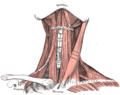
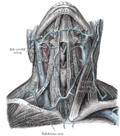
| Submental triangle | |
|---|---|
 Submental triangle | |
 Side of neck, showing chief surface markings (nerves are yellow, arteries are red) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | trigonum submentale |
| TA98 | A01.2.02.006 |
| TA2 | 233 |
| FMA | 61604 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The submental triangle (or suprahyoid triangle) is a division of the anterior triangle of the neck.