
The paired submandibular glands are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. In adult humans, they each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decreases in proportion as parotid gland secretion rises to 50%. The average length of the normal adult human submandibular salivary gland is approximately 27 mm, while the average width is approximately 14.3 mm.

The sublingual gland is a seromucous polystomatic exocrine gland. Located underneath the oral diaphragm, the sublingual gland is the smallest and most diffuse of the three major salivary glands of the oral cavity, with the other two being the submandibular and parotid. The sublingual gland provides approximately 3-5% of the total salivary volume.

Ludwig's angina is a type of severe cellulitis involving the floor of the mouth and is often caused by bacterial sources. Early in the infection, the floor of the mouth raises due to swelling, leading to difficulty swallowing saliva. As a result, patients may present with drooling and difficulty speaking. As the condition worsens, the airway may be compromised and hardening of the spaces on both sides of the tongue may develop. Overall, this condition has a rapid onset over a few hours.

The mylohyoid muscle or diaphragma oris is a paired muscle of the neck. It runs from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity of the mouth. It is named after its two attachments near the molar teeth. It forms the floor of the submental triangle. It elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue, important during swallowing and speaking.

The hyoglossus is a thin and quadrilateral extrinsic muscle of the tongue. It originates from the hyoid bone; it inserts onto the side of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. It acts to depress and retract the tongue.
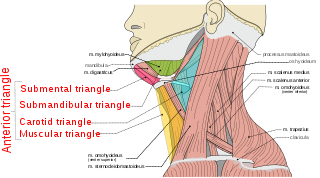
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck.

The deep cervical fascia lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.

The submental artery is the largest branch of the facial artery in the neck. It first runs forward under the mouth, then turns upward upon reaching the chin.
The buccal space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the cheek, and is paired on each side. The buccal space is superficial to the buccinator muscle and deep to the platysma muscle and the skin. The buccal space is part of the subcutaneous space, which is continuous from head to toe.

The submental lymph nodes are 2-3 lymph nodes situated in the submental triangle, between the anterior bellies of the digastric muscle and the hyoid bone.

The submandibular lymph nodes, are some 3-6 lymph nodes situated at the inferior border of the ramus of mandible.
Mouth infections, also known as oral infections, are a group of infections that occur around the oral cavity. They include dental infection, dental abscess, and Ludwig's angina. Mouth infections typically originate from dental caries at the root of molars and premolars that spread to adjacent structures. In otherwise healthy patients, removing the offending tooth to allow drainage will usually resolve the infection. In cases that spread to adjacent structures or in immunocompromised patients, surgical drainage and systemic antibiotics may be required in addition to tooth extraction. Since bacteria that normally reside in the oral cavity cause mouth infections, proper dental hygiene can prevent most cases of infection. As such, mouth infections are more common in populations with poor access to dental care or populations with health-related behaviors that damage one's teeth and oral mucosa. This is a common problem, representing nearly 36% of all encounters within the emergency department related to dental conditions.

The sublingual space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space located below the mouth and above the mylohyoid muscle, and is part of the suprahyoid group of fascial spaces.

The submandibular space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space, and is paired on either side, located on the superficial surface of the mylohyoid muscle between the anterior and posterior bellies of the digastric muscle. The space corresponds to the anatomic region termed the submandibular triangle, part of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The mental space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space, bilaterally located in the chin, between the mentalis muscle superiorly and the platysma muscle inferiorly. These spaces may be created by pathology, e.g., the spread of odontogenic infection. Commonly the origin of the infection is an anterior mandibular tooth with associated periapical abscess which erodes through the buccal cortical plate of the mandibular at a level below the attachment of the mentalis muscle. The mental space also has the mental foramen located laterally on both the right and left sides. This is important as many mandibular nerves pass through these foremens.
Fascial spaces are potential spaces that exist between the fasciae and underlying organs and other tissues. In health, these spaces do not exist; they are only created by pathology, e.g. the spread of pus or cellulitis in an infection. The fascial spaces can also be opened during the dissection of a cadaver. The fascial spaces are different from the fasciae themselves, which are bands of connective tissue that surround structures, e.g. muscles. The opening of fascial spaces may be facilitated by pathogenic bacterial release of enzymes which cause tissue lysis. The spaces filled with loose areolar connective tissue may also be termed clefts. Other contents such as salivary glands, blood vessels, nerves and lymph nodes are dependent upon the location of the space. Those containing neurovascular tissue may also be termed compartments.

The submasseterric space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the face over the angle of the jaw, and is paired on each side. It is located between the lateral aspect of the mandible and the medial aspect of the masseter muscle and its investing fascia. The term is derived from sub- meaning "under" in Latin and masseteric which refers to the masseter muscle. The submasseteric space is one of the four compartments of the masticator space. Sometimes the submasseteric space is described as a series of spaces, created because the masseter muscle has multiple insertions that cover most of the lateral surface of the ramus of the mandible.
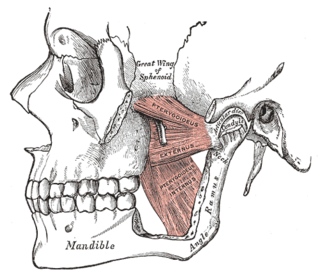
The pterygomandibular space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the head and is paired on each side. It is located between the lateral pterygoid muscle and the medial surface of the ramus of the mandible. The pterygomandibular space is one of the four compartments of the masticator space.

The infratemporal space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the side of the head, and is paired on either side. It is located posterior to the maxilla, between the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone medially and by the base of skull superiorly. The term is derived from infra- meaning below and temporal which refers to the temporalis muscle.

















