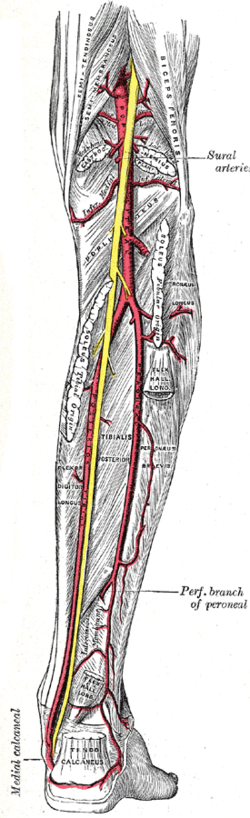
| Popliteal fossa | |
|---|---|
 Popliteal fossa of the right leg. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fossa poplitea |
| TA98 | A01.2.08.013 |
| TA2 | 324 |
| FMA | 22525 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The popliteal fossa (also referred to as hough or kneepit in analogy to the cubital fossa) is a shallow depression located at the back of the knee joint. The bones of the popliteal fossa are the femur and the tibia. Like other flexion surfaces of large joints (groin, armpit, cubital fossa and essentially the anterior part of the neck), it is an area where blood vessels and nerves pass relatively superficially, and with an increased number of lymph nodes.