Related Research Articles

The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e., it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach.

The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals it may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine.

The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four main pulmonary veins, two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary veins are part of the pulmonary circulation.

The bile duct is a part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and cystic duct. It ends by uniting with the pancreatic duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla. It possesses its own sphincter to enable regulation of bile flow.

A pancreaticoduodenectomy, also known as a Whipple procedure, is a major surgical operation most often performed to remove cancerous tumours from the head of the pancreas. It is also used for the treatment of pancreatic or duodenal trauma, or chronic pancreatitis. Due to the shared blood supply of organs in the proximal gastrointestinal system, surgical removal of the head of the pancreas also necessitates removal of the duodenum, proximal jejunum, gallbladder, and, occasionally, part of the stomach.
The Kocher manoeuvre is a surgical procedure to expose structures in the retroperitoneum behind the duodenum and pancreas. In vascular surgery, it is described as a method to expose the abdominal aorta. It usually has been in contrast to midline laparotomy and right retroperitoneal space dissection. These two procedures have been used for diverse cases, but have approximately equivalent outcomes.
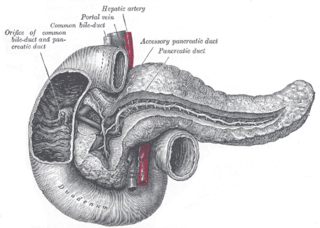
The pancreatic duct, or duct of Wirsung, is a duct joining the pancreas to the common bile duct. This supplies it with pancreatic juice from the exocrine pancreas, which aids in digestion.

A pancreatic pseudocyst is a circumscribed collection of fluid rich in pancreatic enzymes, blood, and non-necrotic tissue, typically located in the lesser sac of the abdomen. Pancreatic pseudocysts are usually complications of pancreatitis, although in children they frequently occur following abdominal trauma. Pancreatic pseudocysts account for approximately 75% of all pancreatic masses.

The ampulla of Vater, hepatopancreatic ampulla or hepatopancreatic duct is the common duct that is usually formed by a union of the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct within the wall of the duodenum. This common duct usually features a dilation ("ampulla"). The common duct then opens medially into the descending part of the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla. The common duct usually measures 2-10mm in length.

Pancreatic divisum is a congenital anomaly in the anatomy of the ducts of the pancreas in which a single pancreatic duct is not formed, but rather remains as two distinct dorsal and ventral ducts. Most individuals with pancreas divisum remain without symptoms or complications. A minority of people with pancreatic divisum may develop episodes of abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting due to acute or chronic pancreatitis. The presence of pancreas divisum is usually identified with cross sectional diagnostic imaging, such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). In some cases, it may be detected intraoperatively. If no symptoms or complications are present, then treatment is not necessary. However, if there is recurrent pancreatitis, then a sphincterotomy of the minor papilla may be indicated.

Annular pancreas is a rare condition in which the second part of the duodenum is surrounded by a ring of pancreatic tissue continuous with the head of the pancreas. This portion of the pancreas can constrict the duodenum and block or impair the flow of food to the rest of the intestines. It is estimated to occur in 1 out of 12,000 to 15,000 newborns. The ambiguity arises from the fact that not all cases are symptomatic.

The foregut in humans is the anterior part of the alimentary canal, from the distal esophagus to the first half of the duodenum, at the entrance of the bile duct. Beyond the stomach, the foregut is attached to the abdominal walls by mesentery. The foregut arises from the endoderm, developing from the folding primitive gut, and is developmentally distinct from the midgut and hindgut. Although the term “foregut” is typically used in reference to the anterior section of the primitive gut, components of the adult gut can also be described with this designation. Pain in the epigastric region, just below the intersection of the ribs, typically refers to structures in the adult foregut.
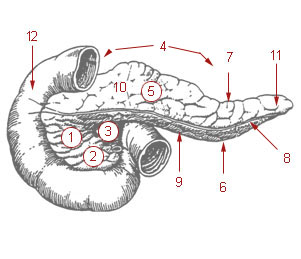
The uncinate process is a small part of the pancreas. The uncinate process is the formed prolongation of the angle of junction of the lower and left lateral borders in the head of the pancreas. The word "uncinate" comes from the Latin "uncinatus", meaning "hooked".

Hemosuccus pancreaticus is a rare cause of hemorrhage in the gastrointestinal tract. It is caused by a bleeding source in the pancreas, pancreatic duct, or structures adjacent to the pancreas, such as the splenic artery, that bleed into the pancreatic duct, which is connected with the bowel at the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. Patients with hemosuccus may develop symptoms of gastrointestinal hemorrhage, such as blood in the stools, maroon stools, or melena, which is a dark, tarry stool caused by digestion of red blood cells. They may also develop abdominal pain. It is associated with pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer and aneurysms of the splenic artery. Hemosuccus may be identified with endoscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy), where fresh blood may be seen from the pancreatic duct. Alternatively, angiography may be used to inject the celiac axis to determine the blood vessel that is bleeding. This may also be used to treat hemosuccus, as embolization of the end vessel may terminate the hemorrhage. However, a distal pancreatectomy—surgery to remove of the tail of the pancreas—may be required to stop the hemorrhage.

The major duodenal papilla is a rounded projection in the duodenum into which the common bile duct and pancreatic duct drain. The major duodenal papilla is, in most people, the primary mechanism for the secretion of bile and other enzymes that facilitate digestion.
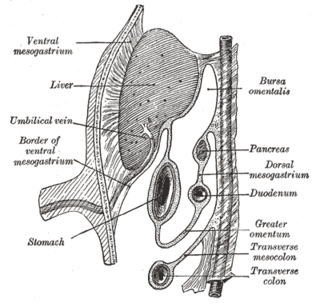
The ventral and dorsal pancreatic buds are outgrowths of the duodenum during human embryogenesis. They join to form the adult pancreas.

Giovanni Domenico Santorini was an Italian anatomist. He was a native of Venice, earning his medical doctorate at Pisa in 1701. He is remembered for conducting anatomical dissections of the human body.
Papillary stenosis is a disturbance of the sphincter of Oddi, a muscular valve, that prevents the opening and release of bile or pancreatic fluids into the duodenum in response to food entering the duodenum.

Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to a group of functional disorders leading to abdominal pain due to dysfunction of the Sphincter of Oddi: functional biliary sphincter of Oddi and functional pancreatic sphincter of Oddi disorder. The sphincter of Oddi is a sphincter muscle, a circular band of muscle at the bottom of the biliary tree which controls the flow of pancreatic juices and bile into the second part of the duodenum. The pathogenesis of this condition is recognized to encompass stenosis or dyskinesia of the sphincter of Oddi ; consequently the terms biliary dyskinesia, papillary stenosis, and postcholecystectomy syndrome have all been used to describe this condition. Both stenosis and dyskinesia can obstruct flow through the sphincter of Oddi and can therefore cause retention of bile in the biliary tree and pancreatic juice in the pancreatic duct.

The sphincter of Oddi, abbreviated as SO, is a muscular valve that in some animals, including humans, controls the flow of bile and pancreatic juice out of the gallbladder and pancreas respectively through the ampulla of Vater into the second part of the duodenum. It is named after Ruggero Oddi.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Skandalakis, editor in chief John E. (2004). Skandalakis' surgical anatomy : the embryologic and anatomic basis of modern surgery. Athens, Greece: PMP. pp. Chapter 16: Small Intestine. ISBN 9603990744.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - ↑ Skandalakis, editor in chief John E. (2004). Skandalakis' surgical anatomy : the embryologic and anatomic basis of modern surgery. Athens, Greece: PMP. pp. Chapter 21. Pancreas. ISBN 9603990744.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - ↑ König, Liebich (2020). Veterinary Anatomy of Domestic Animals (7th ed.). Stuttgart: Thieme. p. 856. ISBN 978-3-13-242933-8.
- ↑ Colledge, Nicki R.; Walker, Brian R.; Ralston, Stuart H. (editors); Britton, Robert (illustrator) (2010). Davidson's principles and practice of medicine (21st ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7020-3084-0.
{{cite book}}:|first3=has generic name (help)