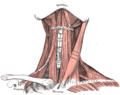
| Muscular triangle | |
|---|---|
 Muscular triangle | |
 Side of neck, showing chief surface markings. (Nerves are yellow, arteries are red.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | trigonum musculare |
| TA98 | A01.2.02.005 |
| TA2 | 236 |
| FMA | 61601 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The inferior carotid triangle (or muscular triangle), is bounded, in front, by the median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum; behind, by the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid; above, by the superior belly of the omohyoid.
Contents
It is covered by the integument, superficial fascia, platysma, and deep fascia, ramifying in which are some of the branches of the supraclavicular nerves.
Beneath these superficial structures are the sternohyoid and sternothyroid, which, together with the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid, conceal the lower part of the common carotid artery.
This vessel is enclosed within its sheath, together with the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve; the vein lies lateral to the artery on the right side of the neck, but overlaps it below on the left side; the nerve lies between the artery and vein, on a plane posterior to both.
In front of the sheath are a few descending filaments from the ansa cervicalis; behind the sheath are the inferior thyroid artery, the recurrent nerve, and the sympathetic trunk; and on its medial side, the esophagus, the trachea, the thyroid gland, and the lower part of the larynx.
By cutting into the upper part of this space, and slightly displacing the sternocleidomastoid, the common carotid artery may be tied below the omohyoid.