Related Research Articles

The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about 5.5 metres long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter.

Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the small bowel or large bowel may be affected. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, bloating and not passing gas. Mechanical obstruction is the cause of about 5 to 15% of cases of severe abdominal pain of sudden onset requiring admission to hospital.

An upper gastrointestinal series, also called a barium swallow, barium study, or barium meal, is a series of radiographs used to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities. A contrast medium, usually a radiocontrast agent such as barium sulfate mixed with water, is ingested or instilled into the gastrointestinal tract, and X-rays are used to create radiographs of the regions of interest. The barium enhances the visibility of the relevant parts of the gastrointestinal tract by coating the inside wall of the tract and appearing white on the film. This in combination with other plain radiographs allows for the imaging of parts of the upper gastrointestinal tract such as the pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, and small intestine such that the inside wall lining, size, shape, contour, and patency are visible to the examiner. With fluoroscopy, it is also possible to visualize the functional movement of examined organs such as swallowing, peristalsis, or sphincter closure. Depending on the organs to be examined, barium radiographs can be classified into "barium swallow", "barium meal", "barium follow-through", and "enteroclysis". To further enhance the quality of images, air or gas is sometimes introduced into the gastrointestinal tract in addition to barium, and this procedure is called double-contrast imaging. In this case the gas is referred to as the negative contrast medium. Traditionally the images produced with barium contrast are made with plain-film radiography, but computed tomography is also used in combination with barium contrast, in which case the procedure is called "CT enterography".

Ileus is a disruption of the normal propulsive ability of the intestine. It can be caused by lack of peristalsis or by mechanical obstruction. The word 'ileus' derives from Ancient Greek εἰλεός (eileós) 'intestinal obstruction'. The term 'subileus' refers to a partial obstruction.
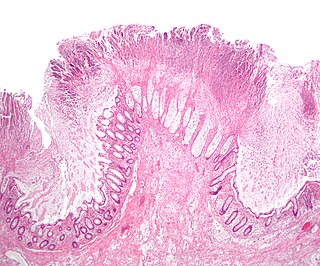
Toxic megacolon is an acute form of colonic distension. It is characterized by a very dilated colon (megacolon), accompanied by abdominal distension (bloating), and sometimes fever, abdominal pain, or shock.
Colic in horses is defined as abdominal pain, but it is a clinical symptom rather than a diagnosis. The term colic can encompass all forms of gastrointestinal conditions which cause pain as well as other causes of abdominal pain not involving the gastrointestinal tract. What makes it tricky is that different causes can manifest with similar signs of distress in the animal. Recognizing and understanding these signs is pivotal, as timely action can spell the difference between a brief moment of discomfort and a life-threatening situation. The most common forms of colic are gastrointestinal in nature and are most often related to colonic disturbance. There are a variety of different causes of colic, some of which can prove fatal without surgical intervention. Colic surgery is usually an expensive procedure as it is major abdominal surgery, often with intensive aftercare. Among domesticated horses, colic is the leading cause of premature death. The incidence of colic in the general horse population has been estimated between 4 and 10 percent over the course of the average lifespan. Clinical signs of colic generally require treatment by a veterinarian. The conditions that cause colic can become life-threatening in a short period of time.

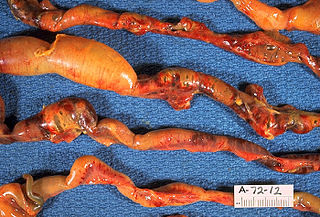
A volvulus is when a loop of intestine twists around itself and the mesentery that supports it, resulting in a bowel obstruction. Symptoms include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, vomiting, constipation, and bloody stool. Onset of symptoms may be rapid or more gradual. The mesentery may become so tightly twisted that blood flow to part of the intestine is cut off, resulting in ischemic bowel. In this situation there may be fever or significant pain when the abdomen is touched.
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is an intestinal disease that affects premature or very low birth weight infants. Symptoms may include poor feeding, bloating, decreased activity, blood in the stool, vomiting of bile, multi-organ failure, and potentially death.
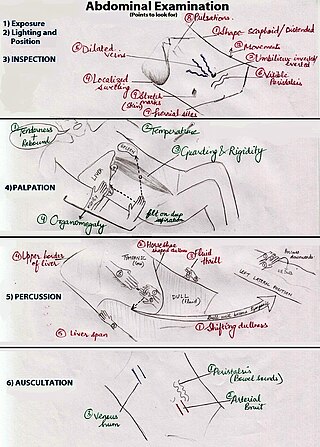
An abdominal examination is a portion of the physical examination which a physician or nurse uses to clinically observe the abdomen of a patient for signs of disease. The abdominal examination is conventionally split into four different stages: first, inspection of the patient and the visible characteristics of their abdomen. Auscultation (listening) of the abdomen with a stethoscope. Palpation of the patient's abdomen. Finally, percussion (tapping) of the patient's abdomen and abdominal organs. Depending on the need to test for specific diseases such as ascites, special tests may be performed as a part of the physical examination. An abdominal examination may be performed because the physician suspects a disease of the organs inside the abdominal cavity (including the liver, spleen, large or small intestines), or simply as a part of a complete physical examination for other conditions. In a complete physical examination, the abdominal exam classically follows the respiratory examination and cardiovascular examination.

Lymphangiectasia, also known as "lymphangiectasis", is a pathologic dilation of lymph vessels. When it occurs in the intestines it is known as intestinal lymphangiectasia, colloquially recognized as Waldmann's disease in cases where there is no secondary cause. The primary defect lies in the inability of the lymphatic system to adequately drain lymph, resulting in its subsequent accumulation and leakage into the intestinal lumen. This condition, first described by Waldmann in 1961, is typically diagnosed in infancy or early childhood. However, it can also manifest in adults, exhibiting a broad spectrum of clinical symptoms.

Ogilvie syndrome, or acute colonic pseudo-obstruction, is the acute dilatation of the colon in the absence of any mechanical obstruction in severely ill patients.

Ischemic colitis is a medical condition in which inflammation and injury of the large intestine result from inadequate blood supply (ischemia). Although uncommon in the general population, ischemic colitis occurs with greater frequency in the elderly, and is the most common form of bowel ischemia. Causes of the reduced blood flow can include changes in the systemic circulation or local factors such as constriction of blood vessels or a blood clot. In most cases, no specific cause can be identified.

Distal intestinal obstruction syndrome (DIOS) involves obstruction of the distal part of the small intestines by thickened intestinal content and occurs in about 20% of mainly adult individuals with cystic fibrosis. DIOS was previously known as meconium ileus equivalent, a name which highlights its similarity to the intestinal obstruction seen in newborn infants with cystic fibrosis. DIOS tends to occur in older individuals with pancreatic insufficiency. Individuals with DIOS may be predisposed to bowel obstruction, though it is a separate entity than true constipation.
Pneumatosis intestinalis is pneumatosis of an intestine, that is, gas cysts in the bowel wall. As a radiological sign it is highly suggestive for necrotizing enterocolitis. This is in contrast to gas in the intestinal lumen. In newborns, pneumatosis intestinalis is considered diagnostic for necrotizing enterocolitis, and the gas is produced by bacteria in the bowel wall. The pathogenesis of pneumatosis intestinalis is poorly understood and is likely multifactorial. PI itself is not a disease, but rather a clinical sign. In some cases, PI is an incidental finding, whereas in others, it portends a life-threatening intra-abdominal condition.
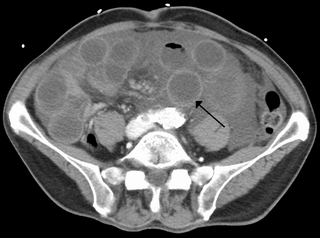
Intestinal ischemia is a medical condition in which injury to the large or small intestine occurs due to not enough blood supply. It can come on suddenly, known as acute intestinal ischemia, or gradually, known as chronic intestinal ischemia. The acute form of the disease often presents with sudden severe abdominal pain and is associated with a high risk of death. The chronic form typically presents more gradually with abdominal pain after eating, unintentional weight loss, vomiting, and fear of eating.
Neonatal bowel obstruction (NBO) or neonatal intestinal obstruction is the most common surgical emergency in the neonatal period. It may occur due to a variety of conditions and has an excellent outcome based on timely diagnosis and appropriate intervention.
The colon cut-off sign is a radiographic finding seen on abdominal radiographs and computed tomography scans. It is characterized by a marked dilatation of the transverse colon, with an abrupt transition to collapsed distal colon, particularly the splenic flexure. This sign is indicative of underlying pathology, most commonly acute pancreatitis.
The kidney bean sign is a radiologic sign observed on abdominal radiographs that indicates the presence of a sigmoid volvulus, a form of bowel obstruction. It is seen as an area of hyperlucency resembling a coffee bean. The opposed walls of adjacent bowel loops form the central cleft while the two sides of the bean represent gas‐filled segments of dilated bowel that form an inverted U‐shape. Air-fluid levels may also be seen in the segments of dilated bowel.
The small bowel feces sign is a radiological finding observed in radiological imaging studies, particularly in cases of small bowel obstruction. It is characterized by the presence of particulate matter resembling fecal material within the lumen of dilated small bowel loops. This sign is most commonly identified on computed tomography (CT) scans and, less frequently, on abdominal radiographs.
The stepladder sign is a radiological finding observed in the context of small bowel obstruction on abdominal X-rays or computed tomography scans. It refers to the appearance of multiple, dilated small bowel loops arranged in a step-like configuration, typically visible in upright or lateral decubitus imaging positions. This sign is indicative of bowel obstruction and is used to identify and localize the site of obstruction, aiding in diagnosis and management.
References
- ↑ Brant, William E.; Helms, Clyde A. (2007). Fundamentals of Diagnostic Radiology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 742. ISBN 9780781761352 . Retrieved 18 September 2019.
- ↑ Levitin, Joseph (1946). "Scout Film of the Abdomen". Radiology. 47 (1). Radiological Society of North America (RSNA): 10–29. doi:10.1148/47.1.10. ISSN 0033-8419. PMID 20992153.