynobiidae.

Karaurus is an extinct genus of stem-group salamander (Caudata) from the Middle to Late Jurassic (Callovian–Kimmeridgian) Karabastau Formation of Kazakhstan. It is one of the oldest salamanders known.

Trigonostylops is an extinct genus of South American meridiungulatan ungulate, from the Late Paleocene to Late Eocene of South America and Antarctica. It is the only member of the family Trigonostylopidae.

The Albanerpetontidae are an extinct family of small amphibians, native to the Northern Hemisphere during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic. The only members of the order Allocaudata, they are thought to be allied with living amphibians belonging to Lissamphibia. Despite a superficially salamander-like bodyform, their anatomy is strongly divergent from modern amphibians in numerous aspects. The fossil record of albanerpetontids spans over 160 million years from the Middle Jurassic to the beginning of the Pleistocene, about 2.13–2 million years ago.

Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2009.
Eoscapherpeton is an extinct genus of giant salamander, known from the Late Cretaceous of Central Asia. Fossils have been found in the Cenomanian aged Khodzhakul Formation and Dzharakuduk Formation, Turonian aged Bissekty Formation and the Coniacian-Santonian aged Aitym Formation of Uzbekistan, the Santonian aged Yalovach Formation of Tajikistan, and the Santonian-lower Campanian aged Bostobe Formation and Campanian aged Darbasa Formation of Kazakhstan.
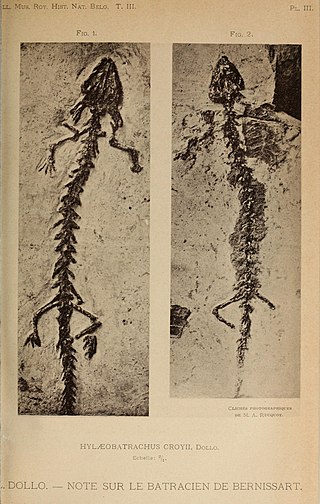
Hylaeobatrachus is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamander, known from the Early Cretaceous of Europe. The type species H. croyii is known from the Sainte-Barbe Clays Formation at the Iguanodon locality of Belgium, and was described by Louis Dollo. An unnamed Hylaeobatrachus-like taxon has also been reported from Las Hoyas, Spain. Both localities are of Barremian age. Hylaeobatrachus belongs to the crown group of modern salamanders, though its exact relationship with modern salamander groups is uncertain. It was neotenic, llike some modern salamanders.
Horezmia is an extinct Mesozoic genus of prehistoric salamanders. The fossils have been found in Russia. It is comparable to modern advanced salamanders, though its phylogenetic placement within Salamandroidea is uncertain.
Kokartus is an extinct genus of prehistoric stem-group salamander (Caudata) from the Middle Jurassic Balabansai Formation of Kyrgyzstan.

Marmorerpeton is an extinct genus of prehistoric stem group-salamanders that lived in Britain during the Bathonian stage of the Middle Jurassic. They are among the oldest known salamanders. Two species were named when the genus was first described by Susan E. Evans et al. in 1988, M. freemani, and M. kermacki, from fragmentary remains found via screenwashing in the Forest Marble Formation of England. Due to the size of their osteocytic lacunae suggesting a large genome size and some morphological characters, like the presence of calcified cartilage in the medulla of its humerus, it was assumed that Marmorerpeton was neotenic. New more complete remains of a new species M. wakei were described in 2022 from the Kilmaluag Formation of the Isle of Skye, Scotland. These conclusively demonstrated that Marmorerpeton was neotenic, and was a member of the family Karauridae, with the other two members of the family, Karaurus and Kokartus being known from the Middle-Late Jurassic of Central Asia. The teeth appear to have been weakly pedicellate.
Valdotriton is a genus of extinct prehistoric salamanders. Its only known species is Valdotriton gracilis. V. gracilis lived during the Late Barremian in what is now Spain. It was found in the Las Hoyas locality. It represents one of the oldest known members of Salamandroidea.
Piceoerpeton is an extinct genus of prehistoric amphibian, containing species known from the latest Cretaceous, Paleocene and Eocene of North America. It is one of the largest known salamanders, and would have approached the cryptobranchid Andrias in size. However, Piceoerpeton is unrelated to the Cryptobranchidae; instead it appears to be a member of the extinct family Scapherpetontidae.

Kentisuchus is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodylian, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae. Fossils have been found from England and France that date back to the early Eocene. The genus has also been recorded from Ukraine, but it unclear whether specimens from Ukraine are referable to Kentisuchus.
The Itat Formation is a geologic formation in western Siberia. It was deposited in the Bajocian to Bathonian ages of the Middle Jurassic. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, including the proceratosaurid Kileskus, as well as fish, amphibians, mammals and many other vertebrates. The formation is noted for bearing significant coal reserves, with large open pit coal mines extracting lignite from the unit currently in operation.

Khurendukhosaurus is a genus of choristodere, a type of amphibious reptile. It is known from Lower Cretaceous rocks of Mongolia and Russia. Two species have been named. The type species, K. orlovi, was named in 1984 by Sigogneau–Russell and Efimov for the fragmentary postcranial skeleton PIN 3386/3. This specimen was discovered in the Albian-age Lower Cretaceous Khuren Dukh Formation Formation at Hüren Dukh, central Mongolia. The lake deposits at this site also contain fossils of the choristoderes Irenosaurus and Tchoiria. Other postcranial bones of K. orlovi have been found at this site as well.
Nesovtriton is an extinct genus of cryptobranchoid salamander known from the Late Cretaceous of Bissekty Formation, in Uzbekistan. It was first named by Pavel P. Skutschas in 2009 and the type species is Nesovtriton mynbulakensis.

The Karauridae are a family of stem-group salamanders (Caudata) that are known from the Middle Jurassic to Late Jurassic in Central Asia and Western Europe. The family includes three members: Karaurus from the Middle-Late Jurassic Karabastau Formation of Kazakhstan, Kokartus from the Middle Jurassic Balabansai Formation of Kyrgyzstan, and Marmorerpeton from the Middle Jurassic Forest Marble Formation of England and Kilmaluag Formation of Scotland. The members are some of the oldest known salamanders. The family is united by several morphological characters, including sculptured skull roof bones. Like some modern salamanders, karaurids were neotenic. Members of the family likely fed via suction feeding on small fish and invertebrates.
Batrachosauroididae is an extinct family of prehistoric salamanders with holarctic distribution. They were paedomorphic and presumably aquatic. They are possibly the sister taxon of Proteidae, an extant family of aquatic salamanders. They are definitively known from the Late Cretaceous to Miocene of North America and Europe. Remains from the earliest Cretaceous (Berriasian) Lulworth Formation of England have tenatively been attributed to this family.

The Batylykh Formation is a geological formation in Yakutia, Russia. It is of an uncertain Early Cretaceous age, probably dating between the Berriasian and the Barremian. It is the oldest unit of the 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) thick Sangar Series within the Vilyuy syneclise. The mudstones, sandstones and shales of the formation were deposited in a fluvial to lacustrine environment.
This list of fossil amphibians described in 2018 is a list of new taxa of fossil amphibians that were described during the year 2018, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to amphibian paleontology that occurred in 2018.











