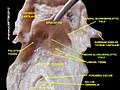
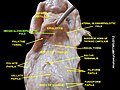
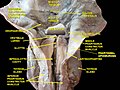
The glottis is the opening between the vocal folds. The glottis is crucial in producing sound from the vocal folds.

The larynx, commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word 'larynx' comes from the Ancient Greek word lárunx ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ
Swallowing, also called deglutition or inglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the body of a human or other animal that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing is an important part of eating and drinking. If the process fails and the material goes through the trachea, then choking or pulmonary aspiration can occur. In the human body the automatic temporary closing of the epiglottis is controlled by the swallowing reflex.

The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra.

The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food into the lungs, forcing the swallowed liquids or food to go along the esophagus toward the stomach instead. It is thus the valve that diverts passage to either the trachea or the esophagus.
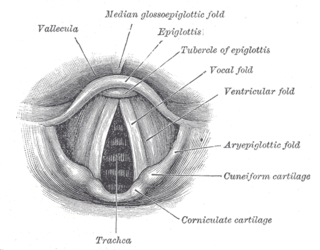
The laryngeal inlet is the opening that connects the pharynx and the larynx.
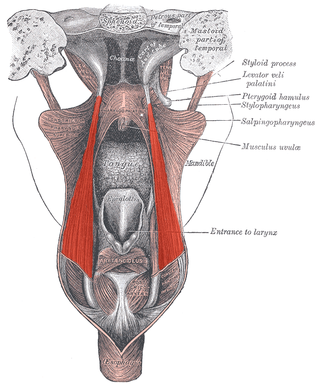
The salpingopharyngeus muscle is a muscle of the pharynx. It arises from the lower part of the cartilage of the Eustachian tube, and inserts into the palatopharyngeus muscle by blending with its posterior fasciculus. It is innervated by vagus nerve via the pharyngeal plexus. It raises the pharynx and larynx during deglutition (swallowing) and laterally draws the pharyngeal walls up. It opens the pharyngeal orifice of the Eustachian tube during swallowing to allow for the equalization of pressure between it and the pharynx.

The middle pharyngeal constrictor is a fan-shaped muscle located in the neck. It is one of three pharyngeal constrictor muscles. It is smaller than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle.

The inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a skeletal muscle of the neck. It is the thickest of the three outer pharyngeal muscles. It arises from the sides of the cricoid cartilage and the thyroid cartilage. It is supplied by the vagus nerve. It is active during swallowing, and partially during breathing and speech. It may be affected by Zenker's diverticulum.

The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a quadrilateral muscle of the pharynx. It is the uppermost and thinnest of the three pharyngeal constrictors.

The stylopharyngeus muscle is a muscle in the head. It originates from the temporal styloid process. Some of its fibres insert onto the thyroid cartilage, while others end by intermingling with proximal structures. It is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve. It acts to elevate the larynx and pharynx, and dilate the pharynx, thus facilitating swallowing.

The superior laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve. It arises from the middle of the inferior ganglion of vagus nerve and additionally also receives a sympathetic branch from the superior cervical ganglion.

The portion of the cavity of the larynx above the vestibular fold is called the laryngeal vestibule; it is wide and triangular in shape, its base or anterior wall presenting, however, about its center the backward projection of the tubercle of the epiglottis. It contains the vestibular folds, and between these and the vocal folds are the laryngeal ventricles.
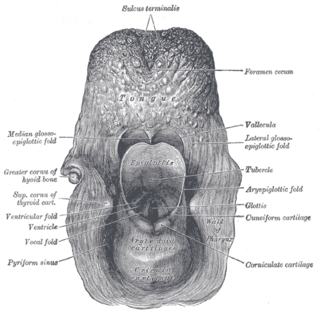
The aryepiglottic folds are triangular folds of mucous membrane of the larynx. They enclose ligamentous and muscular fibres. They extend from the lateral borders of the epiglottis to the arytenoid cartilages, hence the name 'aryepiglottic'. They contain the aryepiglottic muscles and form the upper borders of the quadrangular membrane. They have a role in growling as a form of phonation. They may be narrowed and cause stridor, or be shortened and cause laryngomalacia.

The laryngeal ventricle, is a fusiform fossa, situated between the vestibular and vocal folds on either side, and extending nearly their entire length. There is also a sinus of Morgagni in the pharynx.

The infraglottic cavity is the portion of the larynx situated inferior to the glottis. It is situated between the vocal cords, and the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage where it is continuous with the trachea.
The pharyngobasilar fascia is a fascia of the pharynx. It is situated between the mucous and muscular layers of the pharynx. It is formed as a thickening of the pharyngeal mucosa superior to the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. It attaches to the basilar part of occipital bone, the petrous part of the temporal bone, the medial pterygoid plate, and the pterygomandibular raphe. It diminishes in thickness inferiorly. Posteriorly, it is reinforced by the pharyngeal raphe. It reinforces the pharyngeal wall where muscle is deficient.
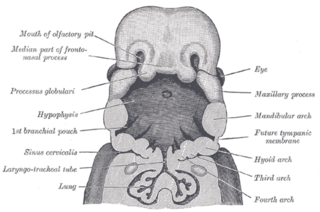
The laryngotracheal groove is a precursor for the larynx and trachea.

The quadrangular membrane is a layer of submucosa. It extends between the lateral margin of the epiglottis, and the apex and fovea triangularis of the ipsilateral arytenoid cartilage. It has free superior and inferior borders.

The pharynx is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx.