| Pectinate line | |
|---|---|
 Pectinate line labeled at bottom center | |
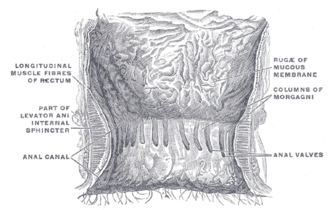 The interior of the anal cami and lower part of the rectum, showing the columns of Morgagni and the anal valves between their lower ends. (Pectinate line visible but not labeled.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | linea pectinata, linea anocutanea |
| TA98 | A05.7.05.009 |
| TA2 | 3015 |
| FMA | 29321 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The pectinate line (also known as the dentate line) is a line which divides the upper two-thirds and lower third of the anal canal. Developmentally, this line represents the hindgut-proctodeum junction.
Contents
It is an important anatomical landmark in humans, and forms the boundary between the anal canal and the rectum according to the anatomic definition. [1] Colorectal surgeons instead define the anal canal as the zone from the anal verge to the anorectal ring (palpable structure formed by the external anal sphincter and the puborectalis muscle). [1] Several distinctions can be made based upon the location of a structure relative to the pectinate line:
| Distinction | Above pectinate line | Below pectinate line |
|---|---|---|
| Lymph drainage | internal iliac [2] | superficial inguinal lymph nodes (below Hilton's white line) |
| Epithelium | columnar epithelium (as is most of the digestive tract - the line represents the end of the part of the body derived from the hindgut) | stratified squamous epithelium, non-keratinized (until Hilton's white line, where the anal verge becomes continuous with the perianal skin containing keratinized epithelium.) |
| Embryological origin [3] | endoderm | ectoderm |
| Artery | superior rectal artery | middle and inferior rectal arteries |
| Vein | superior rectal vein draining into the inferior mesenteric vein and subsequently the hepatic portal system | middle and inferior rectal veins |
| Hemorrhoids classification | internal hemorrhoids (not painful) | external hemorrhoids (painful) |
| Nerves | inferior hypogastric plexus | pudendal nerves |