Related Research Articles
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.
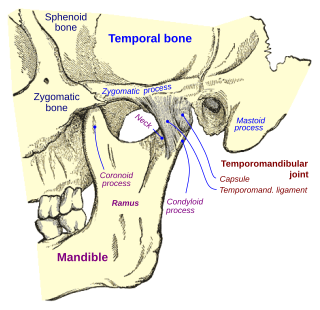
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the condylar process of mandible below; it is from these bones that its name is derived. The joints are unique in their bilateral function, being connected via the mandible.

A hamstring is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from medial to lateral, the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.
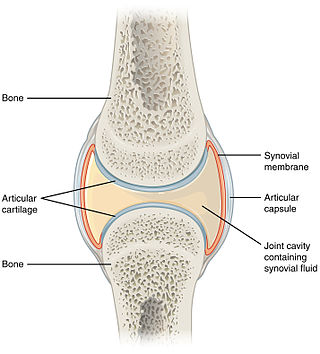
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid. The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer of fibrous membrane, which keeps the bones together structurally, and an inner layer, the synovial membrane, which seals in the synovial fluid.
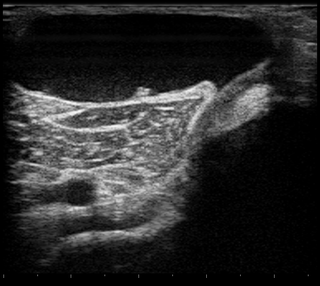
A Baker's cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a type of fluid collection behind the knee. Often there are no symptoms. If symptoms do occur these may include swelling and pain behind the knee, or knee stiffness. If the cyst breaks open, pain may significantly increase with swelling of the calf. Rarely complications such as deep vein thrombosis, peripheral neuropathy, ischemia, or compartment syndrome may occur.

The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.

A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.

The popliteus muscle in the leg is used for unlocking the knees when walking, by laterally rotating the femur on the tibia during the closed chain portion of the gait cycle. In open chain movements, the popliteus muscle medially rotates the tibia on the femur. It is also used when sitting down and standing up. It is the only muscle in the posterior (back) compartment of the lower leg that acts just on the knee and not on the ankle. The gastrocnemius muscle acts on both joints.

The plantaris is one of the superficial muscles of the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, one of the fascial compartments of the leg.

The popliteal fossa is a shallow depression located at the back of the knee joint. The bones of the popliteal fossa are the femur and the tibia. Like other flexion surfaces of large joints, it is an area where blood vessels and nerves pass relatively superficially, and with an increased number of lymph nodes.
The knee examination, in medicine and physiotherapy, is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with knee pain or a history that suggests a pathology of the knee joint.
The middle genicular artery is a small branch of the popliteal artery. It supplies parts of the knee joint.

The oblique popliteal ligament is a broad, flat, fibrous ligament on the posterior knee. It is an extension of the tendon of the semimembranosus muscle. It attaches onto the intercondylar fossa and lateral condyle of the femur. It reinforces the posterior central portion of the knee joint capsule.

In human anatomy, the adductor hiatus also known as hiatus magnus is a hiatus (gap) between the adductor magnus muscle and the femur that allows the passage of the femoral vessels from the anterior thigh to the posterior thigh and then the popliteal fossa. It is the termination of the adductor canal and lies about 8–13.5 cm (3.1–5.3 in) superior to the adductor tubercle.

The posterior compartment of the thigh is one of the fascial compartments that contains the knee flexors and hip extensors known as the hamstring muscles, as well as vascular and nervous elements, particularly the sciatic nerve.

The fat pad sign, also known as the sail sign, is a potential finding on elbow radiography which suggests a fracture of one or more bones at the elbow. It may indicate an occult fracture that is not directly visible. Its name derives from the fact that it has the shape of a spinnaker (sail). It is caused by displacement of the fat pad around the elbow joint. Both anterior and posterior fat pad signs exist, and both can be found on the same X-ray.

Knee pain is pain in or around the knee.

A knee dislocation is an injury in which there is disruption of the knee joint between the tibia and the femur. Symptoms include pain and instability of the knee. Complications may include injury to an artery, most commonly the popliteal artery behind the knee, or compartment syndrome.
The double posterior cruciate ligament sign is a radiological finding seen on magnetic resonance imaging of the knee, specifically in the context of a bucket-handle tear of the medial meniscus. It refers to the appearance of a duplicated posterior cruciate ligament, where the displaced fragment of the torn medial meniscus lies parallel and inferior to the PCL, mimicking a second ligament. The double PCL sign has high specificity for meniscal tears when noted on MRI.
References
- ↑ Hall F (1978). "The fabella sign and radiologic assessment of knee joint effusion". Radiology. 129 (2): 541–2. doi:10.1148/129.2.541a. PMID 704877.
- ↑ Friedman A, Naidich T (1978). "The fabella sign: fabella displacement in synovial effusion and popliteal fossa masses. Normal and abnormal fabello-femoral and fabello-tibial distances". Radiology. 127 (1): 113–21. doi:10.1148/127.1.113. PMID 635171.